Lempeng Tektonik
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the fascinating world of tectonic plates, explaining how the Earth's surface is shaped by their movements. It covers the San Andreas Fault in North America, the Mariana Trench in the Philippines, and the Himalayas in Asia. The script details the theory of plate tectonics, describing how continents were once a single landmass and have since separated due to seafloor spreading. It also discusses the three main types of plate movements: convergent, divergent, and transform, each resulting in different geological features such as mountain ranges, trenches, and volcanic activity. The script provides examples of these phenomena, including the formation of the Atlantic's mid-Atlantic Ridge and the Great Rift Valley in East Africa.
Takeaways
- 🌏 The Earth's surface is shaped by tectonic plate movements, including the San Andreas Fault in North America, the Semangko Fault on Sumatra Island, and the Mariana Trench in the Philippines.
- 🌍 The Earth is composed of several layers, starting with the inner core, outer core, mantle (astenosfer), and the outermost layer, the crust, which is divided into tectonic plates.
- 🧊 The Earth's crust is made up of cold, rigid tectonic plates that float on the hot, plastic asthenosphere, allowing movement similar to floating on a fluid.
- 🌐 The theory of continental drift suggests that the continents were once a single landmass that has since separated due to the movement of the Earth's plates.
- 🌿 Evidence for continental drift includes the distribution of similar fossils found on different continents, such as the ones found in South America and Africa, which are now geographically distant.
- 🔥 Convergent plate movements result in phenomena such as subduction zones, oceanic trenches, mountain ranges, and volcanic activity.
- 🌋 Examples of convergent boundaries include the volcanic arcs and mountain ranges in the Philippines and Japan, formed by the collision of the Philippine Sea Plate with the Pacific Plate and Eurasia.
- 🏞️ Divergent plate movements lead to the formation of mid-ocean ridges and new ocean basins, such as the Atlantic Ocean's Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the Red Sea between Africa and the Arabian Peninsula.
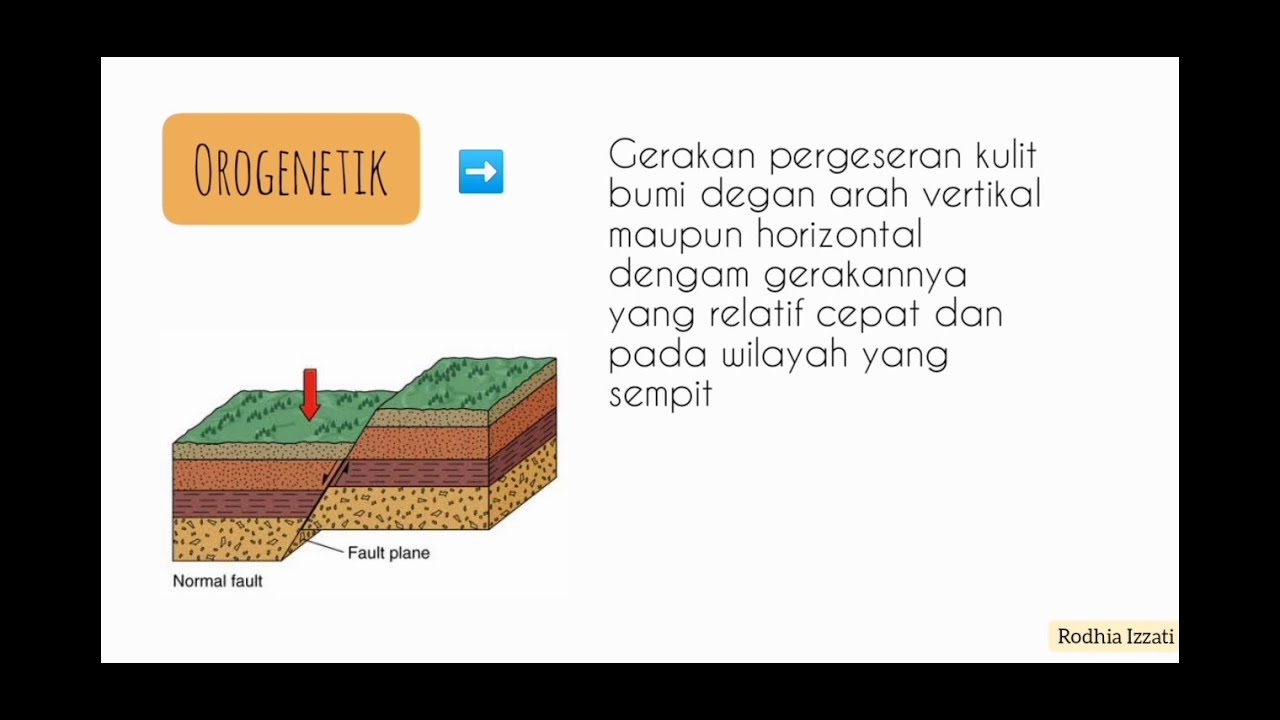
- 🏔️ Transform plate movements, such as the San Andreas Fault, result from horizontal sliding between plates and can cause earthquakes and create fault lines.
- 🌄 The Himalayas in Asia are a result of the collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate, forming one of the highest mountain ranges on Earth, including Mount Everest at 8,848 meters above sea level.
- 📜 The original land surface of the Earth is believed to have been a single continent that split apart due to plate tectonics, as evidenced by the distribution of fossils and geological features.
Q & A
What is the San Andreas Fault and where is it located?
-The San Andreas Fault is a major tectonic plate boundary in North America, stretching over 1300 km and is located in California, USA. It was discovered by geologist Andrew Lawson in 1895.
What are tectonic plates and how many layers of the Earth do they consist of?
-Tectonic plates are rigid segments of the Earth's lithosphere that move over the asthenosphere. The Earth is divided into several layers starting from the inner core, outer core, mantle, and the crust which is the outermost layer.
What is the asthenosphere and its role in plate tectonics?
-The asthenosphere is a part of the Earth's mantle that is hot and plastic, allowing the rigid tectonic plates to float and move over it, contributing to the movement and interactions of the plates.
What is the theory of continental drift and how does it relate to plate tectonics?
-The theory of continental drift suggests that continents were once joined together and have since separated due to the movement of the Earth's crust, which is now explained by the movement of tectonic plates.
What evidence supports the idea that continents were once a single landmass?
-The distribution of similar fossils, such as those found in South America and Africa, supports the idea that these continents were once connected and have since drifted apart.
What are the three types of plate movements and how do they affect the Earth's surface?
-The three types of plate movements are convergent (plates moving towards each other), divergent (plates moving away from each other), and transform (plates sliding past each other), each resulting in different geological features such as mountains, oceanic trenches, and volcanic activity.
What is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and how is it formed?
-The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an underwater mountain range formed by the divergent movement of the South American and African tectonic plates, causing the seafloor to spread apart and create new oceanic crust.
What is the significance of the Himalayan mountain range in the context of plate tectonics?
-The Himalayas are significant as they are the result of the convergent movement between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate, creating one of the highest mountain ranges on Earth, including Mount Everest at 8848 meters above sea level.
What is the Sumatran fault and how does it relate to the movement of tectonic plates?
-The Sumatran fault is a result of transform movement between the Eurasian Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate, creating a series of mountains along the island of Sumatra.
What are the geological phenomena that occur at convergent plate boundaries?
-At convergent plate boundaries, phenomena such as subduction zones, volcanic arcs, oceanic trenches, and mountain ranges can occur due to the interaction of oceanic and continental plates.
How can one observe the effects of plate tectonics in Indonesia?
-In Indonesia, particularly on the island of Sumatra, one can observe the effects of plate tectonics in the form of the Sumatran fault and the Barisan Mountains, which are the result of transform movements between tectonic plates.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

CHAPTER 6: EARTH'S STRUCTURE AND ITS DEVELOPMENT | Part 1: Earth's Structure and Plate Tectonics ...

Mengenal Apa Itu Lempeng Tektonik? - Fakta Menarik

Jenis Jenis Pergerakan Lempeng Tektonik
Tenaga Endogen Part 1 : TEKTONISME

วิชาโลกดาราศาสตร์อวกาศ - ทฤษฎีการแปรสัณฐาน

KEB02 Tektonik Lempeng | Materi OSN/KSN Kebumian SMA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
