Computação Quântica - Fundamentos e Aplicações - Aula 02
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the creation and control of quantum bits (qubits) in quantum computing, highlighting the challenges of maintaining quantum states. Various qubit modalities are discussed, including superconductors, trapped ions, photons, neutral atoms, and quantum dots. Each approach has its own advantages and limitations in terms of coherence, sensitivity to external interference, and operational complexity. The video emphasizes the need for isolating qubits to preserve their quantum states, and the ongoing research to identify the ideal qubit technology for scalable quantum computing applications.
Takeaways
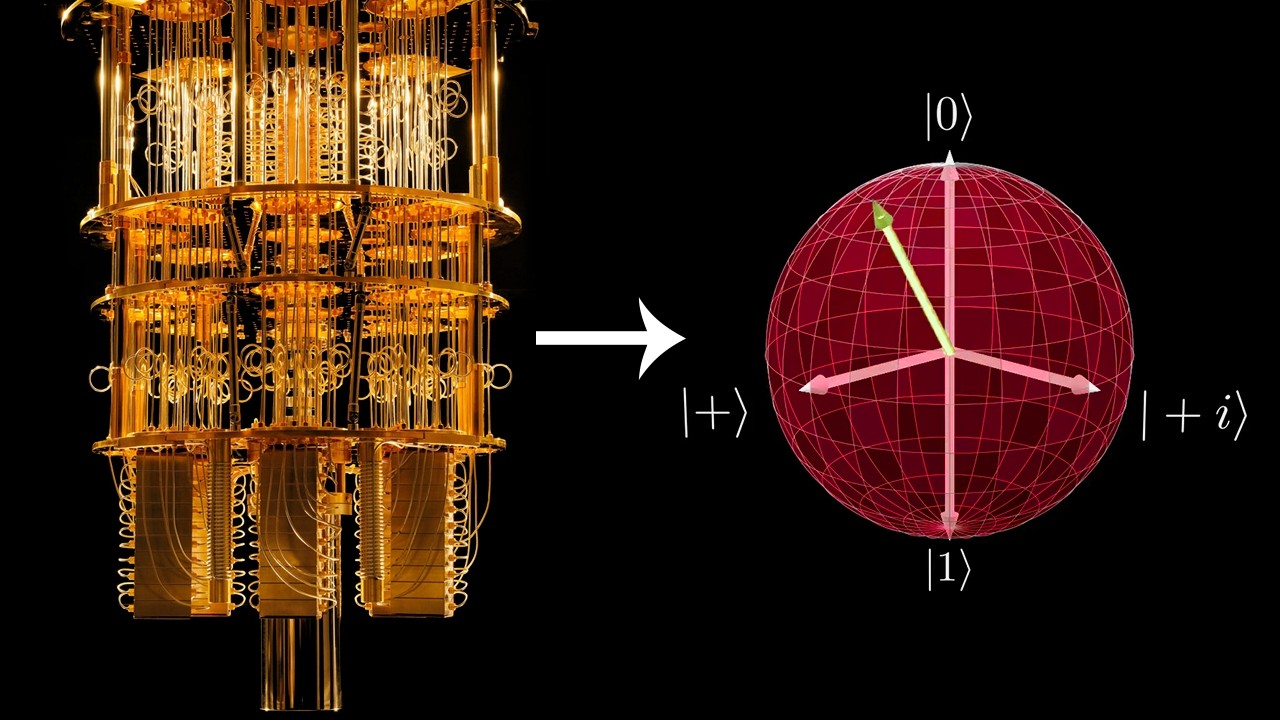
- 😀 A qubit is a quantum bit that exists in a superposition of 0 and 1 until measured, at which point its state collapses to either 0 or 1.
- 😀 External observers or forces, including the universe itself, influence the qubit's state, making it a challenge to maintain a qubit's coherence.
- 😀 Isolating a qubit from external interference is crucial for preserving its quantum state and preventing premature collapse.
- 😀 Qubits must be manipulated with precision, and their operational environment must be carefully controlled to maintain their quantum properties.
- 😀 Superconducting qubits use magnetic flux in a superconducting circuit, but they require extremely low temperatures to operate.
- 😀 Trapped ion qubits use the state of ions controlled by lasers. They are highly accurate but require complex infrastructure and precision.
- 😀 Photon qubits use the polarization or frequency of photons to represent information. They are less sensitive to external interference and are ideal for high-speed communication.
- 😀 Neutral atom qubits rely on the energy state of neutral atoms. They are more resistant to environmental disturbances but still require vacuum conditions for proper functioning.
- 😀 Quantum dots and diamond-based qubits are alternative methods for creating quantum information, each with unique advantages and challenges.
- 😀 Different qubit creation techniques present varied challenges, such as temperature requirements, infrastructure complexity, and susceptibility to external disturbances.
- 😀 Research is ongoing to determine the most scalable and reliable qubit technology to drive the future of quantum computing.
Q & A
What is a qubit and how is it different from a classical bit?
-A qubit (quantum bit) is the fundamental unit of information in quantum computing. Unlike classical bits that can only be either 0 or 1, a qubit can exist in a superposition of both 0 and 1 simultaneously. This allows quantum computers to perform computations in parallel, providing a potential advantage over classical computers.
Why is it difficult to maintain the state of a qubit?
-Maintaining the state of a qubit is difficult because it is highly sensitive to external factors. Once a qubit is measured or interacts with its environment, it collapses into a definite state (0 or 1). Additionally, external forces such as electromagnetic fields, temperature fluctuations, or even light can cause a qubit to lose its quantum state, leading to a loss of information (decoherence).
What is decoherence and how does it affect quantum computation?
-Decoherence is the process by which a quantum system loses its quantum coherence due to interaction with the environment, collapsing the qubit's superposition of states into one definite state. This loss of coherence can disrupt quantum computations and is one of the major challenges in building practical quantum computers.
What are the key challenges in isolating qubits from external interference?
-Isolating qubits from external interference requires preventing interactions with external forces like temperature fluctuations, electromagnetic fields, and radiation. This isolation is crucial to prevent the qubit from prematurely collapsing its superposition state and losing information. Maintaining extremely low temperatures, using vacuum environments, and shielding from electromagnetic noise are common methods to achieve isolation.
What is the significance of superposition in quantum computing?
-Superposition is a fundamental property of quantum systems where a qubit can exist in a combination of both 0 and 1 states at the same time. This ability enables quantum computers to process many possibilities simultaneously, offering the potential for much faster and more efficient computations for certain tasks compared to classical computers.
How do superconducting qubits work, and what are their challenges?
-Superconducting qubits are created using circuits that represent qubits through magnetic flux. These circuits can maintain a superposition of states, but to preserve the quantum state, the qubits need to be kept at extremely low temperatures. The main challenge with superconducting qubits is their need for these low temperatures to function effectively, which requires complex cooling systems.
What are trapped ion qubits and what advantages do they offer?
-Trapped ion qubits use the energy states of individual ions to represent qubits. Lasers are used to manipulate these ions, changing their energy levels to encode information. Trapped ion qubits offer long coherence times and high precision in operations, but they require complex infrastructure, including precise laser control and a vacuum environment.
Why are photon qubits advantageous for quantum communication?
-Photon qubits are advantageous for quantum communication because photons can travel at the speed of light, allowing for fast and efficient transmission of quantum information. Photons are also less sensitive to interference, making them ideal for long-distance quantum communication, such as through optical fibers.
What is the role of neutral atoms in quantum computing?
-Neutral atoms are used as qubits by utilizing the energy states of the atoms. These atoms are less sensitive to external disturbances compared to other qubit types, making them more resilient in noisy environments. However, neutral atom qubits require complex manipulation techniques and a vacuum environment to operate effectively.
What is the primary challenge in scaling quantum computers using different qubit types?
-The primary challenge in scaling quantum computers is maintaining the quantum state of qubits while performing computations on a large scale. Each qubit type—whether superconducting, trapped ion, photon, or neutral atom—faces its own set of challenges, including the need for complex isolation, precision control, and low temperatures. As quantum computers scale, these challenges multiply, making it difficult to ensure that all qubits maintain coherence and function properly.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

క్వాంటం సైన్స్ తో కంప్యూటర్ విప్లవం ఎలా ? || Computer Revoluation With Quantam Science ||

Computação Quântica - Fundamentos e Aplicações - Aula 03
Quantum Computers: Explained VISUALLY

ക്വാണ്ടം യുഗം വരുന്നു | Google Quantum Computer | Willow chip | Malayalam | Sahapadi

Quantum Computers, Explained With Quantum Physics
Quantum Computers Explained – Limits of Human Technology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
