Konsep Dasar Teorema Pythagoras
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the historical origins and practical applications of Pythagoras' theorem. It explains that the theorem, which defines the relationship between the sides of a right-angled triangle, was known to the Babylonians and Egyptians long before Pythagoras. The theorem is crucial for calculating areas, taxes, inheritances, and constructing pyramids. The video also covers how to use the theorem to determine the type of triangle and calculate the height of various geometric shapes. It highlights the theorem's significance in trigonometry, architecture, woodworking, navigation, and everyday problem-solving, emphasizing its widespread utility.
Takeaways
- 📚 The Pythagorean theorem has been known and proven for a long time, with evidence dating back to the Babylonians around 1900-1600 BCE.
- 🌏 The theorem was independently discovered by different ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, Indians, and Chinese.
- 🔍 The theorem is named after Pythagoras, a Greek philosopher and mathematician, who introduced it to the Greek society and made it widely known, despite not being the first to discover it.
- 📐 The Pythagorean theorem describes the relationship between the lengths of the sides of a right-angled triangle, specifically that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
- 🧮 Mathematically, the theorem is expressed as (a^2 = b^2 + c^2), where a is the hypotenuse and b and c are the other two sides.
- 🔑 The theorem is only applicable to right-angled triangles, which have one angle measuring 90°.
- 🔍 There are different types of triangles based on the Pythagorean theorem: acute triangles (where all angles are less than 90°), obtuse triangles (with one angle between 90° and 180°), and right-angled triangles (with one angle exactly 90°).
- 🏗️ The Pythagorean theorem has practical applications in daily life, such as calculating land area for tax or inheritance purposes, building pyramids, and in navigation.
- 🎓 At the high school level, the theorem serves as a foundation for trigonometry.
- 🏙️ The theorem is not just for solving math problems in school; it is used by architects to calculate roof slopes, install sloping floors, and ensure right angles in carpentry work.
- 🌳 It can also be used to measure the height of buildings, towers, and cliffs, and to calculate the volume of a prism by finding its height.
Q & A
What is the Pythagorean theorem?
-The Pythagorean theorem describes the relationship between the lengths of the sides of a right-angled triangle. It states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
When was the Pythagorean theorem first discovered?
-The Pythagorean theorem was discovered and proven a long time ago. Historical records suggest that the Babylonians found combinations of Pythagorean triples between 1900 and 1600 BCE.
Why was the Pythagorean theorem important in ancient times?
-In ancient times, the Pythagorean theorem was useful for everyday life, such as calculating land area for tax or inheritance purposes, building pyramids, and dealing with water.
Why is the theorem named after Pythagoras instead of the Babylonians?
-Pythagoras was a Greek philosopher and mathematician who lived around the 6th century BCE. Although the theorem was known before his time, he was the first to introduce it to the Greek society and make it famous worldwide.
What is a Pythagorean triple?
-A Pythagorean triple consists of three positive integers a, b, and c, such that a² + b² = c². These are the lengths of the sides of a right-angled triangle.
How can you use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse?
-You can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse (c) by using the formula c² = a² + b², where a and b are the lengths of the other two sides.
What are the different types of triangles in relation to the Pythagorean theorem?
-There are three types of triangles in relation to the Pythagorean theorem: acute triangles (where all angles are less than 90°), obtuse triangles (where one angle is between 90° and 180°), and right-angled triangles (where one angle is exactly 90°).
Can the Pythagorean theorem be used to calculate the height of other geometric shapes?
-Yes, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to calculate the height of other geometric shapes such as trapezoids, calculate diagonals in rectangles and squares, and find the height of a prism to calculate its volume.
What is the significance of the Pythagorean theorem in trigonometry?
-In high school mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem serves as a foundation for trigonometry, which is essential for understanding the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles.
How is the Pythagorean theorem applied in real-world scenarios?
-The Pythagorean theorem is used by architects to calculate roof slopes, by builders to ensure right angles in construction, by navigators to determine the shortest path to a location, and by surveyors to measure the height of trees, towers, and cliffs.
What are some common Pythagorean triples?
-Some common Pythagorean triples include (3, 4, 5), (5, 12, 13), and (7, 24, 25). These are sets of three numbers that satisfy the equation a² + b² = c².
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

How many ways are there to prove the Pythagorean theorem? - Betty Fei

ASAL MULA TEORI PYTHAGORAS

HISTORY OF MATHEMATICS | CHAPTER-I
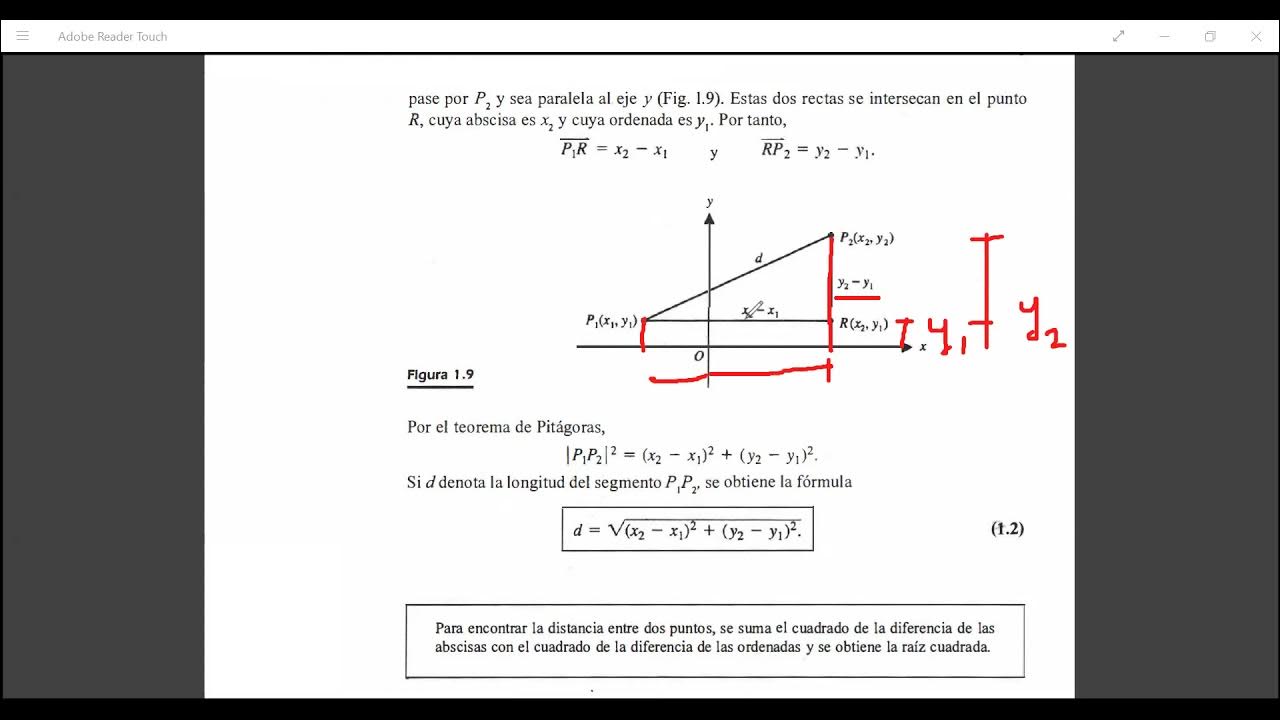
Distancia entre dos puntos

What Is Pythagoras Theorem? | PYTHAGORAS THEOREM | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz

The History of Non-Euclidean Geometry - Sacred Geometry - Part 1 - Extra History
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
