1 Introdução aos derivados de cana de açúcar
Summary
TLDRThe video introduces the fascinating world of sugarcane derivatives, covering both the well-known and lesser-known byproducts. It explores sugar, ethanol, cachaça, and other familiar products, along with more industrial applications such as biofuels, amino acids, and plastics. The presenter discusses the geographical distribution of sugarcane cultivation and its impact on global industries. With a focus on the versatility of sugarcane, the video highlights its role in multiple sectors, including biotechnology, cosmetics, and even construction materials. Overall, it offers a deep dive into the significant economic and industrial contributions of sugarcane.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sugarcane is the primary crop in Brazil, cultivated for over four centuries and plays a major role in the country's economy and identity.
- 😀 The sugarcane plant, originally from Southeast Asia, thrives in tropical climates, especially around the equator and specific regions of the world.
- 😀 There are over 260 derivatives of sugarcane, with the most common being ethanol, sugar, cachaça, rapadura, molasses, and brown sugar.
- 😀 In addition to food products, sugarcane derivatives are used in industries such as biotechnology, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and even cosmetics.
- 😀 The production of sugarcane involves several byproducts like bagasse and vinasse, which are crucial for energy production and other industrial uses.
- 😀 Sugarcane’s geographical distribution is essential for understanding where it can be most effectively grown and processed.
- 😀 The sugarcane industry supports both artisanal and industrial production methods, with varying processes for products like cachaça and ethanol.
- 😀 The transformation of sugarcane into various products begins with the extraction of the juice, which can be further processed into different food and industrial items.
- 😀 The production of sugarcane derivatives has a broad scope, affecting multiple sectors including food, construction, plastics, and even eco-friendly materials.
- 😀 The course aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of sugarcane’s impact across diverse industries, focusing on both well-known and lesser-known derivatives.
Q & A
What is the main focus of this course?
-The main focus of the course is on the various derivatives of sugarcane, which include both well-known and less-known products, such as ethanol, sugar, cachaça, and other industrial and artisanal products.
How long has sugarcane been cultivated in Brazil?
-Sugarcane has been cultivated in Brazil for over four centuries, and it plays a significant role in the country’s agricultural and industrial sectors.
Where did sugarcane originally come from?
-Sugarcane originated from Southeast Asia, specifically from the tropical regions, and was introduced to Brazil around 1516, arriving from Madeira Island, Portugal.
What are some of the classical derivatives of sugarcane mentioned in the script?
-The classical derivatives of sugarcane mentioned in the script include ethanol, sugar, cachaça, rapadura, melado (molasses), and brown sugar (açúcar mascavo).
What are some of the industrial derivatives of sugarcane?
-Industrial derivatives of sugarcane include products used in biotechnology, chemistry, pharmaceuticals, food, and structural products like paper, plastics, and biofuels.
What is the significance of the geographical distribution of sugarcane?
-The geographical distribution of sugarcane is important for understanding which regions of the world are best suited for its cultivation, primarily around the equator and tropical zones where the climate is optimal for its growth.
What is the difference between melado and melaço?
-Melado and melaço are both sugarcane derivatives, but they differ in terms of composition and usage. Melado is a thicker syrup used in various products, while melaço is typically a by-product of the sugar refining process.
What is the role of bagaço (sugarcane bagasse) in sugarcane derivatives?
-Bagaço, or sugarcane bagasse, is the fibrous residue left after extracting juice from the cane. It is used in various industrial processes, including bioenergy production and manufacturing paper and building materials.
How does the production of ethanol and cachaça relate to the sugarcane industry?
-Ethanol and cachaça are two primary products derived from sugarcane. Ethanol is used as fuel and in industrial applications, while cachaça is a distilled alcoholic beverage, particularly significant in Brazil’s cultural and artisanal sectors.
What are some lesser-known products derived from sugarcane?
-Some lesser-known products derived from sugarcane include amino acids, proteins, yeast, and biogas, as well as materials for cosmetics, plastics, and cement.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
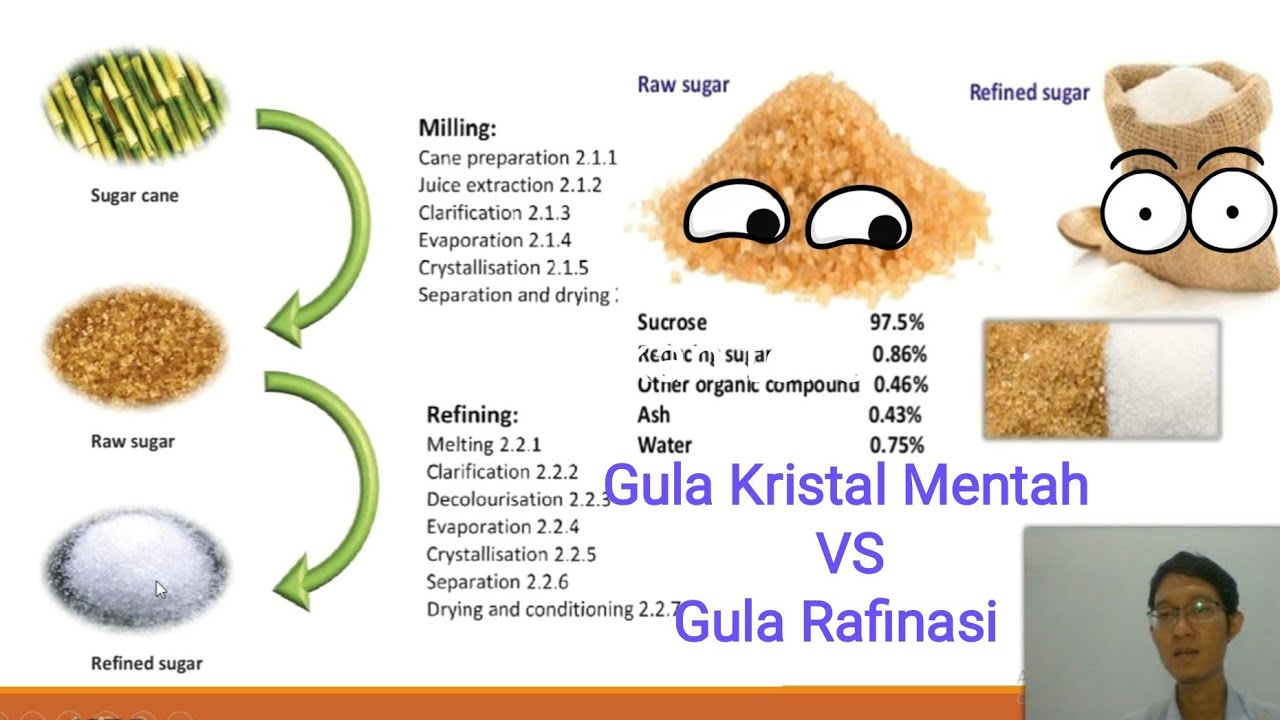
Ekstraksi Tebu menjadi Nira - Diagram Alir Proses Industri Gula (part 1/4)

Gaudí's FIRST House in Barcelona!

The Subway's Leftovers | NYC Subway Remnants and Provisions Part 1: Manhattan

Planta de comer? Conheça as PANCs e aprenda como cultivar

15 Alternatives to FAANG 😎 | Companies paying more than FAANG! 🔥💯 CTC Breakup

How I Earned 1 MILLION+ Chase Ultimate Reward Points
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
