Civil 3D - 3: Profil Trase
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed guide on designing vertical road profiles, focusing on the creation and calculation of cutting points, the analysis of gradients, and the design of vertical curves. The process involves using tools like Microsoft Excel and 3D modeling software to ensure that the road profile meets design specifications, including critical slope, gradient calculations, and curve lengths. The video also covers the importance of meeting design criteria for both uphill and downhill segments, ensuring safety and functionality in road design.
Takeaways
- 😀 Begin by importing the existing terrain data into the design software to set up the road profile view.
- 😀 Define start and end points for the road (A and B) with their respective elevations (e.g., 38m and 188m).
- 😀 Use Microsoft Excel to calculate vertical cut points and segment slopes, ensuring consistent gradients.
- 😀 Gradients should be calculated as the elevation difference divided by horizontal distance between points.
- 😀 Ensure that curves in the road have uniform gradients to maintain smooth transitions, especially during turns.
- 😀 Calculate the critical length of slopes using design standards and verify if the calculated length meets the allowed criteria.
- 😀 Vertical curves need to be calculated separately for convex and concave shapes, each with distinct formulas.
- 😀 Use appropriate design standards to determine the maximum permissible gradient and adjust road design accordingly.
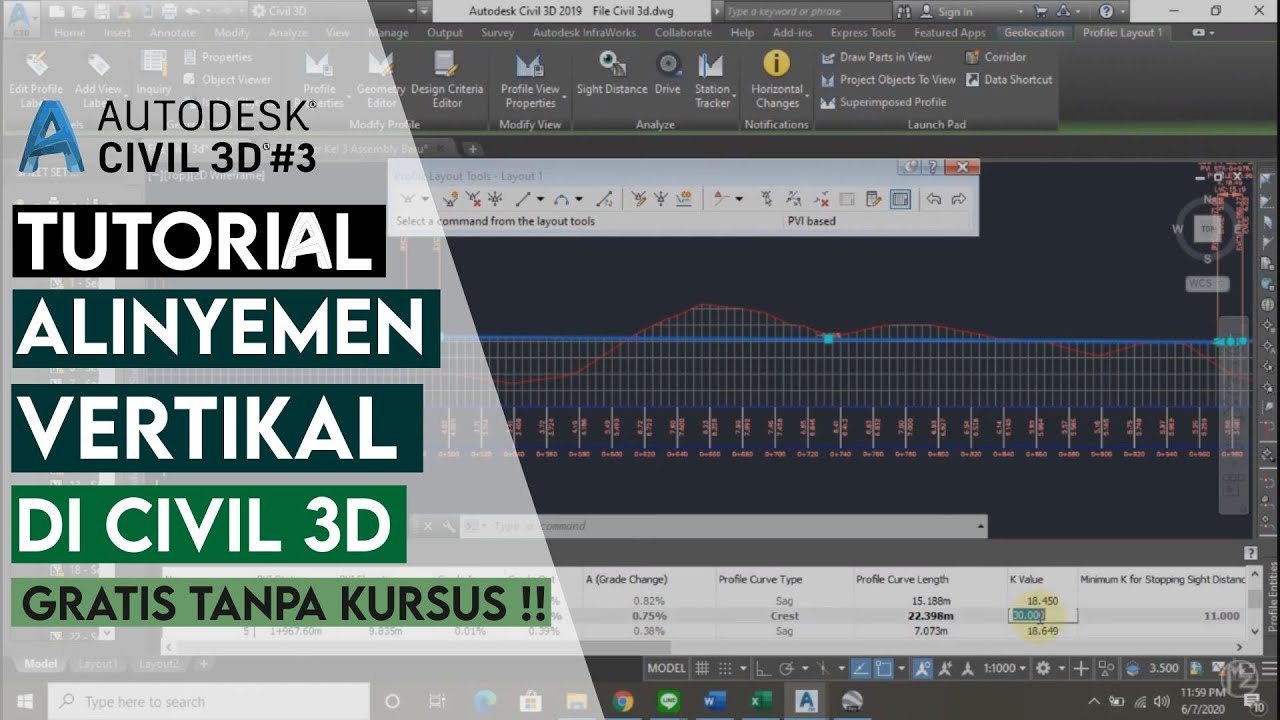
- 😀 After calculation, draw the vertical profile in 3D modeling software, ensuring proper elevation transitions.
- 😀 Adjust visual elements like line colors and thickness for clarity and ease of reference during the design process.
- 😀 Once the vertical profile is finalized, continue with additional design steps, such as creating cross-sections and road corridors.
Q & A
What is the first step in designing the vertical profile of a road or street?
-The first step is to load the existing terrain file from the previously designed phase and select the profile view in the software.
What does the term 'elevation' refer to in this design process?
-Elevation refers to the vertical height of a point relative to a base level, such as sea level, used to determine the start and end points for the road design.
How do you calculate the gradient of a road segment?
-The gradient is calculated by subtracting the elevation difference between two points and dividing it by the horizontal distance (or the road length) between those points.
What is the importance of determining the critical slope length in road design?
-Determining the critical slope length is essential to ensure that the road can accommodate vehicles without difficulty, especially when climbing steep gradients, as per the design requirements.
What is the role of the critical slope graph in the design process?
-The critical slope graph helps determine the maximum allowable slope for a vehicle at a given speed and gradient. It is used to compare against calculated gradients to ensure the road is safe for traffic.
What does 'gradients must be the same for curves' mean in road design?
-This means that the gradient on both sides of a curve must be equal to avoid abrupt changes in slope, which could affect vehicle stability and comfort.
What software tools are used in the design process described in the transcript?
-Microsoft Excel is used for calculations, while 3D CAD software is employed to create the vertical profile and visualize the road design.
How is the length of a vertical curve determined?
-The length of a vertical curve is determined by the change in the road's gradient and the maximum allowable length based on speed and vehicle climbing capacity.
What do the terms 'convex' and 'concave' curves refer to in vertical road profile design?
-Convex curves curve upward, while concave curves curve downward. These curves are treated differently in calculations due to their different effects on vehicle movement.
What steps are involved in drawing the vertical profile in 3D software?
-First, auxiliary lines are drawn to help guide the profile. Then, using the software, the design is created by inputting the elevation and slope values for each segment, ensuring that the profile matches the design parameters calculated in Excel.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)