Electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum | Physics | Khan Academy
Summary
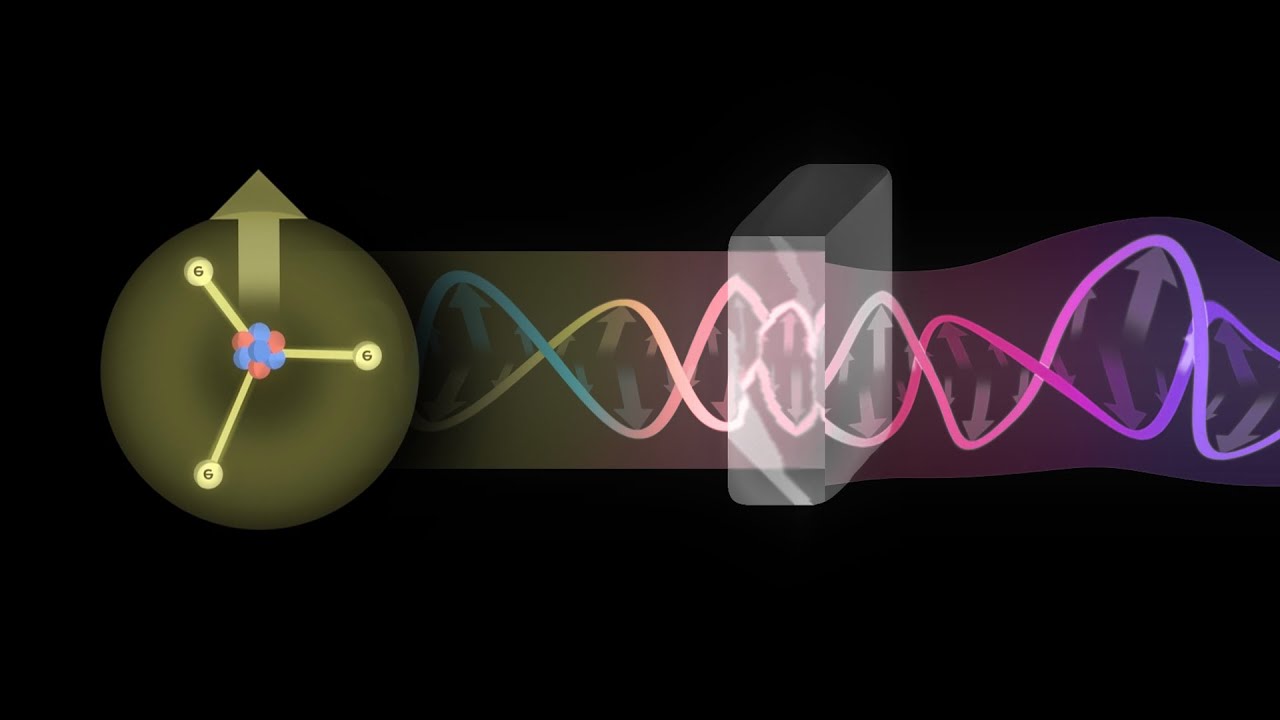
TLDRThe video explains how electric and magnetic fields interact to create electromagnetic waves. A changing electric field can induce a magnetic field, and vice versa, forming a self-sustaining wave that propagates through space, even in a vacuum. These waves, known as electromagnetic waves, travel at the speed of light and include visible light, radio waves, X-rays, and more. The video also highlights the electromagnetic spectrum, emphasizing the visible light range, and describes how higher frequencies like ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays can be more dangerous due to their higher energy.
Takeaways
- 🔋 A positive charge creates an electric field that radiates outward.
- 💡 A current in a wire generates a magnetic field looping around it.
- 🔄 A changing electric field can induce a magnetic field, even without current.
- ⚡ A changing magnetic field can generate a changing electric field, creating a feedback loop.
- 📡 Electromagnetic waves can be created by oscillating electric or magnetic fields, such as in antennas.
- 🌐 Electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum without needing a medium.
- 🧲 Electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves are perpendicular to each other and the wave's direction of travel.
- 🌈 The visible light spectrum is just a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum, with wavelengths between 400 and 750 nanometers.
- ☀️ Ultraviolet light has higher frequency and energy than visible light, making it potentially harmful to humans.
- 📻 The electromagnetic spectrum includes various regions, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Q & A
What is an electric field and how is it created?
-An electric field is a region around a charged particle where an electric force would be exerted on other charged particles. It is created by a positive charge and points radially outward from the charge.
How does a current in a wire create a magnetic field?
-A current in a wire creates a magnetic field that loops around the wire, with the field lines forming concentric circles around the wire.
What is a changing electric field and how does it relate to magnetic fields?
-A changing electric field is one where the electric potential varies over time or space. This change can induce a magnetic field even in regions with no current, as discovered by James Clerk Maxwell.
How does a changing magnetic field create an electric field?
-A changing magnetic field induces an electric field according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. This is the principle behind transformers and inductors.
What is the significance of James Clerk Maxwell's discovery regarding electromagnetic fields?
-James Clerk Maxwell discovered that a changing electric field can create a changing magnetic field, and vice versa, leading to the concept of electromagnetic waves that can propagate through space without a medium.
How can you create a changing electric field?
-A changing electric field can be created by moving a charge up and down or oscillating it, similar to how an antenna works.
What is an electromagnetic wave and how does it propagate?
-An electromagnetic wave is a wave that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that propagate through space at the speed of light. They propagate outward from their source, perpendicular to both the electric and magnetic fields.
Why do electromagnetic waves not need a medium to travel?
-Electromagnetic waves do not need a medium because they are self-propagating, with the electric field creating the magnetic field and vice versa, allowing them to travel through a vacuum.
What is the relationship between the electric field, magnetic field, and the direction of travel of an electromagnetic wave?
-The electric field and magnetic field of an electromagnetic wave are perpendicular to each other and both are perpendicular to the direction of travel of the wave.
What is the speed of electromagnetic waves and how is it related to light?
-The speed of electromagnetic waves is the speed of light, approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second. Light is a special type of electromagnetic wave that is visible to the human eye.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum and where does the visible spectrum fit into it?
-The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. The visible spectrum is a small part of this spectrum, lying between infrared and ultraviolet light, with wavelengths between approximately 400 nanometers (violet) and 750 nanometers (red).
Why are higher frequency electromagnetic waves more dangerous?
-Higher frequency electromagnetic waves are more dangerous because they carry more energy per photon. This higher energy can cause more damage to biological tissues, such as DNA damage leading to mutations or cell death.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES In 20 Minutes || Complete Chapter For JEE Main/Advanced

Fisika kelas 12 | Gelombang Elektromagnetik (GEM)

Voltage, Current, Electricity, Magnetism

¿Qué es el electromagnetismo? | 101 Videos
The origin of Electromagnetic waves, and why they behave as they do

El Campo Electromagnético, cómo surgen las fuerzas Eléctricas y Magnéticas
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
