Video Praktikum Systema Endocrinon
Summary
TLDRThis video script is a comprehensive guide to the human endocrine system, which regulates metabolism alongside the nervous system to maintain homeostasis. It explains the differences between neurotransmitters and hormones, the latter being produced by endocrine glands with high vascularization to distribute hormones throughout the body. The script delves into the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and pancreatic islets, highlighting their locations, structures, and functions, including the production of hormones like insulin and thyroid hormones.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The video discusses the endocrine system, which controls metabolism and works alongside the nervous system to maintain body homeostasis.
- 💉 Neurons produce neurotransmitters that transmit signals quickly, while endocrine glands produce hormones that act more slowly.
- 🩺 Endocrine glands are invaginations of epithelial tissue with high vascularization, allowing hormones to be released into the bloodstream.
- 🌐 Hormones circulate throughout the body, affecting cells far from the gland that produced them.
- 🧠 The pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is located in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone and consists of the anterior and posterior parts.
- 🔍 The anterior pituitary contains chromophil cells, which are composed of acidophil and basophil cells, and chromophobes.
- 🧬 The posterior pituitary, or pars nervosa, is made up of neural endings from the hypothalamus and contains cells that store hormones.
- 🌡️ The thyroid gland is located in the neck and is composed of a stroma and parenchyma, which includes thyroid follicles and colloid surrounded by follicular cells.
- 🥖 The islets of Langerhans in the pancreas are the endocrine part that produces hormones, visible as dark spots under a microscope.
- 🔵 Victoria blue staining can detect the presence of insulin, causing it to appear blue, and can also differentiate between alpha and delta cells.
Q & A
What is the main function of the endocrine system?
-The endocrine system controls the body's metabolism and works alongside the nervous system to regulate the body's homeostasis.
How does the endocrine system differ from the nervous system in terms of action?
-The nervous system produces neurotransmitters that transmit impulses quickly, while the endocrine system produces hormones that act more slowly.
What is the role of vascularization in the endocrine system?
-High vascularization in the endocrine system allows hormones to be released into the bloodstream, affecting cells that are distant from the gland.
Where is the pituitary gland located?
-The pituitary gland is located in the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone.
What are the main parts of the pituitary gland mentioned in the script?
-The main parts of the pituitary gland mentioned are the anterior pituitary (pars distalis) and the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis).
What types of cells are found in the anterior pituitary?
-The anterior pituitary contains chromophil cells, which are composed of acidophil and basophil cells, and chromophob cells.
What is the function of the neurohypophysis?
-The neurohypophysis is the neural part of the pituitary gland and contains the axon terminals where hormones are stored.
Where is the thyroid gland located?
-The thyroid gland is located in the anterior region of the neck, behind the cartilaginous thyroid cartilage.
What are the main components of the thyroid gland's structure?
-The thyroid gland's structure includes the stroma, which consists of a capsule and dense connective tissue, and the parenchyma, which is made up of thyroid follicles and parafollicular cells.
What is the role of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas?
-The islets of Langerhans are the endocrine part of the pancreas responsible for hormone production.
How can Victoria blue staining help in the study of the pancreas?
-Victoria blue staining can detect the presence of insulin, making it possible to visualize the islets of Langerhans as blue-colored structures.
What additional information can Victoria blue staining provide about the islets of Langerhans?
-Victoria blue staining can also differentiate between alpha and delta cells within the islets of Langerhans.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 3 Module 3 | The Power and Control of the Nervous System

CONTROL AND COORDINATION in 60 Minutes | Science Chapter 7 | Class 10th CBSE Board

Chemical and Nervous Control for Plants and Animals | Group 5 of 12 - Kendall | Biology

SISTEM KOORDINASI, REPRODUKSI, DAN HOMEOSTATIS PADA MANUSIA (PART 1) - IPA KELAS 9 SMP
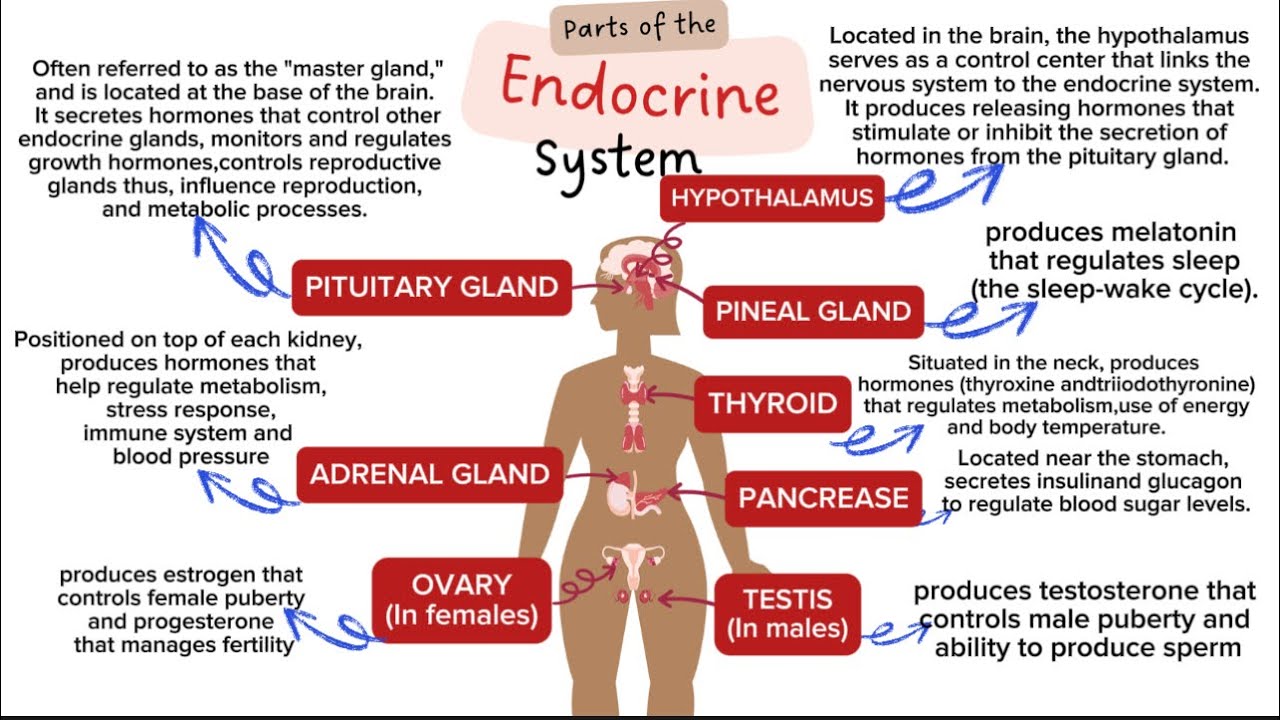
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM : What It Is, Parts and Functions of the Endocrine System.

SISTEM ENDOKRIN : BIOLOGI SMA KELAS 11
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
