Voltage, Current, Electricity, Magnetism
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the fundamentals of electricity and magnetism, starting with charged particles and their interactions through electric fields. It covers voltage, current, and how batteries push charged particles through circuits. The script then explores magnetic fields generated by moving charges, spinning particles, and currents, introducing concepts like magnets and electric motors. It explains electromagnetic induction, alternating and direct currents, and how changing fields create waves. Finally, it links these principles to real-world applications, including power generation, radios, cell phones, and visible light, highlighting how different electromagnetic waves vary in frequency, from radio waves to X-rays and gamma rays.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Particles can carry positive or negative charges, and like charges repel while opposite charges attract.
- 🔋 Voltage represents the energy per charged particle, similar to the height of a mountain for falling rocks.
- 💡 Current is the flow of charged particles per second, and the total power depends on both voltage and current.
- 🔌 Batteries create an electric field that pushes charged particles through wires, but do not create the particles themselves.
- 💡 In a circuit, if one light bulb breaks, it can either stop all current (series) or leave others unaffected (parallel).
- 🧲 Moving charged particles generate magnetic fields, which exert forces on other moving charges.
- 🌀 Magnetic fields can be generated by current through wires, and reversing current reverses the magnetic field.
- ⚙️ Electric motors work by using changing currents to rotate magnets through their magnetic fields.
- 🌐 Changing magnetic fields create electric fields and vice versa, forming electromagnetic waves like radio, light, and X-rays.
- 🔄 AC (Alternating Current) has voltage and current that constantly change direction, while DC (Direct Current) flows in one direction.
- 🌈 Visible light is a type of electromagnetic wave with higher frequency than radio waves, and different colors correspond to slightly different frequencies.
- ☢️ Extremely high-frequency electromagnetic waves, such as X-rays and gamma rays, have more energy than visible light.
Q & A
What happens when particles have the same charge versus opposite charges?
-Particles with the same charge repel each other, while particles with opposite charges attract each other due to the electric fields they create.
How can voltage be compared to the height of a mountain?
-Voltage is like the height of a mountain because it represents the energy each charged particle has. Just as rocks falling from a higher elevation have more energy, higher voltage gives charged particles more energy.
What is the relationship between voltage, current, and power in a circuit?
-The total power in a circuit is the voltage multiplied by the current. Voltage is the energy per charged particle, and current is the number of particles flowing per second.
Do batteries create charged particles?
-No, batteries do not create charged particles. They create an electric field that pushes existing charged particles along the circuit.
What is the difference between electric fields and magnetic fields?
-All charged particles create electric fields, but only moving charged particles create magnetic fields. Magnetic fields exert a force on other moving charged particles.
How is a magnet created at the particle level?
-A magnet is created when many charged particles spin in the same direction within a material. This alignment produces a magnetic field, with a North and South Pole.
How do electric motors use magnetic fields?
-Electric motors work by changing the direction of current through a wire, which reverses the magnetic field. By constantly changing the current, the magnetic field can rotate, causing the motor to spin.
How do power plants generate electricity using magnets?
-Power plants rotate magnets to create a changing magnetic field, which induces an electric field that pushes charged particles in wires. This generates electricity, often as AC (alternating current) where voltage and current alternate direction.
What is the difference between AC and DC electricity?
-AC (Alternating Current) changes direction periodically, whereas DC (Direct Current) flows in a single direction. Batteries provide DC, while power plants often generate AC.
How are electromagnetic waves formed?
-Electromagnetic waves form when changing magnetic fields create electric fields, and changing electric fields create magnetic fields. This chain reaction propagates as a wave, which includes radio waves, visible light, and X-rays, differing mainly in frequency.
What distinguishes visible light from other electromagnetic waves?
-Visible light is an electromagnetic wave with a higher frequency than radio waves. Each color of visible light corresponds to a slightly different frequency, and waves with even higher frequencies, like X-rays and gamma rays, carry more energy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Listrik Statis ( Muatan Listrik - Hukum Coulomb - Medan Listrik - Beda Potensial & Energi Listrik )
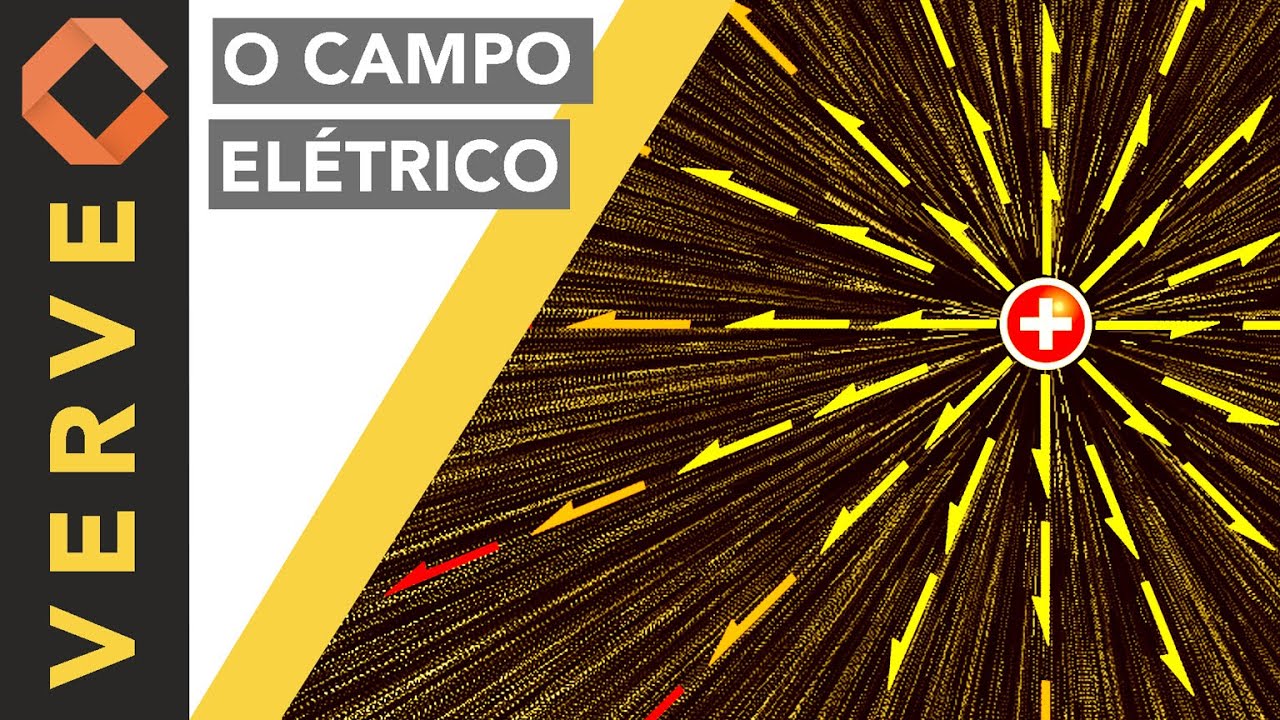
Campo elétrico: Tudo que você precisa saber sobre um dos campos mais importantes da Física

Magnetism: Crash Course Physics #32

💯 Outline how electricity and magnetism are related | Motors and Generators

Force at a distance! Induced magnets and domain theory!
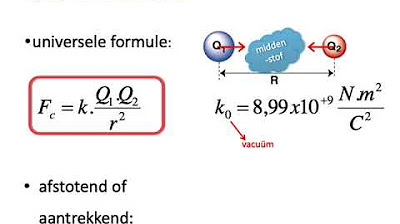
We1 EM ww
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)