MUTASI : KELAS 12 SMA BIOLOGI
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the presenter explains the concept of mutations in biology, specifically targeting the 12th-grade syllabus. The video covers various types of mutations, including gene and chromosomal mutations, and their effects on DNA. Topics such as silent, missense, and nonsense mutations, along with frame-shift mutations and the differences between transition and transversion, are explored in detail. The presenter also discusses the causes of mutations, such as mutagens, and their different types—physical, chemical, and biological. Lastly, chromosomal mutations like aneuploidy, deletion, duplication, and inversion are explained, helping viewers understand the complex genetic processes behind mutations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mutations are random changes in genetic material (DNA) or chromosomes, which can be inherited but are not always passed down.
- 😀 Mutations can be caused by physical, chemical, or biological mutagens. Examples include UV radiation, chemicals like colchicine, and viruses or bacteria.
- 😀 Mutations can be classified into two types based on their location: somatic mutations (affecting body cells, not inherited) and germinal mutations (affecting gametes, inherited).
- 😀 Gene mutations can be divided into types such as silent mutation (no effect on amino acid sequence), missense mutation (changes amino acid), and nonsense mutation (creates a stop codon).
- 😀 Frameshift mutations involve the insertion or deletion of bases, causing a shift in the reading frame of the gene, resulting in significant changes to the amino acid sequence.
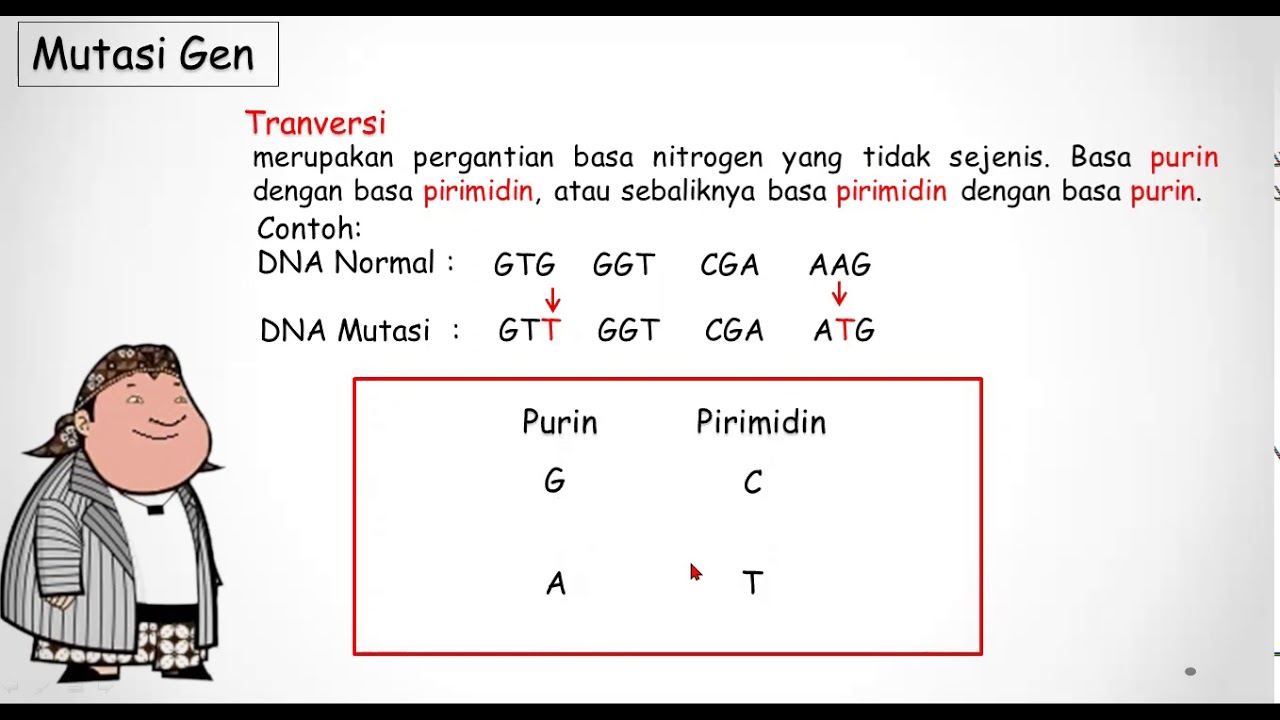
- 😀 Transition mutations occur when a purine base is replaced by another purine or a pyrimidine by another pyrimidine, while transversion mutations involve the replacement of purine with pyrimidine or vice versa.
- 😀 Chromosomal mutations include changes in chromosome structure such as deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation, and karyotype alterations like aneuploidy and polyploidy.
- 😀 Aneuploidy is the gain or loss of chromosomes, leading to conditions like monosomy (one chromosome missing) or trisomy (one extra chromosome).
- 😀 Polyploidy involves the addition of an entire set of chromosomes, and is used in agriculture to create seedless fruits or larger crops.
- 😀 Karyotype alterations, like inversions or translocations, can involve changes in the order or position of genes on chromosomes, potentially disrupting gene function and leading to genetic disorders.
Q & A
What is a mutation in genetics?
-A mutation is a change in the genetic material (DNA) or chromosomes, which occurs randomly and may be inherited. It can be caused by various factors and may result in either harmful or beneficial effects.
What is the difference between natural and artificial mutations?
-Natural mutations occur spontaneously, often due to environmental factors like UV radiation. Artificial mutations are induced by humans through controlled processes, often in laboratory settings, to achieve specific outcomes.
What are mutagens and what types exist?
-Mutagens are agents that cause mutations. There are three main types: physical mutagens (e.g., UV rays, gamma rays), chemical mutagens (e.g., alcohol, antibiotics), and biological mutagens (e.g., bacteria and viruses).
What is the difference between somatic and germinal mutations?
-Somatic mutations occur in somatic cells and are not passed down to offspring. Germinal mutations happen in gametes (reproductive cells) and can be inherited by the next generation.
What is a silent mutation?
-A silent mutation is a type of gene mutation where the change in the DNA sequence does not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of the protein, thus having no apparent effect.
What is a missense mutation?
-A missense mutation occurs when a change in the DNA sequence leads to a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein, which may affect the protein’s function.
What is a nonsense mutation?
-A nonsense mutation occurs when a change in the DNA sequence results in a premature stop codon, which causes the translation of the protein to halt early, often resulting in a nonfunctional protein.
What is a frameshift mutation?
-A frameshift mutation is caused by the insertion or deletion of one or more bases in the DNA sequence, causing a shift in the reading frame. This results in a completely different amino acid sequence downstream of the mutation.
What are transition and transversion mutations?
-Transition mutations involve a purine replacing another purine, or a pyrimidine replacing another pyrimidine. Transversion mutations involve a purine replacing a pyrimidine, or vice versa.
What are chromosomal mutations and what types exist?
-Chromosomal mutations involve changes in the structure or number of chromosomes. Types include aneuploidy (changes in chromosome number), chromosomal deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
MUTASI _ Bagian 1 (Mutasi GEN)_Biologi Kls XII

26. Piramida Energi

CARA MUDAH MENENTUKAN UKURAN PEMUSATAN DATA TUNGGAL

Translasi Vertikal Hal 1-13 Bab 1 TRANSFORMASI FUNGSI Kelas 12 SMA SMK Kurikulum Merdeka

Rangka Aksial dan Rangka Apendikular - Sistem Rangka - Biologi Kelas XI

PERTUMBUHAN DAN PERKEMBANGAN: BIOLOGI 12 IPA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
