Bahan-bahan Listrik dan Elektronika
Summary
TLDRThe video provides a comprehensive overview of electrical materials and electronics, categorizing them into conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. It explains the properties of each type, such as conductivity, resistivity, and atomic structure. The discussion includes practical examples of materials, their uses, and the importance of understanding their characteristics for safe and effective application in electrical devices. Additionally, it touches on semiconductor types and their role in electronic components like diodes and transistors, emphasizing their significance in modern technology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Materials used in electricity and electronics are categorized into two main types: based on their properties and types.
- 🔌 Conductors are materials that effectively conduct electricity due to their high valence electron count, with examples like copper and aluminum.
- 🛡️ Insulators are materials that resist the flow of electricity, having very few valence electrons, such as plastic and rubber.
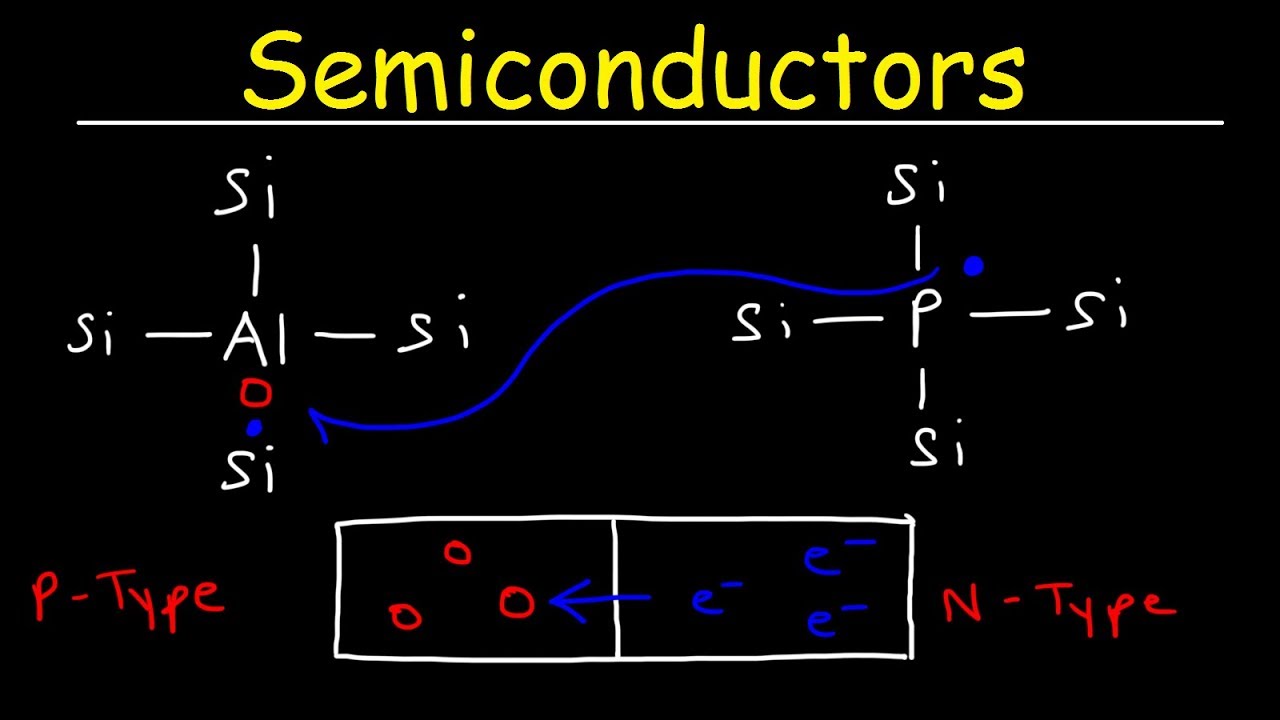
- ⚡ Semiconductors have conductivity levels between conductors and insulators, acting as conductors under certain conditions, with common examples including silicon and germanium.
- 📊 Electrical properties include electrical, mechanical, chemical, and physical properties, which determine how materials behave under various conditions.
- 🧪 Intrinsic semiconductors are pure and have balanced electron counts, while extrinsic semiconductors have added impurities that enhance conductivity.
- 🟢 P-type semiconductors are created by doping with materials that have fewer valence electrons, while N-type semiconductors are doped with materials that have more valence electrons.
- 🔍 Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in one direction and act as conductors or insulators based on applied voltage.
- 🔄 Transistors can regulate current flow and function as electronic switches, with types including PNP and NPN.
- 🖥️ Integrated circuits (ICs) combine multiple components, allowing for complex electronic functions in a compact format, vital for modern electronic devices.
Q & A
What are the two main categories of electrical materials mentioned in the transcript?
-Electrical materials are divided into two categories: based on their properties and based on their types.
What are the five properties of electrical materials?
-The five properties are electrical, mechanical, chemical, physical, and a combination of these properties.
What is a conductor and what are its key characteristics?
-A conductor is a material that can efficiently conduct electrical current. Key characteristics include high conductivity, high mechanical strength, small thermal expansion coefficient, and large elasticity.
Can you list some examples of conductive materials?
-Examples of conductive materials include copper, tin, gold, iron, and aluminum.
What defines an insulator?
-An insulator is a material that does not conduct electricity well, characterized by high resistance and a strong atomic structure with few free electrons.
What materials are considered insulators?
-Common insulators include paper, plastic, wood, rubber, ceramics, and glass.
What is a semiconductor and how does it function?
-A semiconductor is a material that has conductivity between conductors and insulators. It can behave as an insulator or conductor depending on temperature and external energy applied.
What are intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors?
-Intrinsic semiconductors are pure materials without impurities, while extrinsic semiconductors are doped with impurities to modify their electrical properties.
What are the two types of extrinsic semiconductors?
-The two types are p-type (positive) and n-type (negative) semiconductors, which differ based on the type of doping used.
What is the function of diodes in electronic components?
-Diodes are components that allow current to flow in one direction only, acting as a conductor in forward bias and an insulator in reverse bias.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)