Anexos da Pele: Sistema Tegumentar 4/4 | Anatomia etc
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the appendages of the skin, focusing on hair, glands, and nails. Hair, which is found all over the body except for palms and soles, is classified into vellus (fine) and terminal (thicker and pigmented) types. These hair structures are connected to hair follicles, which are nourished by a dermal papilla. Sebaceous glands produce sebum to protect the hair and skin, while sweat glands regulate body temperature. The two types of sweat glands—eccrine and apocrine—serve different roles. Finally, nails, composed of keratinized cells, protect fingertip areas and help with grasping. The lesson concludes by highlighting the importance of these skin appendages in bodily functions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The skin appendages (or cutaneous appendages) are structures that assist in skin functions like protection and temperature regulation, and include hair, glands, and nails.
- 😀 Hair is an accessory structure of the skin, present on almost the entire skin surface, except for the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
- 😀 There are two types of hair: velus hair (fine, less pigmented) and terminal hair (longer, more pigmented), each with different follicle depths and locations.
- 😀 Hair plays important roles in protection, such as eyebrow hairs protecting the eyes from sweat, and scalp hair protecting from UV radiation.
- 😀 Hair also helps in temperature regulation and light touch perception due to sensory receptors associated with hair follicles.
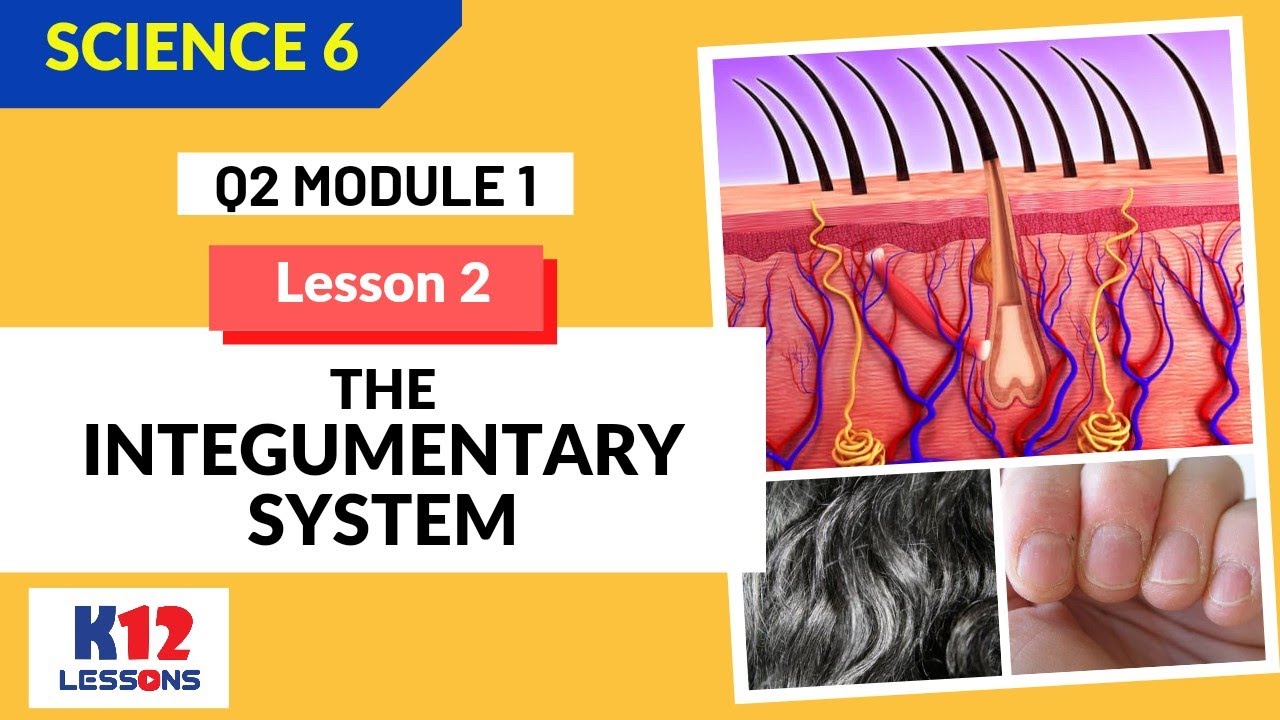
- 😀 Hair is composed of keratinized, dead cells held together by proteins. The part inside the skin is called the root, and the visible part is called the shaft.
- 😀 Hair follicles are invaginations of epidermal cells, and the base of the follicle is called the bulb, where germinative cells undergo mitosis for hair growth.
- 😀 The hair bulb is nourished by the vascularized dermal papilla, and the follicle also includes sebaceous glands and an arrector pili muscle.
- 😀 Sebaceous glands produce sebum, an oily substance that prevents hair from drying out and helps maintain skin flexibility.
- 😀 Sweat glands (sudoriferous glands) help in temperature regulation. There are two types: eccrine glands (found all over the body) and apocrine glands (found in specific areas like the armpits).
- 😀 Apocrine glands become active after puberty and their sweat contains more lipids and proteins, which are broken down by bacteria on the skin, creating body odor (bromhidrosis).
- 😀 Nails are keratinized, hard, and compacted dead cells that protect the fingertips and help with grasping objects. The nail matrix is responsible for nail growth.
Q & A
What are skin appendages, and what role do they play in the body?
-Skin appendages are structures that assist in the skin's functions, such as protection and temperature regulation. They include hair, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and nails.
What are the two main types of hair found on the human body?
-The two main types of hair are vellus hair, which is fine and less pigmented, and terminal hair, which is thicker, longer, and pigmented.
Where are hair follicles located on the body, and which areas lack them?
-Hair follicles are located on almost every part of the skin, except for the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet.
What is the function of hair in the human body?
-Hair serves several functions, including protection (e.g., eyebrows protect the eyes from sweat), temperature regulation, and sensory perception (detecting light touch).
What structures are associated with hair follicles?
-Hair follicles are associated with sebaceous glands, which produce sebum, and the arrector pili muscle, which causes hair to stand up (piloerection).
What is the difference between eccrine and apocrine sweat glands?
-Eccrine glands are spread across the body and are responsible for regulating body temperature by producing sweat. Apocrine glands are located in specific areas like the armpits and groin, and they become active at puberty, secreting a sweat that leads to body odor when metabolized by bacteria.
How do sebaceous glands contribute to the skin’s health?
-Sebaceous glands produce sebum, an oily substance that helps to prevent the skin and hair from drying out, reduces water loss from the skin, and keeps the skin soft and flexible.
What is bromhidrosis, and how does it relate to sweat?
-Bromhidrosis refers to the unpleasant odor produced by sweat, particularly from apocrine glands. It occurs when bacteria metabolize the sweat, especially in areas like the armpits.
What is the structure of a hair follicle, and what role does the bulb play?
-The hair follicle is an invagination of the epidermis, and at the base of the follicle is the bulb, where the hair grows. The bulb houses germinative cells that undergo mitosis to produce the hair, and it is nourished by the papilla dermis, a vascularized structure.
How do nails contribute to body functions, and where do they grow from?
-Nails protect the fingertips and help with grasping objects. They grow from the matrix ungueal, a region located beneath the base of the nail, which contains living cells responsible for nail growth.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)