Pertemuan 2 : Citra Digital, Sampling, dan Quantization - Part 1 : Apa itu citra digital ?
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses digital image processing, starting with the definition of a digital image, its spatial coordinates (x, y), and intensity (f), referred to as pixels. It explains the difference between digital image processing, image editing, and computer graphics, highlighting the focus on improving software for image processing. The video also covers key areas like image analysis, computer vision, and three levels of processing (low, mid, high). Each level involves tasks such as noise reduction, segmentation, and object recognition, progressing towards understanding and interpreting digital images with cognitive functions.
Takeaways
- 📷 Digital images are represented as a two-dimensional function where x and y are spatial coordinates, and f(x, y) represents the intensity (or gray level) at those coordinates.
- 💻 Digital image processing involves processing or manipulating digital images using computers, distinguishing it from digital image editing, which typically uses existing software like Photoshop or Corel.
- 🔧 Digital image editing focuses on manipulating digital images using software, while digital image processing is more about designing and developing software to improve image manipulation.
- 🖼️ Computer graphics differs from digital image processing by focusing on the synthesis of images from geometric models, particularly in 3D space.
- 👁️ Digital image processing extends beyond human vision by using imaging technologies like gamma rays, ultrasound, and electron microscopes to capture data beyond the visible light spectrum.
- 🌐 Digital image processing is widely applicable across various industries and has been recognized for solving significant social and economic challenges.
- 🤖 Image processing transitions into image analysis and computer vision, particularly when the goal is to understand the content of an image, often using artificial intelligence.
- 🔍 The scope of digital image processing can be categorized into three levels: low-level (e.g., noise reduction and contrast enhancement), mid-level (e.g., segmentation and object recognition), and high-level (e.g., object understanding and computer vision).
- 🛠️ Low-level image processing focuses on basic tasks like enhancing contrast or sharpening images, where both input and output are still digital images.
- 🧠 High-level image processing incorporates cognitive functions to make sense of the recognized objects, moving towards computer vision and more advanced image understanding.
Q & A
What is a digital image?
-A digital image is represented as a two-dimensional function f(x, y), where x and y are spatial coordinates, and f represents the intensity or gray level at those coordinates.
What are the elements of a digital image called?
-The elements of a digital image are called pixels, which are the smallest units in an image that have specific locations and intensity values.
What is digital image processing?
-Digital image processing refers to the use of digital computers to process and manipulate digital images to improve or modify them.
How is digital image processing different from image editing?
-Image editing focuses on manipulating digital images using software like Photoshop, while digital image processing involves designing and improving the software and algorithms used for processing images.
What is the difference between digital image processing and computer graphics?
-Digital image processing deals with improving and analyzing digital images, whereas computer graphics is focused on synthesizing images from geometric descriptions, especially in 3D models.
What is the role of digital image processing in human vision?
-Digital image processing can enhance and extend human vision by processing images in a broader spectrum than visible light, including gamma rays and radio waves, which are beyond human perception.
What are some practical applications of digital image processing?
-Digital image processing has applications in a variety of fields, including medical imaging (ultrasound, MRI), satellite imaging, and economic and social problem-solving.
What is the difference between image processing, image analysis, and computer vision?
-Image processing focuses on improving images, image analysis is about extracting meaningful information from images, and computer vision involves interpreting the content of images using artificial intelligence.
What are the three levels of digital image processing?
-The three levels are: low-level processing (basic operations like noise reduction and contrast enhancement), mid-level processing (tasks like segmentation and object recognition), and high-level processing (interpreting and understanding objects in images).
What is the significance of high-level image processing?
-High-level image processing involves associating recognized objects in images with cognitive understanding, making it essential for tasks like object detection in computer vision and AI systems.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Spatial Filtering Introduction with An Example | Digital Image Processing

Pertemuan 2: Citra Digital, Sampling, dan Quantization-Part 5: Konsep dasar Sampling & Quantization

2. CARA MUDAH MENGHITUNG MEMORI PENYIMPANAN CITRA/GAMBAR

Linear Transformation
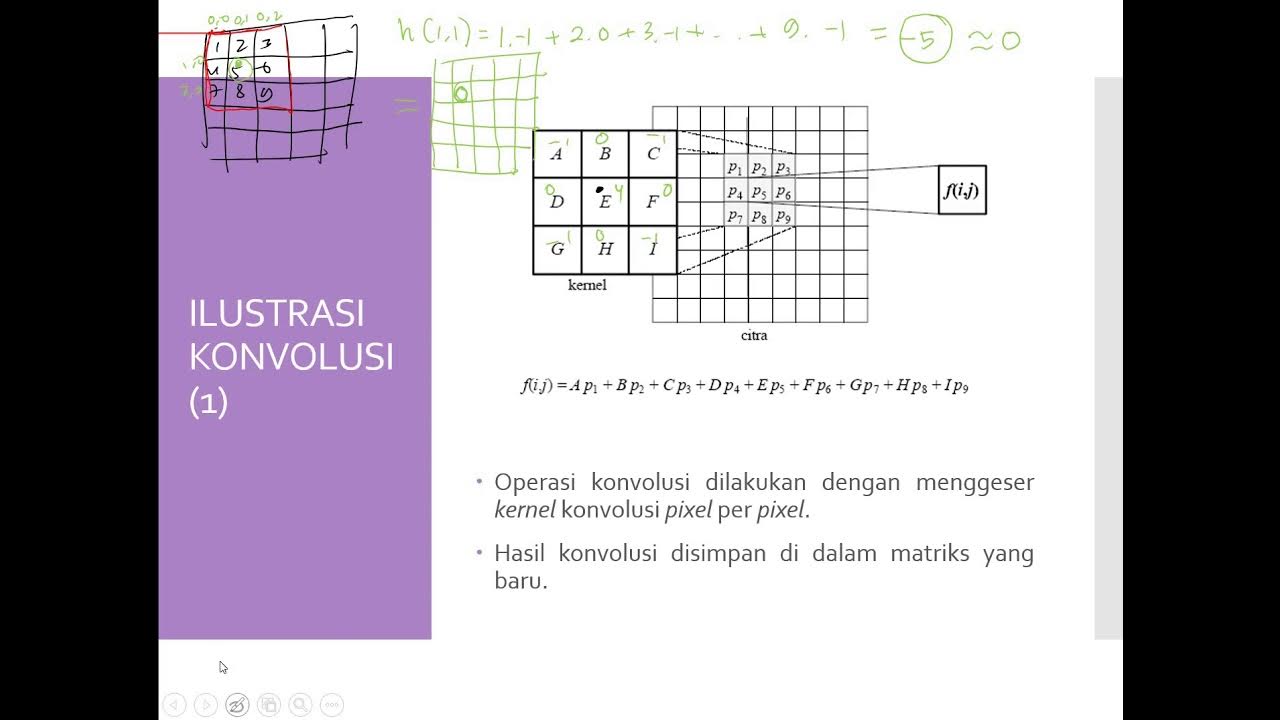
Konvolusi Citra Digital

Pertemuan 2 : Citra Digital, Sampling, dan Quantization - Part 2 : Sejarah citra digital dan PCD
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
