FISIKA Kelas 11 - Hukum Pascal | GIA Academy
Summary
TLDRIn this video, viewers learn about Pascal's Law, a fundamental principle in fluid mechanics. The law states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions. Through everyday examples such as hydraulic brakes, elevators, and hydraulic presses, the video explains how this principle is applied in various devices. The content also includes practical problem-solving examples to demonstrate how force and pressure relate in different systems. Viewers will gain a clear understanding of Pascal's Law and its widespread applications in technology and daily life.
Takeaways
- 😀 Pascal's Law states that the pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
- 😀 The law is demonstrated through everyday examples like balloons filled with air and bicycle pumps, where pressure is spread throughout the medium.
- 😀 Blaise Pascal, the French physicist, discovered the principle behind Pascal's Law through simple experiments in 1653.
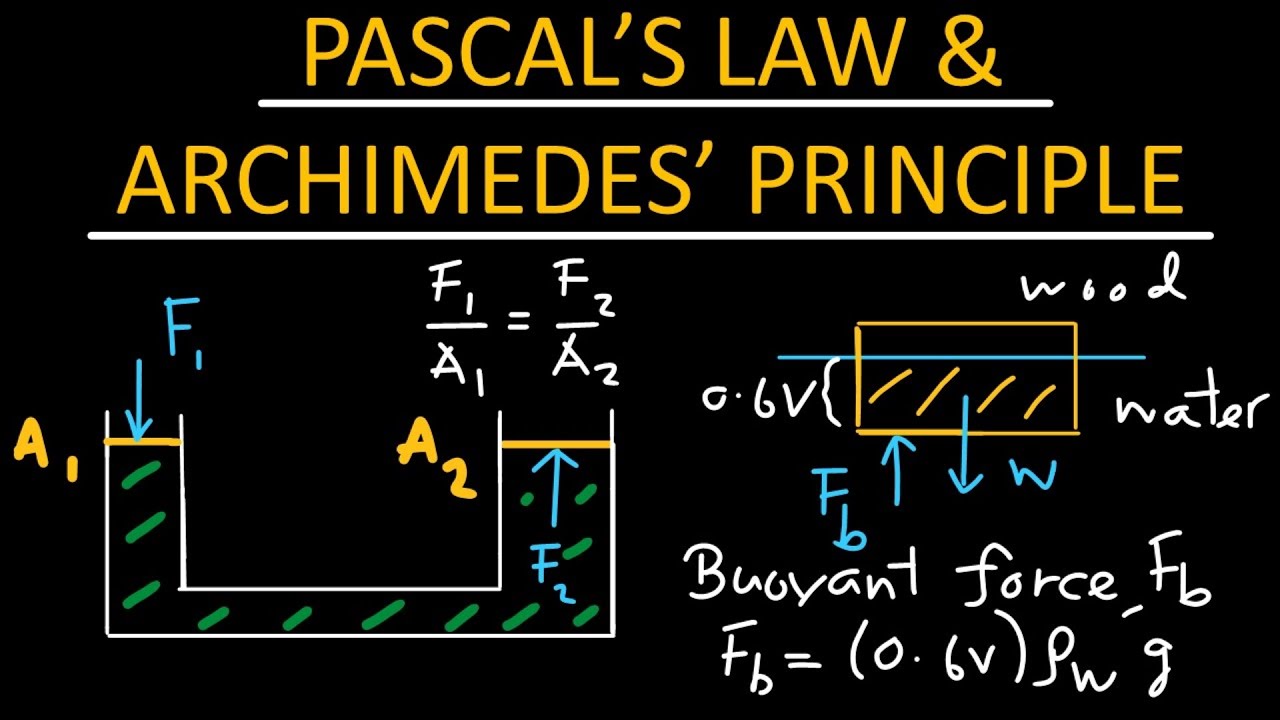
- 😀 Pascal's Law can be mathematically expressed as P1 = P2, or F1 / A1 = F2 / A2, where P represents pressure, F represents force, and A represents area.
- 😀 In hydraulic systems, Pascal's Law is applied to create a mechanical advantage, allowing smaller forces to move larger loads, such as in car brakes or elevators.
- 😀 Hydraulic lifts, like those used in elevators, utilize fluid pressure to lift heavy objects, reducing the effort required to move them.
- 😀 Hydraulic presses used in industries apply pressure to form or shape materials like metal by utilizing the same principle.
- 😀 Everyday tools like hydraulic pumps, surgical tables, and even wheelchairs often rely on Pascal's Law to function smoothly and efficiently.
- 😀 Hydraulic systems are commonly used in medical fields, such as in adjusting the height of operating tables and dental chairs for comfort and precision.
- 😀 A series of practical problems related to Pascal’s Law illustrate how the force and area relationships can be used to calculate the required forces in hydraulic systems.
Q & A
What is Pascal's Law?
-Pascal's Law states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to all portions of the fluid and to the walls of its container. This means that pressure in a confined fluid is evenly distributed in all directions.
Who proposed Pascal's Law and when?
-Pascal's Law was proposed by Blaise Pascal in 1653 after he conducted an experiment involving water-filled plastic bags to observe how pressure is transmitted through liquids.
What is the mathematical formula of Pascal's Law?
-The formula for Pascal's Law is: P1 / A1 = P2 / A2, where P1 and P2 are the pressures on small and large areas, A1 and A2 are the areas of those surfaces. The equation shows that pressure is inversely proportional to area in a hydraulic system.
What does the equation F1 / A1 = F2 / A2 represent?
-This equation represents the relationship between the force (F1 and F2) and the area (A1 and A2) in a hydraulic system. It shows that when a small force is applied to a smaller area, it is transmitted to a larger area, multiplying the force accordingly.
Can you explain the principle of hydraulic systems using Pascal's Law?
-Yes! In a hydraulic system, when pressure is applied to a small piston, it is transmitted equally through the fluid to a larger piston. The force on the large piston is larger because of the greater area, which is how hydraulic lifts, brakes, and presses work.
How does Pascal's Law apply to car hydraulic brakes?
-In car hydraulic brakes, when the brake pedal is pressed, the pressure from the pedal is transmitted through the brake fluid to the brake pads. This enables the car to stop with a much higher force than the pressure initially applied to the pedal.
What is the role of Pascal's Law in elevators (lifts)?
-Elevators use Pascal's Law by applying pressure to the hydraulic fluid, which then lifts the elevator car. The pressure is transferred evenly through the fluid to the large piston, which raises the car to the desired floor.
What are some everyday devices that use Pascal's Law?
-Everyday devices that use Pascal's Law include hydraulic lifts, car brakes, hydraulic presses, wheelchairs, dental chairs, and even some operating tables. These devices rely on the transfer of pressure through fluids to perform their functions.
What is the relationship between the size of the piston and the force applied in a hydraulic system?
-In a hydraulic system, the force is proportional to the area of the piston. If a smaller piston is used, a higher pressure is required to move the same force. Larger pistons distribute the force over a larger area, which allows them to lift heavier loads with less force.
How can you solve a problem involving Pascal's Law with given forces and areas?
-To solve a Pascal's Law problem, use the equation F1 / A1 = F2 / A2. By substituting the known values for forces and areas, you can solve for the unknown value, such as the force on a larger piston or the area needed to lift a certain weight.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)