Collisions: Crash Course Physics #10
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the physics of collisions, exploring momentum and impulse as key factors in how objects interact. It clarifies the difference between elastic and inelastic collisions, emphasizing that momentum is always conserved, regardless of the collision type. The concept of center of mass is introduced as crucial for understanding motion, especially in objects with uneven mass distribution. The episode is educational, providing a foundational understanding of these principles with relatable examples.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Physics explores various phenomena including collisions, which are significant in understanding how objects interact.
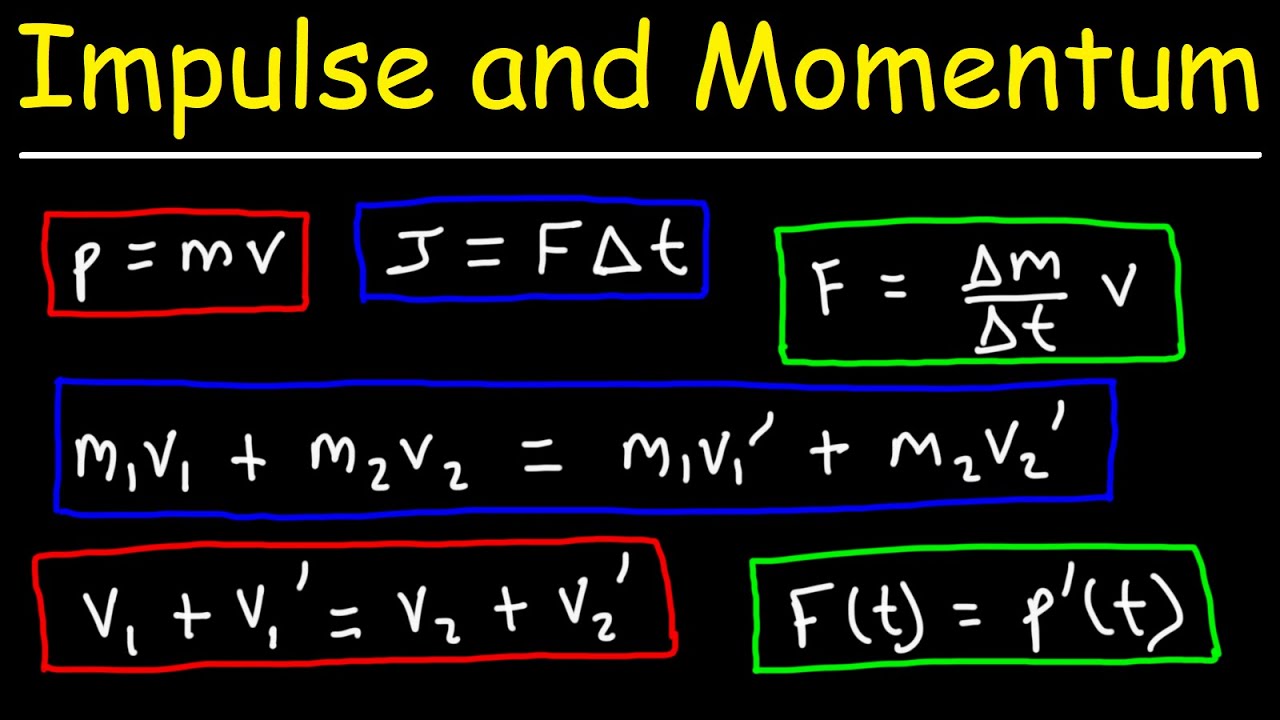
- 📚 Two critical concepts in collision physics are momentum, defined as mass times velocity, and impulse, which is the integral of net force over time.
- 🎱 Collisions can be classified as elastic, where kinetic energy is conserved, or inelastic, where kinetic energy is not conserved but momentum is.
- 🤔 In real-world scenarios, perfect elastic collisions are rare due to energy losses typically as heat or sound.
- 🏓 The conservation of momentum is a universal principle in collisions, ensuring that the total momentum before and after a collision remains constant.
- 🔄 Impulse is a useful measure in collision analysis, as it helps to describe the change in momentum during the brief time of impact.
- 🧲 Perfectly inelastic collisions occur when objects stick together, resulting in maximum kinetic energy loss but still conserving momentum.
- 🌐 Center of mass is a crucial concept for understanding the motion of objects, especially those with uneven mass distribution.
- 📏 The center of mass can be calculated using the formula that sums the product of each mass and its distance from a reference point, divided by the total mass.
- 🔄 Newton's laws, particularly the second and third laws, play a foundational role in understanding the dynamics of collisions.
Q & A
What are the two main qualities that need to be considered when studying collisions in physics?
-The two main qualities to consider when studying collisions in physics are momentum and impulse.
What is the relationship between Newton's second law and the concept of momentum?
-Newton's second law states that the net force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. Momentum is an object's mass times its velocity, and the net force is equal to the change in mass-times-velocity over time, which is the derivative of momentum with respect to time.
How is momentum defined in the context of physics?
-Momentum in physics is defined as an object's mass times its velocity, representing the object's tendency to remain in motion.
What is impulse in physics, and how is it related to force?
-Impulse in physics is the integral of the net force on an object over time, which represents the change in momentum. It is related to force as it is the product of the force applied and the time over which it acts.
How does the concept of impulse help in describing collisions?
-Impulse helps in describing collisions because it accounts for the very quick changes in forces that occur during a collision, allowing us to calculate the overall effect of the collision on an object's momentum.
What is the difference between elastic and inelastic collisions?
-Elastic collisions are those in which kinetic energy is neither created nor destroyed, while in inelastic collisions, kinetic energy is not conserved and is typically converted into other forms of energy like heat or sound.
Why is it said that elastic collisions are not found in real life?
-Elastic collisions are not found in real life because there is always some energy loss in a collision, usually as heat or sound, which means that kinetic energy is not perfectly conserved.
What is the law that ensures the conservation of momentum in all collisions?
-The conservation of momentum in all collisions is ensured by Newton's third law, which states that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
What is a perfectly inelastic collision, and how does it differ from other inelastic collisions?
-A perfectly inelastic collision is one where objects stick together upon impact, losing as much kinetic energy as possible to other forms of energy. It differs from other inelastic collisions in that it results in the objects becoming a single unit after the collision.
What is the center of mass, and why is it important in understanding how objects move?
-The center of mass is the average position of all the mass in a system, and it is important in understanding how objects move because it helps to describe the motion of objects that do not have a uniform mass distribution, especially during collisions or rotations.
How can the position of the center of mass be calculated for a system with multiple masses?
-The position of the center of mass for a system with multiple masses can be calculated using the equation that sums the product of each individual mass and its distance from a chosen starting point, divided by the total mass in the system.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Fisika SMA - Impuls & Momentum (3) - Hukum Kekekalan Momentum (I)
Impulse and Momentum - Formulas and Equations - College Physics

FISIKA Kelas 10 - Momentum & Impuls | GIA Academy

Momentum and Impulse | Grade 9 Science Quarter 4 Week 3 Lesson

MOMENTUM, IMPULS, DAN HUKUM KEKEKALAN MOMENTUM | Momentum, Impuls dan Tumbukan #1 - Fisika Kelas 10

Quantidade de Movimento Explicada (Momento) | Episódio 3
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
