Cement Manufacturing Process with the Portland Cement Association
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Tyler Leigh explains the process of modern cement production, highlighting its significant energy consumption and environmental impact. Cement, a key ingredient in concrete, is produced by calcining materials like limestone, which releases CO2. The process involves heating raw materials in a kiln to produce clinker, which is then ground with gypsum and limestone to form cement. The video also touches on the chemistry of cement, the use of various materials like slag and fly ash, and the importance of gypsum in controlling cement's setting properties.
Takeaways
- 🛠️ Cement production consumes around 6% of the world's energy, highlighting its significant environmental impact.
- 🌍 Concrete, made with cement, is the second most used material globally, but its production is energy-intensive.
- 🔥 Producing cement generates approximately 5% of global man-made CO2 emissions, contributing to its carbon footprint.
- 🧪 The calcination process, where limestone is heated to produce lime and carbon dioxide, contributes about 60% of cement-related CO2 emissions.
- ⚖️ For every 1 pound of cement produced, about 0.9 pounds of CO2 is released into the atmosphere.
- 🔧 Key raw materials for cement include limestone, sand, clay, shale, slag, and fly ash, often using industrial byproducts like medical waste and tires for fuel.
- ⚙️ Clinker is formed in a kiln through a process of heating these raw materials and is later ground with gypsum and limestone to create cement.
- 🧱 The main oxides in cement are calcium oxide (C), silicon dioxide (S), aluminum oxide (A), and iron oxide (F), which combine to form compounds essential for strength.
- 🏭 The preheater tower in a cement plant helps remove moisture and initiates the calcination process to improve energy efficiency.
- 🌀 Clinker is rapidly cooled and ground into cement powder, with gypsum added to control setting time and improve strength development.
Q & A
What is cement, and why is it significant in modern construction?
-Cement is a key ingredient in concrete, which is the second most used material in the world. Its production consumes around 6% of the world's energy, making it both essential and energy-intensive.
How much CO2 is emitted for every pound of cement produced?
-For every pound of cement produced, approximately 0.9 pounds of CO2 are emitted. This highlights the environmental impact of cement production.
What are the major raw materials used in cement production?
-The major raw materials used in cement production include limestone (for calcium oxide), sand (for silica), clay or shale (for aluminum), slag (for iron), and fly ash from coal plants.
What is clinker, and why is it important in cement production?
-Clinker is a key intermediate product in cement production. It is produced in a kiln by heating raw materials like limestone and then ground with gypsum and limestone to create cement.
What is calcining, and why is it significant in cement production?
-Calcining is the process of heating materials to break them apart. In cement production, limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated to produce lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide. This process accounts for about 60% of the CO2 emissions from cement production.
What are the four major oxides in modern Portland cement?
-The four major oxides in modern Portland cement are calcium oxide (C), silicon dioxide (S), aluminum oxide (A), and iron oxide (F). These combine during clinker formation to create different compounds crucial for cement's properties.
What role do gypsum and limestone play in the final grinding process of cement?
-Gypsum is added to regulate the setting time of the cement, while limestone is often added to reduce CO2 emissions and production costs. Limestone also acts as an inert filler.
Why does the cement industry often add waste products like slag and fly ash?
-The cement industry uses waste products like slag from the iron industry and fly ash from coal plants to reduce the environmental impact, recycle materials, and improve the chemical properties of cement.
What are the minor oxides found in cement, and why are they significant?
-Minor oxides in cement include magnesium oxide (M), sodium oxide, and potassium oxide (alkalis). These contribute to the overall chemical properties of the cement and can affect things like reactivity and durability.
How is clinker cooled after it comes out of the kiln, and why is this important?
-Clinker is rapidly cooled after exiting the kiln to make it more reactive. This rapid cooling helps preserve certain polymorphs, making the clinker more suitable for cement production.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Satu Masalah Lingkungan yang Jarang Dibahas

Sering Lihat Tapi Gak Tau Proses Pembentukannya? Begini Cara Pembuatan Semen Dari Awal Hingga Akhir

How to cool our homes (even without ACs)

VIDEO RISET 03
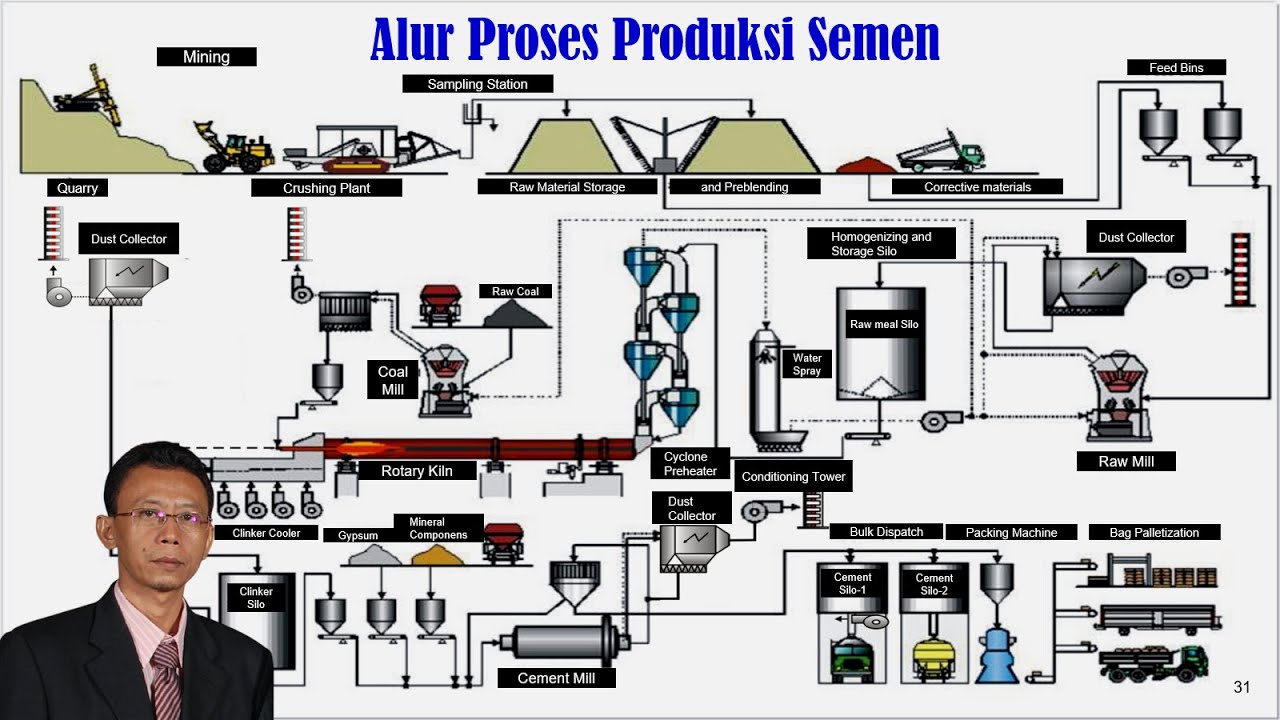
Alur Proses Produksi Semen (Tahapan Proses Produksi Semen)_Indonesia

The big problem with cement, and how to fix it
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
