Video Pembelajaran Materi Konduktivitas
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Kakashi and Timur Va explain the concept of electrical conductivity in materials, covering three types: conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. They illustrate the differences between these materials using various examples such as copper wire, pencils, and paper clips. The presenters also demonstrate a simple experiment to test the conductivity of different materials by using a battery and light bulbs to observe whether the materials allow electricity to flow. Conductors light up the bulbs, while insulators do not. The video aims to make the concept of conductivity clear and accessible for learners.
Takeaways
- 😀 Conductivity is the ability of a material to conduct electricity, and it is classified into three categories: conductors, insulators, and semiconductors.
- 😀 Conductors are materials that allow electricity to flow easily due to their low resistance, such as metals like copper, iron, and zinc.
- 😀 Insulators resist the flow of electricity and have high resistance, often because their valence electrons are not free to move.
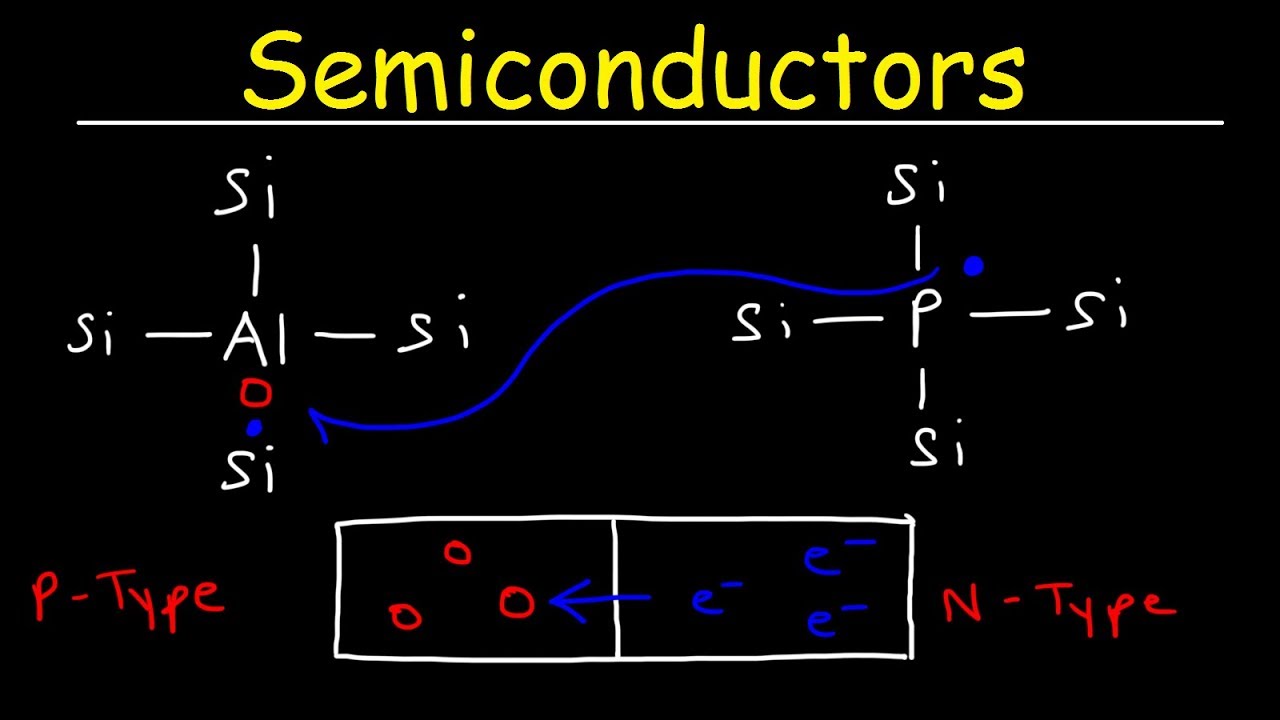
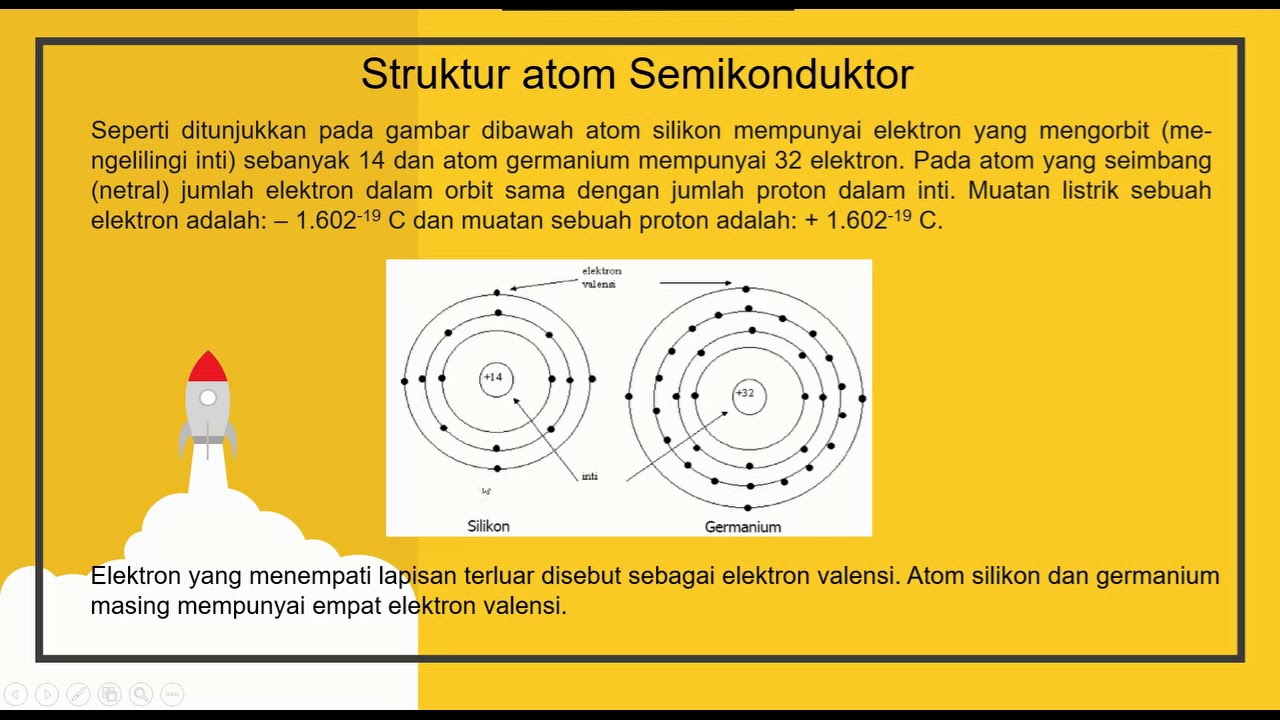
- 😀 Semiconductors can act as both conductors and insulators depending on specific conditions or treatments, with silicon being a common example.
- 😀 Conductors have key characteristics such as allowing the flow of electricity, being made of pure materials, and having low resistance.
- 😀 Insulators have high resistance and typically do not allow electricity to flow. They are often used to prevent electrical accidents.
- 😀 The test for determining conductivity in materials involves a simple circuit with a battery and light bulbs, where the bulb lights up if the material is a conductor.
- 😀 Copper wire, when tested, lights up the bulb, showing that it is a conductor.
- 😀 Materials like pens and cotton swabs are insulators because they do not light up the bulb when placed in the circuit.
- 😀 The demonstration clearly shows the practical differences between conductors and insulators in a hands-on manner.
- 😀 The lesson ends with a conclusion emphasizing that copper and clips are conductors, while pens and cotton swabs are insulators.
Q & A
What is conductivity?
-Conductivity is the property that allows a material to conduct electrical current. It refers to the ability of a substance to transfer electric charges.
What are the three types of materials based on conductivity?
-The three types of materials based on conductivity are conductors, insulators, and semiconductors.
What is a conductor?
-A conductor is a material that allows the easy flow of electric current or heat. It has a relatively low resistivity, meaning it can conduct electricity efficiently.
What are the characteristics of a conductor?
-A conductor typically can conduct heat or electric current, does so quickly, is made from pure materials, and is often hard. Common examples are iron, copper, and aluminum.
What is an insulator?
-An insulator is a material that resists the flow of electric current. It has high resistivity and does not allow easy movement of electrical charges.
What are the characteristics of an insulator?
-An insulator has properties that block electric current, high resistivity, and its valence electrons are difficult to move due to large energy gaps in the material.
What is a semiconductor?
-A semiconductor is a material that can behave as both a conductor and an insulator, depending on certain conditions. An example is silicon.
How do you test the conductivity of a material?
-To test the conductivity, a simple setup can be used with a battery, wires, and lamps. If the lamp lights up when connected to the material, it is a conductor; if not, it is an insulator.
What happens when a conductor is tested in the setup with the battery and lamp?
-When a conductor, like copper wire, is placed in the test setup, the lamp lights up, indicating that the material is conducting electricity.
What happens when an insulator is tested in the same setup?
-When an insulator, such as a pen or cotton swab, is placed in the test setup, the lamp does not light up, indicating that the material does not conduct electricity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)