Transpor membran lengkap- difusi sederhana, osmosis, difusi terfasilitasi, pompa NA+/K+, biologi sel
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the intricate processes of cellular membrane transport, highlighting both passive and active transport mechanisms. It explains how molecules move across the cell membrane through diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion, and contrasts these with active transport processes like the Na+/K+ pump, cotransport, endocytosis, and exocytosis. The script aims to clarify the importance of these mechanisms in maintaining cellular function and balance.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The script discusses the concept of membrane transport, which is the mechanism of moving molecules into or out of a cell through the cell membrane.
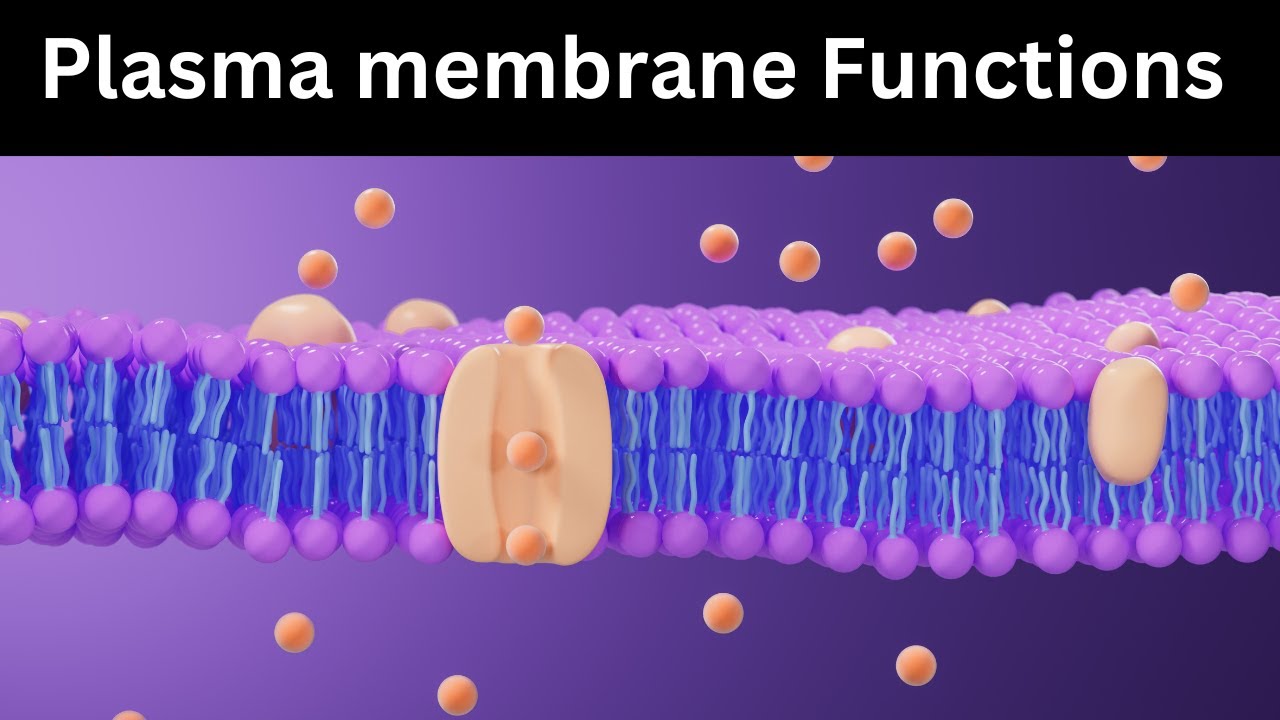
- 📚 It explains that the cell membrane is semi-permeable, allowing only certain molecules to pass through, such as nonpolar molecules like carbon dioxide and oxygen, and small polar molecules like water.
- 🚫 Large polar molecules and charged molecules, such as glucose and ions, cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer without assistance.
- 🔋 Membrane transport is categorized into two types based on energy usage: passive transport, which does not require energy, and active transport, which does require energy to move substances against a concentration gradient.
- 🌀 Passive transport includes simple diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion. These processes involve the movement of particles down a concentration gradient without the use of energy.
- 💧 Osmosis is specifically the movement of solvents, like water, across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher solute concentration to an area of lower solute concentration.
- 🔄 Facilitated diffusion involves the use of membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers, to help substances move along their concentration gradient.
- ⚡ Active transport requires energy, usually in the form of ATP, to move substances against their concentration gradient, such as the Na+/K+ pump which maintains the concentration of these ions across the cell membrane.
- 🔄 Cotransport is an active transport mechanism where the movement of one substance is linked to the movement of another, often against its concentration gradient, as seen in the transport of sucrose into the vacuoles of plant cells.
- 🚀 Endocytosis and exocytosis are active transport processes involving the movement of large particles in or out of the cell, where the particles are enclosed within a membrane-bound vesicle.
- 🌐 The script also mentions the educational nature of the channel 'Biologi Kitty' and encourages viewers to like, comment, and subscribe for more biology content.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the script?
-The main topic discussed in the script is the mechanisms of membrane transport, including passive and active transport, and various types of transport such as diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
What is the basic structure of the cell membrane mentioned in the script?
-The basic structure of the cell membrane mentioned in the script is the phospholipid bilayer, which includes integral proteins that are related to membrane transport.
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules in terms of passing through the cell membrane?
-Nonpolar molecules, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, can pass through the cell membrane more easily compared to polar molecules and large ions, which cannot cross the phospholipid bilayer without assistance.
What are the two main categories of membrane transport based on energy usage?
-The two main categories of membrane transport based on energy usage are passive transport, which does not require energy, and active transport, which requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient.
What is diffusion and how does it relate to the concentration gradient?
-Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, either through or without a membrane. It is a passive process that does not require energy as it moves along the concentration gradient.
Can you explain the concept of osmosis as described in the script?
-Osmosis is the movement of water or solvent through a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher solvent concentration to an area of lower solvent concentration. It is driven by differences in solute concentration and can result in isosmotic, hypertonic, or hypotonic conditions relative to the cell.
What is facilitated diffusion and how does it differ from simple diffusion?
-Facilitated diffusion is the movement of molecules or substances along the concentration gradient with the help of membrane proteins, such as channels or carriers. It differs from simple diffusion in that it requires the assistance of these proteins to transport substances that cannot easily cross the cell membrane on their own.
What are the examples of active transport mentioned in the script?
-Examples of active transport mentioned in the script include the Na+/K+ pump, cotransport, endocytosis, and exocytosis. These processes require energy, usually in the form of ATP, to move substances against their concentration gradient.
How does the Na+/K+ pump maintain the concentration of ions inside and outside the cell?
-The Na+/K+ pump is a protein carrier that actively transports Na+ ions out of the cell and K+ ions into the cell, against their concentration gradients. This helps to maintain a higher concentration of K+ inside the cell and a higher concentration of Na+ outside the cell.
What is cotransport and how does it relate to the transport of sucrose into a vacuole?
-Cotransport is an active transport mechanism where the movement of one molecule is linked to the movement of another molecule, often against its concentration gradient. In the case of sucrose transport into a vacuole, the cotransport of H+ ions down their concentration gradient powers the transport of sucrose against its concentration gradient into the vacuole.
Can you describe the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis as mentioned in the script?
-Endocytosis is the process where particles are brought into the cell by the cell membrane forming a vesicle around the particle. Exocytosis is the opposite process where particles are expelled from the cell as the vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and releases its contents. These processes are used for the transport of large particles or molecules that cannot pass through the membrane by simple or facilitated diffusion.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Cell Membrane Transport - Transport Across A Membrane - How Do Things Move Across A Cell Membrane

SEL 3 (Transport Zat Melalui Membran Sel)
Cell Membrane Functions Explained | Transport Mechanisms & Structure | Biology Animation

Active and Passive Transport

General Biology I - Transport Mechanisms - Part I

BIOLOGI Kelas 11 - Bioproses Sel (Transpor Membran) | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
