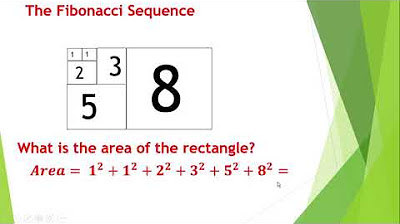Understanding The Fibonacci Spiral
Summary
TLDRGareth Manfred from 'Restore the Planet' introduces the Fibonacci sequence, a series of numbers found in nature, starting with 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, and so on. He demonstrates how to create a Fibonacci spiral using graph paper and simple geometry, illustrating the sequence's connection to natural forms like galaxies and sunflowers. The tutorial shows how to draw squares based on the sequence and construct a spiral using circles, reflecting the universe's intricate patterns.
Takeaways
- 🔢 The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers starting with 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, and so on, where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones.
- 🌿 This sequence is found throughout nature, from the arrangement of galaxies to the pattern of seeds in sunflowers.
- 📐 To visually represent the Fibonacci sequence, one can start by drawing squares on graph paper, with each square's side length corresponding to a number in the sequence.
- 🎨 The squares are connected to form a larger square, and this process can be repeated to create a pattern that reflects the growth seen in the Fibonacci sequence.
- 🌀 By using circles and a cross to guide the drawing, one can create a spiral that mimics the curves found in natural phenomena, such as the shape of galaxies.
- 📏 Each square in the Fibonacci pattern should occupy one quarter of the circle used to draw the spiral, ensuring that the spiral's shape is consistent with the mathematical sequence.
- 🖌️ Artists have various methods to draw the Fibonacci spiral, but the method shared in the script aims to closely align with natural forms.
- 🌐 The completed Fibonacci spiral closely resembles the spiral patterns seen in galaxies, showcasing the connection between mathematics and the cosmos.
- 📝 The script is an educational resource, aiming to help viewers understand the Fibonacci sequence and its applications in geometry and nature.
- 🌟 The presenter, Gareth Manfred, encourages viewers to have a great day, emphasizing the positive and educational nature of the content.
Q & A
What is the Fibonacci sequence?
-The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, usually starting with 0 and 1. It goes 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, and so on, continuing indefinitely.
How is the Fibonacci sequence generated?
-The Fibonacci sequence is generated by adding the last two numbers in the sequence. For example, starting with 1 and 1, the next number is 2 (1+1), then 3 (1+2), then 5 (2+3), and so on.
Why is the Fibonacci sequence significant in nature?
-The Fibonacci sequence is significant in nature because it appears in the arrangement of many natural structures, such as the spirals in galaxies, the pattern of seeds in sunflowers, and the branching of trees.
How does the Fibonacci sequence translate into physical geometry?
-The Fibonacci sequence translates into physical geometry by using squares whose sides are the Fibonacci numbers. These squares can be arranged to form larger patterns, such as spirals, which mimic natural forms.
What is the purpose of using graph paper when drawing the Fibonacci sequence?
-Using graph paper when drawing the Fibonacci sequence helps ensure that the squares are evenly and symmetrically placed with consistent measurements, which simplifies the process of creating accurate geometric representations.
How are the squares connected to form a Fibonacci spiral?
-The squares are connected by drawing lines that form perfect squares, with each subsequent square having a side length that is the next number in the Fibonacci sequence.
What is the role of circles in constructing the Fibonacci spiral?
-Circles are used to construct the Fibonacci spiral by drawing a circle that is divided into four equal parts by a cross, with each arm of the cross being the length of the current square. The spiral is then drawn within one quarter of this circle.
Why is the method of using circles to construct the spiral considered to closely match nature?
-The method of using circles to construct the Fibonacci spiral is considered to closely match nature because it replicates the organic, curving patterns found in natural phenomena such as the spirals in galaxies and the arrangement of leaves on a stem.
What is the significance of the cross when drawing the Fibonacci spiral?
-The significance of the cross when drawing the Fibonacci spiral is to ensure that the circle used for the spiral is properly aligned with the square, with each arm of the cross being the length of the square's side, ensuring that the spiral fits within the square.
How does the completed Fibonacci spiral relate to the twisting motions of a galaxy?
-The completed Fibonacci spiral relates to the twisting motions of a galaxy by mimicking the logarithmic spiral patterns observed in the arms of galaxies, which are believed to be influenced by the arrangement of stars and interstellar matter.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)