Bab 3 PPB : Pengukuran Kinerja
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture covers the importance of performance measurement in business process modeling. It explains how performance metrics help businesses identify areas for improvement, track progress, and evaluate the success of improvement initiatives. The lecture explores traditional and operational performance measures, including financial, quality, speed, and reliability metrics. The speaker emphasizes the need for a comprehensive system to monitor and evaluate business performance, using both quantitative and qualitative indicators. The session also introduces various approaches for setting performance targets and aligning them with organizational processes for sustained competitive advantage.
Takeaways
- 😀 Performance measurement is essential for self-assessment and evaluating progress, as it helps organizations understand what needs to be improved and track development over time.
- 😀 Performance measurement allows for comparisons between organizations and industries, helping to evaluate if improvements have been effective and identify areas requiring further development.
- 😀 Financial metrics often conflict with operational improvement efforts, as they focus on direct monetary outcomes, while operational improvements are typically seen in areas like defect reduction or order fulfillment time.
- 😀 Modern performance measurement systems are more operationally focused, tracking ongoing performance through continuous monitoring of relevant metrics and exposing negative trends.
- 😀 Financial measurement is one of the traditional ways to assess performance, providing simple green or red signals to show financial surplus or deficit.
- 😀 Other performance measurement systems include those focused on time, quality, cost, flexibility, and reliability, offering insights into operational performance.
- 😀 Key operational performance goals include quality, speed, reliability, flexibility, and cost, which together build a competitive advantage for organizations.
- 😀 Competitive factors, such as customer expectations for low prices and high quality, define the performance goals that companies must prioritize to stay ahead of competitors.
- 😀 Performance measurement can be quantitative (e.g., time and cost), qualitative (e.g., customer satisfaction), or financial (e.g., profit margins), each offering different insights into an organization’s performance.
- 😀 The process of performance measurement can be seen as a balance between results-oriented metrics (common in Western management) and process-oriented metrics (emphasized in Japanese management).
- 😀 A comprehensive performance measurement system should be designed around organizational goals and processes, with clear identification of responsibilities and objectives across different levels.
Q & A
What is performance measurement in business processes?
-Performance measurement is the process of assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of a business or project by using specific metrics or standards. It helps monitor progress and evaluate the success of a project or process, ensuring that goals are being met.
Why is performance measurement important for businesses?
-Performance measurement is important because it allows businesses to identify areas that need improvement, track progress over time, compare performance with competitors, and evaluate the success of improvement initiatives.
What are traditional performance measures, and what is their limitation?
-Traditional performance measures are primarily financial metrics like profit margins or return on investment. The limitation is that they often conflict with improvement efforts that are more operational, such as reducing defects or improving production speed, which are harder to quantify financially.
How have performance measurement systems evolved in recent years?
-In recent years, performance measurement systems have shifted focus toward more operational metrics, such as reducing production defects, improving order fulfillment times, and ensuring customer satisfaction. These systems aim to measure ongoing performance rather than just financial outcomes.
What are the key elements of an operational performance measurement system?
-Key elements include continuous monitoring of relevant performance aspects, forming a performance dashboard to track trends, and identifying negative trends that require corrective actions to improve performance.
What are some of the key operational performance goals businesses should focus on?
-Businesses should focus on goals related to quality, speed, reliability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. These factors help drive competitiveness and overall success in business operations.
What is the difference between financial and non-financial performance measures?
-Financial performance measures focus on monetary aspects such as profit margins or revenue growth. Non-financial measures focus on operational aspects, like delivery times, customer satisfaction, or production quality, which are not directly expressed in financial terms.
What is the role of qualitative measures in performance measurement?
-Qualitative measures assess more subjective aspects of performance, such as customer satisfaction, employee engagement, or the effectiveness of leadership. These are harder to quantify but provide essential insights into overall business health and potential areas for improvement.
How can performance measurement help with business competitiveness?
-Performance measurement allows a business to evaluate its performance relative to competitors in key areas like price, quality, and delivery. This helps identify strengths and weaknesses, enabling the company to improve its competitive edge and meet customer expectations more effectively.
What are the seven steps suggested by Chandan (2003) for designing a performance measurement system?
-Chandan's seven steps for designing a performance measurement system include: 1) Identifying all involved processes, 2) Defining and limiting core processes, 3) Determining responsibilities and functions of processes, 4) Identifying and defining subprocesses, 5) Defining responsibilities of subprocesses, 6) Breaking down subprocesses into activities, and 7) Aligning targets across hierarchical levels.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

MPB 9_1 Process_Aware Information Systems

Bab 1 PPB (Pemodelan Proses Bisnis) : Apa itu Proses Bisnis?

Sistem Pengendalian Manajemen Pengukuran kinerja tradisional 1

Performance Measurement

Practical Research 2 Lesson 1: Introduction to Quantitative Research
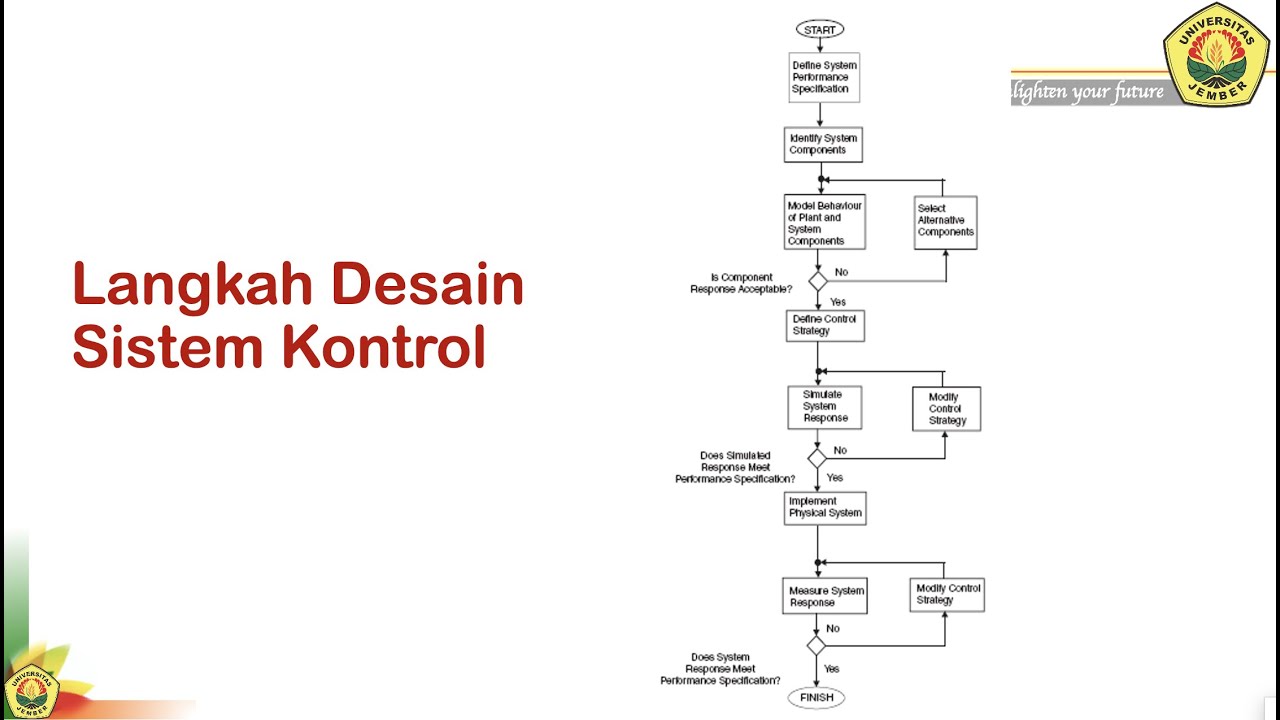
SK#1c Sistem Kontrol: Langkah - langkah Desain
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
