SEL 3 (Transport Zat Melalui Membran Sel)
Summary
TLDRThis educational Indonesian biology lesson delves into the intricate mechanisms of cellular transport across the plasma membrane. It explains the vital role of transport in maintaining life, including the exchange of nutrients, gases, and ions, and the removal of metabolic waste. The lesson distinguishes between passive transport, facilitated by concentration gradients, and active transport, which requires energy. It also covers osmosis, ion pumps, cotransport, and the cellular processes of exocytosis and endocytosis, providing a comprehensive overview of how cells manage their internal and external environments.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson is focused on the biological concept of cell membranes, specifically the third part about transport mechanisms through the plasma membrane.
- 🔬 The main purpose of transport through the plasma membrane is to bring in nutrients and facilitate the exchange of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as to regulate the concentration of ions and waste products of metabolism.
- 🌟 There are two types of transport across the plasma membrane: passive and active transport. Passive transport does not require energy and occurs due to concentration differences.
- 💧 Passive transport includes diffusion, facilitated diffusion through specific protein channels, and osmosis, which is the movement of water from a lower to a higher solute concentration.
- 🔋 Active transport, on the other hand, moves substances against their concentration gradient and requires energy in the form of ATP. It includes processes like the sodium-potassium pump and co-transport.
- 🚰 Osmosis is a type of passive transport that specifically refers to the movement of solvent molecules, such as water, across a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to one of higher solute concentration.
- 🔄 The sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport that exchanges sodium ions out of the cell for potassium ions into the cell, maintaining the ionic balance necessary for cellular function.
- 🔄 Co-transport is a form of active transport where the movement of one substance is coupled with the movement of another, often requiring the same energy source, such as ATP.
- 📦 Exocytosis and endocytosis are processes where large particles or molecules are transported across the plasma membrane through vesicles, involving the fusion or invagination of the membrane.
- 🔬 Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a specific type of endocytosis where specific molecules bind to receptors on the cell surface, leading to the formation of vesicles that transport these molecules into the cell.
- 🌱 The lesson concludes with a transition to the next topic, which will be about plant tissues, indicating a continuation of the biological study in subsequent lessons.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the biology lesson discussed in the script?
-The main topic of the biology lesson is the study of cells, specifically focusing on the third part about the mechanisms of transport through the plasma membrane.
Why is transport through the plasma membrane essential for living organisms?
-Transport through the plasma membrane is essential as it allows for the entry of nutrients and the exchange of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as the regulation of ion concentrations and the removal of metabolic waste, thus maintaining the cell's functionality and stability.
What are the two main types of transport mechanisms through the plasma membrane mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of transport mechanisms through the plasma membrane are passive transport and active transport.
Can you explain what is meant by passive transport in the context of the script?
-Passive transport refers to the movement of substances across the plasma membrane without the use of energy, occurring due to a concentration gradient. It includes processes like diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis.
What is diffusion and how does it relate to the script's discussion on passive transport?
-Diffusion is the process where molecules, particles, ions, or gases move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached. In the script, it is mentioned as part of passive transport, with examples such as the spreading of perfume in a room.
What is facilitated diffusion and how does it differ from simple diffusion?
-Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of large molecules through specific protein channels or transport proteins in the plasma membrane. Unlike simple diffusion, it aids the movement of larger molecules that cannot directly pass through the membrane.
What is osmosis and why is it considered a type of diffusion?
-Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules, typically water, from an area of lower solute concentration (hypotonic) to an area of higher solute concentration (hypertonic) across a semipermeable membrane. It is considered a type of diffusion because it involves the movement from a region of higher solvent concentration to one of lower concentration.
What is active transport and how does it differ from passive transport?
-Active transport is the movement of substances across the plasma membrane against the concentration gradient, from a lower to a higher concentration, and it requires energy in the form of ATP. Unlike passive transport, active transport moves substances against their concentration gradient and requires energy.
Can you give an example of active transport mentioned in the script?
-An example of active transport mentioned in the script is the sodium-potassium pump, which uses ATP to exchange sodium ions out of the cell for potassium ions into the cell, maintaining the ion concentration differences across the plasma membrane.
What are the other types of active transport mentioned in the script besides the sodium-potassium pump?
-Besides the sodium-potassium pump, the script also mentions cotransport (or secondary active transport) and antiport as types of active transport, where two different substances are moved across the membrane simultaneously, often with one being transported against its concentration gradient.
What are exocytosis and endocytosis, and how do they relate to the script's discussion on active transport of large molecules?
-Exocytosis and endocytosis are processes of active transport of large molecules or particles. Exocytosis involves vesicles containing macromolecules fusing with the plasma membrane to expel substances outside the cell, while endocytosis involves the cell engulfing large molecules through the plasma membrane, such as during phagocytosis or pinocytosis.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Transpor membran lengkap- difusi sederhana, osmosis, difusi terfasilitasi, pompa NA+/K+, biologi sel

Temp1 Cap3 Epi2 Membrana y Citoesqueleto

SEL 2 (Struktur sel dan fungsinya)
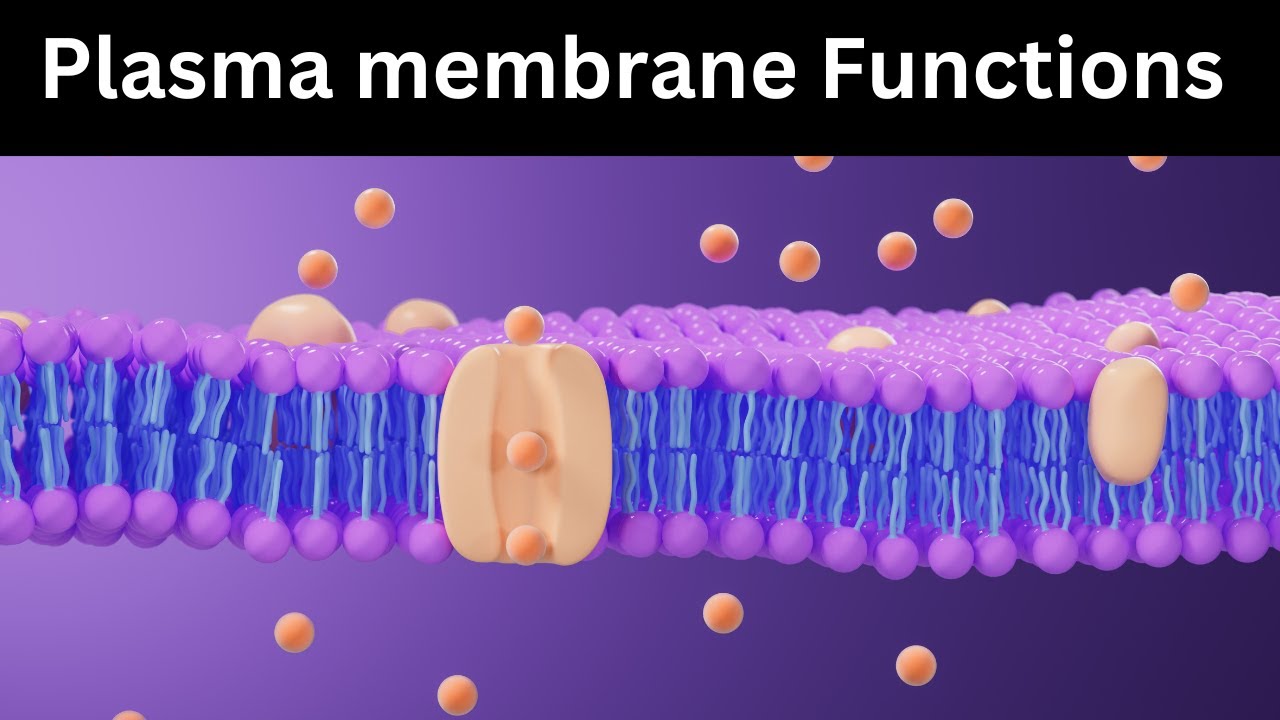
Cell Membrane Functions Explained | Transport Mechanisms & Structure | Biology Animation

Membrane Transport in Cells Symport, Antiport, Cotransport Animation

General Biology I - Transport Mechanisms - Part I
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)