Plano inclinado con rozamiento (Bachillerato)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we solve a physics problem involving a block sliding down an inclined plane. The block experiences forces such as weight, normal force, and friction. By analyzing the forces in both the x and y axes, we use Newton’s second law to find the acceleration of the block. The key equation reveals that the acceleration depends on the gravitational force, the incline angle, and the coefficient of friction. The final calculation gives an acceleration of 3.62 m/s², demonstrating how the block descends the plane under the given conditions.
Takeaways
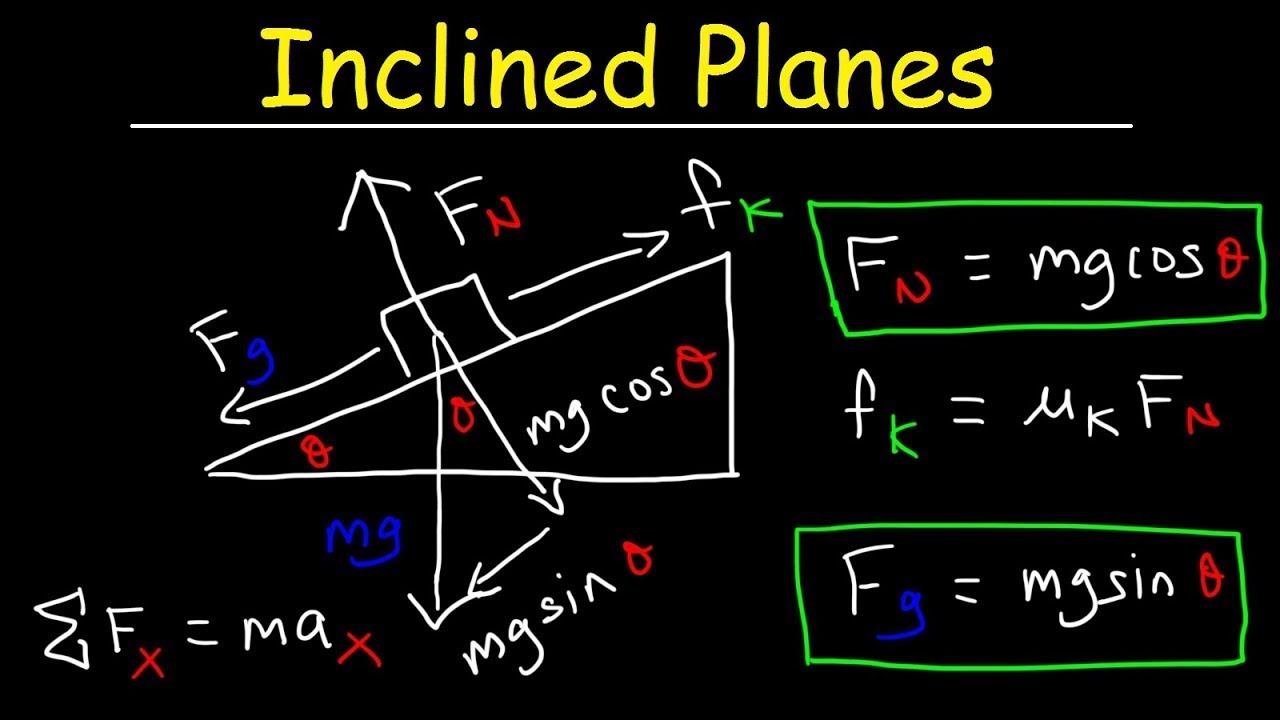
- 😀 The problem involves a block of mass m on an inclined plane, which is at a 30° angle to the horizontal.
- 😀 The coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is 0.15, a dimensionless quantity.
- 😀 The goal is to calculate the acceleration of the block as it slides down the inclined plane.
- 😀 Forces acting on the block include weight (mg), normal force (N), and frictional force (F_r).
- 😀 The weight of the block is decomposed into two components: horizontal (P_x) and vertical (P_y).
- 😀 The normal force is perpendicular to the surface of the plane and is equal to the vertical component of the weight (P_y).
- 😀 The frictional force (F_r) opposes the motion and is calculated as the product of the coefficient of friction (μ) and the normal force.
- 😀 Newton's second law is applied in both the x and y directions to set up the equations of motion for the block.
- 😀 The block only accelerates along the x-axis, as the acceleration in the y-direction is zero (no vertical motion).
- 😀 The acceleration is found to be independent of the mass of the block, and it depends on the gravitational constant (g), the angle of the incline, and the coefficient of friction.
- 😀 The numerical solution yields an acceleration of 3.62 m/s², which is the final result of the problem.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the problem described in the video?
-The main objective is to calculate the acceleration of a block with mass 'm' as it slides down an inclined plane with a 30° angle to the horizontal, taking into account friction.
What is the coefficient of friction used in the problem?
-The coefficient of friction between the block and the inclined plane is 0.15.
What forces are acting on the block in this problem?
-The forces acting on the block are the weight (mg), the normal force (N), and the frictional force (F_r).
How is the weight of the block decomposed in this scenario?
-The weight of the block is decomposed into two components: a horizontal component (P_x = mg sin(α)) parallel to the incline, and a vertical component (P_y = mg cos(α)) perpendicular to the incline.
Why is the acceleration in the vertical direction zero?
-The acceleration in the vertical direction is zero because the block does not move vertically; it only moves horizontally along the inclined plane.
What is the relationship between the normal force and the vertical component of the weight?
-The normal force (N) is equal to the vertical component of the weight (P_y), which is given by N = mg cos(α).
What equation is used to find the acceleration of the block along the incline?
-The equation used is Newton's second law applied to the x-axis: P_x - F_r = ma_x, where P_x is the component of the weight along the incline, F_r is the frictional force, and a_x is the acceleration along the incline.
How is the frictional force calculated?
-The frictional force (F_r) is calculated using the formula F_r = μN, where μ is the coefficient of friction and N is the normal force. In this case, F_r = μmg cos(α).
What is the final formula for calculating the acceleration of the block?
-The final formula for calculating the acceleration of the block is a_x = g(sin(α) - μ cos(α)).
What is the value of the acceleration obtained for the block in this problem?
-The acceleration of the block is approximately 3.62 m/s², calculated using the values of g = 9.8 m/s², α = 30°, and μ = 0.15.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Introduction to Inclined Planes

Usaha dan Energi • Part 6: Contoh Soal Hubungan Usaha, Energi, dan Daya (1)
#fisica #diagramas #cuerpolibre FISICA - COMO SE REALIZA UN DIAGRAMAS DE CUERPO LIBRE?

PIANO INCLINATO - piano inclinato fisica, reazione vincolare - Live Versione Corta

Work due to Friction equals Change in Mechanical Energy Problem by Billy

Past Board Exam Problem about Friction SOLVED! (Mechanics)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
