Grade 8 Math Q1 Ep 6 Simplifying Rational Algebraic Expressions
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video by Deaf Ed TV, Teacher Joshua guides viewers through the process of simplifying rational algebraic expressions, a crucial skill for Grade 8 mathematics. The video explains how to identify and simplify fractions, using factoring to reduce expressions to their simplest form. It covers various examples, including monomials and polynomials, and emphasizes the importance of recognizing when an expression is already in its simplest form. The lesson concludes with a quiz to test understanding, reinforcing the concept that mathematics is about critical thinking and problem-solving.
Takeaways
- 📘 The video is an educational session on simplifying rational algebraic expressions for grade 8 mathematics, led by Teacher Joshua.
- 🍕 An example uses a pizza divided into eight slices to illustrate fractions, where taking two slices leaves six, simplifying to three-fourths.
- 🔢 Simplifying fractions involves writing them in the lowest terms by dividing out common factors from the numerator and denominator.
- 🧩 The video explains that rational algebraic expressions are like fractions, with both the numerator and denominator being polynomials.
- 🔍 To simplify expressions, common factors in the numerator and denominator are identified and divided out.
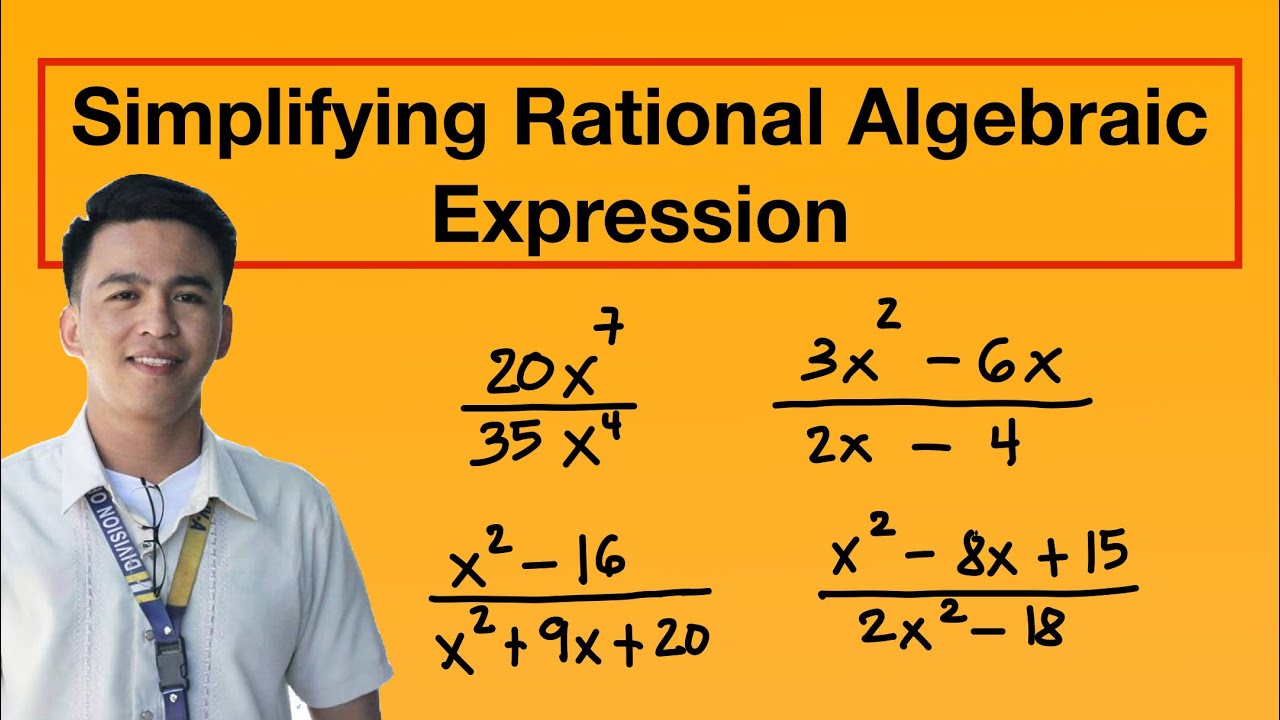
- 🌟 The video uses the example of simplifying \( \frac{28x^3}{7x^4} \) to \( \frac{4}{x} \) by factoring and dividing common terms.
- ✅ The concept of relatively prime is introduced, where if the numerator and denominator share no common factors, the expression is already in simplest form.
- 👨🔬 Albert Einstein's quote about simplicity is mentioned, emphasizing the importance of not oversimplifying to the point of losing meaning.
- 📚 The video provides a step-by-step guide on simplifying rational expressions, including factoring and dividing common terms.
- 📉 The session concludes with a quiz to test the viewer's understanding of simplifying rational algebraic expressions, with five questions and their solutions provided.
Q & A
What are rational algebraic expressions?
-Rational algebraic expressions are fractions where both the numerator and the denominator are polynomials, with the denominator not equal to zero.
How can you determine if a rational expression is undefined?
-A rational expression is undefined when the denominator is equal to zero. You find the excluded values by setting the denominator to zero and solving for the variable.
What is the fraction of pizza slices left if two out of eight slices are taken?
-If two out of eight slices of pizza are taken, six slices are left, which is represented by the fraction 6/8.
How can you simplify the fraction 6/8?
-The fraction 6/8 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common factor, which is 2, resulting in the simplified fraction 3/4.
What is the simplified form of the expression 28x^3 over 7x^4?
-The expression 28x^3 over 7x^4 can be simplified by factoring out common factors. The simplified form is 4/x after factoring and dividing the common factors.
How can you factor the numerator and denominator of the expression 3x - 12 over 5x - 20?
-The numerator 3x - 12 has a greatest common factor of 3, and the denominator 5x - 20 has a greatest common factor of 5. Factoring these out and simplifying gives the expression in its simplest form as 3/5.
What does it mean for the numerator and denominator of a rational expression to be relatively prime?
-The numerator and denominator of a rational expression are relatively prime if they have no common factors, which means the expression is already in its simplest form and cannot be simplified further.
Who is Albert Einstein and what is his famous equation?
-Albert Einstein is a renowned scientist known for his contributions to physics and mathematics, including the theory of relativity. His famous equation is E=mc^2, which relates energy (E) to mass (m) and the speed of light (c).
What is the simplest form of the expression a^3 + b^3 over a^2 - b^2?
-The simplest form of the expression a^3 + b^3 over a^2 - b^2 is a^2 - ab + b^2 over a - b, after factoring the numerator as a sum of cubes and the denominator as a difference of squares.
How can you determine if a rational expression is in its simplest form?
-A rational expression is in its simplest form if the numerator and denominator are relatively prime, meaning they have no common factors, or if all common factors have been divided out.
What is the process for simplifying a rational algebraic expression?
-To simplify a rational algebraic expression, first write the numerator and denominator in factored form, then divide out any common factors. If there are no common factors, the expression is already in its simplest form.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Simplifying Rational Algebraic Expressions - Grade 8 Math

SHS General Mathematics Q1 Ep2: Rational Functions

Addition and Subtraction of Rational Algebraic Expressions I Señor Pablo TV

SIMPLIFYING RATIONAL ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSION || GRADE 8 MATHEMATICS Q1

Grade 8 Math Q1 Ep1: Factoring Polynomials

Factoring Polynomials using Greatest Common Monomial Factor
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
