Grade 8 Math Q1 Ep2: Factoring Special Products
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Teacher Joshua guides Grade 8 students through the process of factoring polynomials, focusing on special products like perfect squares and cubes. He explains how to factor the difference of two squares and cubes using the FOIL method and introduces mnemonics like 'SOP' for remembering the signs in factoring. The video includes practical examples, such as calculating the area of a picture frame and the volume needed for packing materials, to illustrate the concepts. The lesson concludes with a quick quiz to reinforce learning, emphasizing the importance of practice in mastering mathematical skills.
Takeaways
- 📘 The video is an educational session focused on grade 8 mathematics, specifically on factoring polynomials.
- 🔢 The concept of perfect squares and cubes is introduced, which are numbers or expressions that can be expressed as a power of two or three, respectively.
- 📐 The video explains the multiplication of polynomials using the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last).
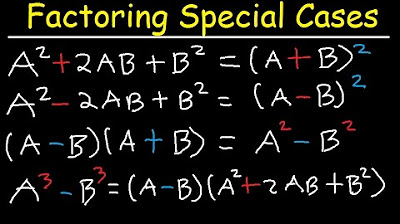
- 🔍 Special products like the difference of two squares (a^2 - b^2) and the sum/difference of two cubes are discussed, highlighting their unique patterns.
- 📝 The process of factoring polynomials is likened to reversing the process of multiplication, starting from the product to find the factors.
- 🎨 An example using a square wooden panel helps illustrate the concept of factoring a difference of two squares in a practical context.
- 🧩 The video uses a Rubik's cube analogy to describe the complexity and variability of solving mathematical problems, emphasizing the importance of recognizing patterns.
- 🔄 The mnemonic 'SOP' (Same, Opposite, Positive) is introduced to help remember the signs in factoring the sum and difference of two cubes.
- 📦 A practical example involving a larger and smaller box is used to demonstrate the application of factoring a difference of two cubes.
- 📚 The video concludes with a recap of the special products covered and a call to practice these concepts through additional exercises.
Q & A
What is the focus of the lesson in the Deaf Ed TV video?
-The focus of the lesson is on factoring polynomials, specifically special products like perfect squares, perfect cubes, the difference of two squares, and the sum and difference of two cubes.
What is a perfect square number?
-A perfect square number is a number or expression that can be expressed as the power of two, such as 3 squared (3^2) or y raised to the sixth (y^6).
How many perfect squares are in the first five whole numbers?
-The first five perfect squares are 1 (1^2), 4 (2^2), 9 (3^2), 16 (4^2), and 25 (5^2).
What is the difference of two squares in algebraic terms?
-The difference of two squares is an algebraic expression of the form a^2 - b^2, which can be factored into (a + b)(a - b).
What is the mnemonic 'SOP' used for in factoring polynomials?
-The mnemonic 'SOP' stands for 'Same Opposite Positive' and is used to remember the signs in the factoring of the sum or difference of two cubes.
How is the area of a square calculated?
-The area of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by itself, or side^2.
What is the volume of a cube with a side length of 5 inches?
-The volume of a cube with a side length of 5 inches is 125 cubic inches, calculated as 5^3.
How do you factor the expression 3w^2 - 48?
-The expression 3w^2 - 48 is factored by first taking out the greatest common factor, which is 3, resulting in 3(w^2 - 16), and then recognizing it as a difference of squares, factoring it into 3(w + 4)(w - 4).
What is the factored form of 16a^6 - 25b^2?
-The factored form of 16a^6 - 25b^2 is (4a^3 + 5b)(4a^3 - 5b), recognizing it as a difference of two squares.
What is the volume of empty space in a larger box with a side length of 5 inches when a smaller box with an unknown side length x is placed inside?
-The volume of empty space is the volume of the larger box minus the volume of the smaller box, which is 125 - x^3 cubic inches, and can be factored as (5 - x)(25 + 5x + x^2).
How does the video conclude about the approach to solving mathematical problems?
-The video concludes that there are many ways to solve a problem in mathematics, and it emphasizes the importance of focusing on the steps, patterns, and processes observed in factoring polynomials.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

[Tagalog] First periodical test #math8 #periodicaltest #firstquarter #factoringpolynomials PART I
Factoring Binomials & Trinomials - Special Cases

Factoring Polynomials using Greatest Common Monomial Factor

Grade 8 Math Q1 Ep 6 Simplifying Rational Algebraic Expressions

Grade 8 Math Q1 Ep1: Factoring Polynomials
Simplifying Rational Algebraic Expressions - Grade 8 Math
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
