Velocity-time Graphs
Summary
TLDRIn this instructional video, the presenter explains the concepts of velocity and its representation through velocity-time graphs. They clarify the distinction between speed and velocity, emphasizing the importance of direction. By walking through examples of drawing and interpreting these graphs, viewers learn how to calculate acceleration from the slope and distance from the area under the graph. The video also discusses the differences between distance and displacement, particularly when the graph crosses the time axis. Overall, it serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding motion in one dimension.
Takeaways
- 😀 Velocity is defined as speed with direction, distinguishing it from mere speed.
- 📈 In one-dimensional motion, positive and negative values indicate forward and backward movement.
- 📝 A velocity-time graph's vertical axis represents velocity (V), while the horizontal axis represents time (t).
- ⏳ Acceleration is shown as the slope (gradient) of the line on a velocity-time graph.
- 📏 The area under the graph represents the distance traveled, while displacement considers direction.
- 🛣️ When an object accelerates, the change in velocity over time creates a straight line on the graph.
- 📐 The formula for the area of a trapezium is essential for calculating distances in velocity-time graphs.
- 📊 To find acceleration, calculate the gradient: change in velocity divided by change in time.
- 🚫 If the velocity dips below the time axis, it indicates a change in direction, affecting displacement calculations.
- 🔄 Understanding the distinction between distance and displacement is crucial in solving physics problems.
Q & A
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
-Velocity includes both speed and direction, while speed only measures how fast an object is moving.
How can velocity be represented in one-dimensional motion?
-In one-dimensional motion, velocity can be indicated using positive or negative values to show direction (e.g., +3 m/s for right and -3 m/s for left).
What does it mean when an object is 'at rest' in terms of velocity?
-An object is 'at rest' when its velocity equals zero (0 m/s).
What do the axes on a velocity-time graph represent?
-The vertical axis represents velocity (V, in m/s) and the horizontal axis represents time (t, in seconds).
How do you calculate acceleration from a velocity-time graph?
-Acceleration is calculated using the gradient (slope) of the graph, with the formula: Acceleration = Change in Velocity / Change in Time.
What does the area under a velocity-time graph represent?
-The area under the velocity-time graph represents the distance traveled by the object.
What is the distinction between distance and displacement?
-Distance is the total length of the path traveled, while displacement is the shortest distance from the initial to the final position, considering direction.
How do you find the area of a trapezium on a velocity-time graph?
-To find the area of a trapezium, use the formula: Area = 1/2 * (Sum of parallel sides) * height.
What happens to the velocity-time graph when an object decelerates to rest?
-The graph will show a downward slope returning to the time axis, indicating that velocity decreases to zero.
Why is it important to distinguish between positive and negative areas on the velocity-time graph?
-Positive areas represent motion in one direction, while negative areas represent motion in the opposite direction; this affects calculations of displacement.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Interpreting motion data | Physics | Khan Academy

Velocity vs time graphs

GERAK LURUS BERUBAH BERATURAN (GLBB) - GERAK LURUS (FISIKA SMA)
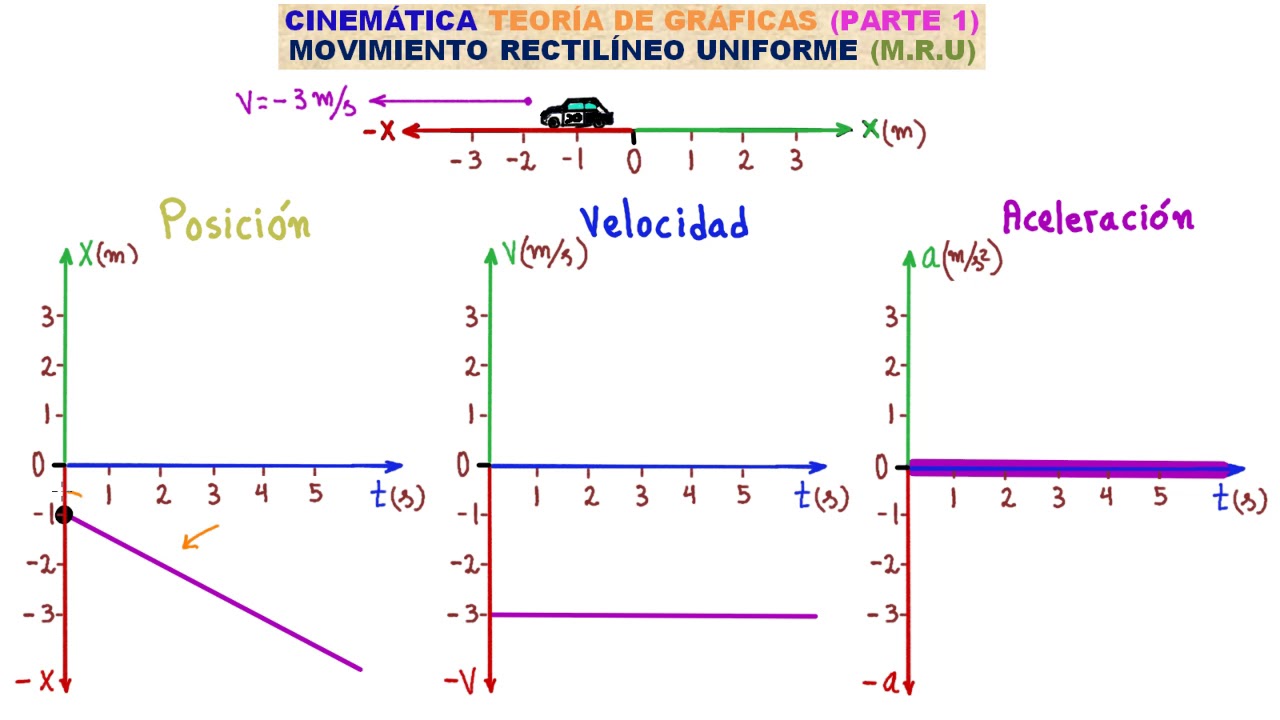
CINEMÁTICA. GRÁFICAS DEL M.R.U TEORÍA 1 [APRENDE LOS GRÁFICOS DE POSICIÓN, VELOCIDAD Y ACELERACIÓN]
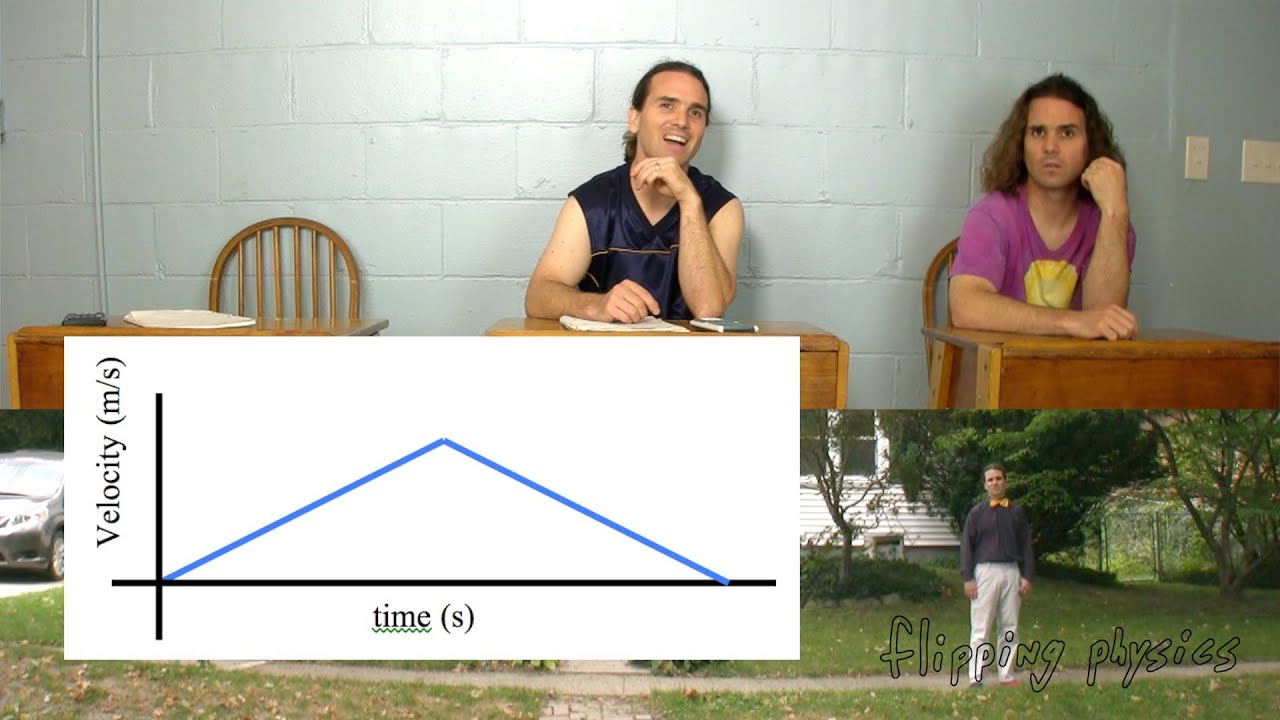
Walking Position, Velocity and Acceleration as a Function of Time Graphs

Il moto rettilineo uniforme
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
