Alam Semesta Bisa Teratur Karena Ada Yang Mengatur? Kata Siapa ..!! - Ryu Hasan
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of entropy in the universe and life’s resistance to disorder. It explains how life, despite the universe's tendency toward chaos, fights entropy by maintaining internal order, such as through cellular processes like ion exchange. The speaker discusses the evolution of life, the rise of human cooperation, and the importance of societal rules in fostering large-scale collaboration. The video also highlights human competition and the challenges of adhering to rules, noting that people often fail to follow guidelines due to lack of training and cooperation, rather than natural inclination.
Takeaways
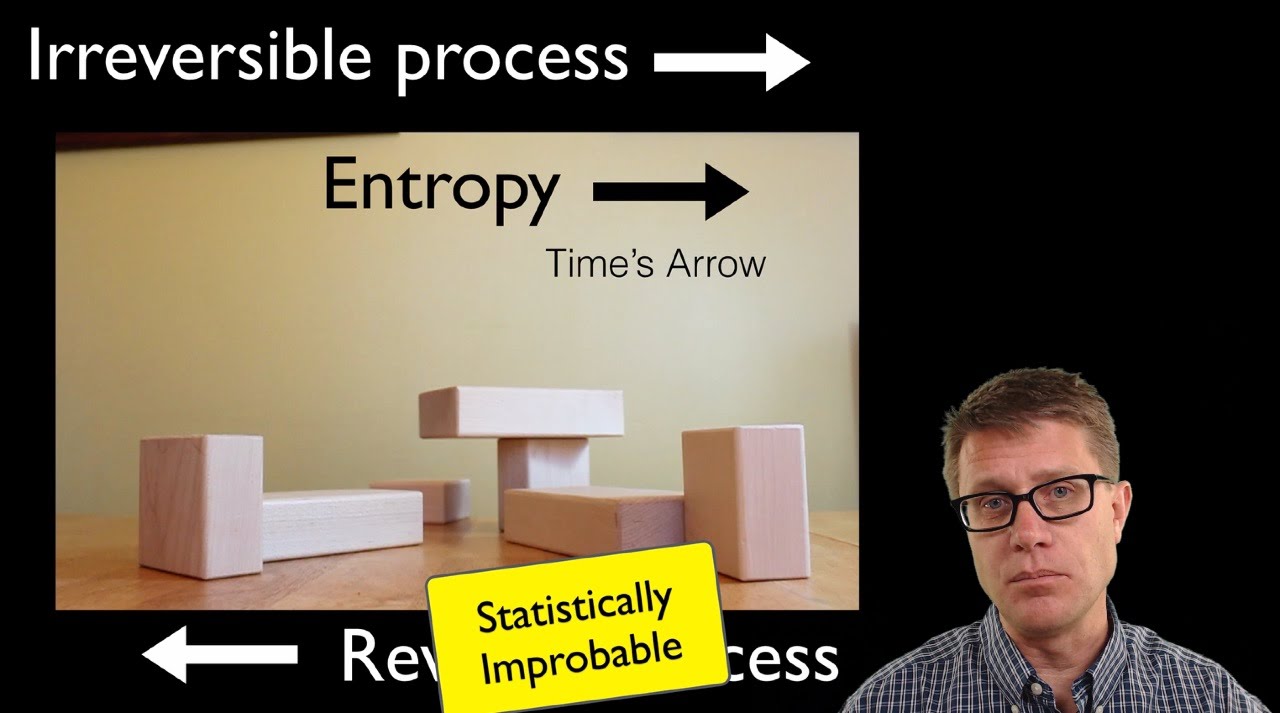
- 😀 The universe naturally tends towards disorder, a concept known as entropy, which is governed by the second law of thermodynamics.
- 😀 Life, as a system, actively resists entropy by creating organized structures and processes that oppose disorder.
- 😀 The first form of life on Earth, a single cell, began around 3.5 billion years ago, with DNA playing a key role in organizing life’s complexity.
- 😀 Even though entropy increases overall in the universe, life reduces local entropy by maintaining internal order through energy usage.
- 😀 While many species face extinction, life overall continues to grow and diversify, outpacing the rate of extinction in terms of new species creation.
- 😀 Human beings, unlike most other animals, have developed large-scale cooperation, which has been essential for survival and advancement.
- 😀 Competition and self-interest are natural tendencies, but humans have evolved complex systems of cooperation that allow for societal development.
- 😀 The growth of cooperation in human societies has been facilitated by shared rules and narratives, such as laws and cultural agreements.
- 😀 The human struggle to follow rules often stems from a lack of training or cultural conditioning in cooperation and self-discipline.
- 😀 Human societies face challenges of competition even within their own groups, as seen in social conflicts and competition for resources and status.
- 😀 Larger, more complex human groups are more successful at cooperation, but only up to a certain point. Beyond a certain size, groups tend to fragment into smaller, less cohesive units.
Q & A
What is entropy, and how does it relate to the universe?
-Entropy refers to the natural tendency of systems to move toward disorder or randomness. The speaker explains that the universe, by its nature, tends to become more disordered over time. This process is in line with the second law of thermodynamics, which states that entropy in a closed system will tend to increase. The universe as a whole is moving toward greater disorder, although local systems (such as life) can momentarily reduce entropy.
How does life resist entropy?
-Life resists entropy by maintaining order through complex processes, such as cellular activities that involve energy consumption. The speaker explains that living organisms fight entropy by reducing disorder within their systems, using energy to create and sustain order, such as in the case of ion pumps like the sodium-potassium pump, which helps maintain cellular functions.
What is the role of ATP in cellular processes?
-ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the primary energy currency in cells. The speaker explains that ATP is essential for the sodium-potassium pump and other cellular processes that maintain the order and function of cells. ATP provides the energy needed to move ions like sodium and potassium across cell membranes, maintaining cellular structure and function.
How does life evolve to fight entropy over time?
-Over time, life on Earth has evolved complex systems that counteract entropy. Initially, life began as simple single-celled organisms, but as evolution progressed, it led to more complex multicellular organisms. The increase in biomass and the development of new species (despite mass extinctions) demonstrate that life continues to combat entropy by increasing complexity and diversity.
What is the significance of mass extinctions in the context of life and entropy?
-The speaker discusses how life has undergone five major mass extinctions, but despite the loss of many species, life on Earth has continued to thrive. New species emerge to fill ecological niches, increasing biomass and countering entropy. The extinctions serve as a reminder that life evolves and adapts, even in the face of massive disruptions.
Why do species compete, and how does this relate to survival?
-Species, including humans, compete for resources like food, mates, and territory. This competition is a fundamental aspect of life, driven by evolutionary pressures. The speaker explains that this competition is often a necessary part of survival and the natural order, but cooperation also emerges in more advanced species, such as humans.
How does human cooperation differ from that of other species?
-Humans have evolved the ability to cooperate in large groups, which sets them apart from other species. The speaker highlights that humans can work together in large numbers and create complex systems of cooperation, unlike other species like chimpanzees, which can only manage smaller groups. This ability to cooperate in larger groups has been key to human success.
What role do narratives and shared stories play in human cooperation?
-Narratives and shared stories, such as those found in religion, politics, or cultural myths, are powerful tools that humans use to unite large groups. These narratives create a sense of shared purpose and identity, which enables people to work together even if they don’t know each other personally. This is a major factor in human success and social organization.
Why is it important to train individuals to follow rules in society?
-The speaker emphasizes that people are naturally competitive and may not instinctively follow rules or cooperate. In order to build effective societies, individuals must be trained to respect rules and cooperate. This training helps people understand the importance of following agreements and working together for the collective good.
What does the speaker mean by 'training' in the context of human behavior?
-In the context of human behavior, 'training' refers to the process of instilling the values and practices that encourage cooperation, respect for rules, and social order. The speaker suggests that societies function best when individuals are taught from a young age to work together, follow laws, and respect norms. This type of training helps individuals to overcome their natural tendency to compete and disregard rules.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)