Process Strategies
Summary
TLDRThe video script explores various manufacturing processes, highlighting how companies like BP and Honda select processes based on product variety and volume demand. It discusses continuous processes for standardized products, assembly lines for mass production, batch processing for lower volume products, and job shops for highly customized items. The goal is to balance efficiency and flexibility for high-quality, cost-effective production.
Takeaways
- 😀 Manufacturing processes are chosen based on product variety and volume of demand.
- 🔍 Gasoline is a standardized product with little variety, suitable for continuous production processes.
- 👓 Eyeglasses are custom-made, requiring a job shop process with high flexibility and individual customization.
- 🏭 BP refines crude oil into various products using continuous processes, operating 24/7 to meet constant demand.
- 🚗 Honda uses an assembly line (mass production) for making cars, allowing some customization within a repetitive process.
- 🏗️ Caterpillar employs batch processing for producing a variety of construction and agricultural equipment in lower volumes.
- 🛠️ The product process matrix helps manufacturers find the most efficient production methods based on variety and volume.
- 🌐 Continuous processes are highly automated and require specialized equipment, making them ideal for high-volume, standardized products.
- 🏗️ Batch processing allows for flexibility in equipment and production, suitable for lower-volume, varied products.
- 👨🏫 Skilled workers using general-purpose tools are crucial in job shops, where each product is unique and requires customization.
- 🔄 Hybrid manufacturing processes are becoming common, combining elements of continuous, batch, and job shop methods to meet diverse product needs.
Q & A
What are the two main considerations for selecting a manufacturing process?
-The two main considerations for selecting a manufacturing process are the variety of the product and the volume of demand. Variety refers to how much the product changes from customer to customer, while volume refers to the amount of product needed by consumers.
Why is gasoline considered a standardized product?
-Gasoline is considered a standardized product because, although there may be a small variety between different blends, the product remains consistent within each blend.
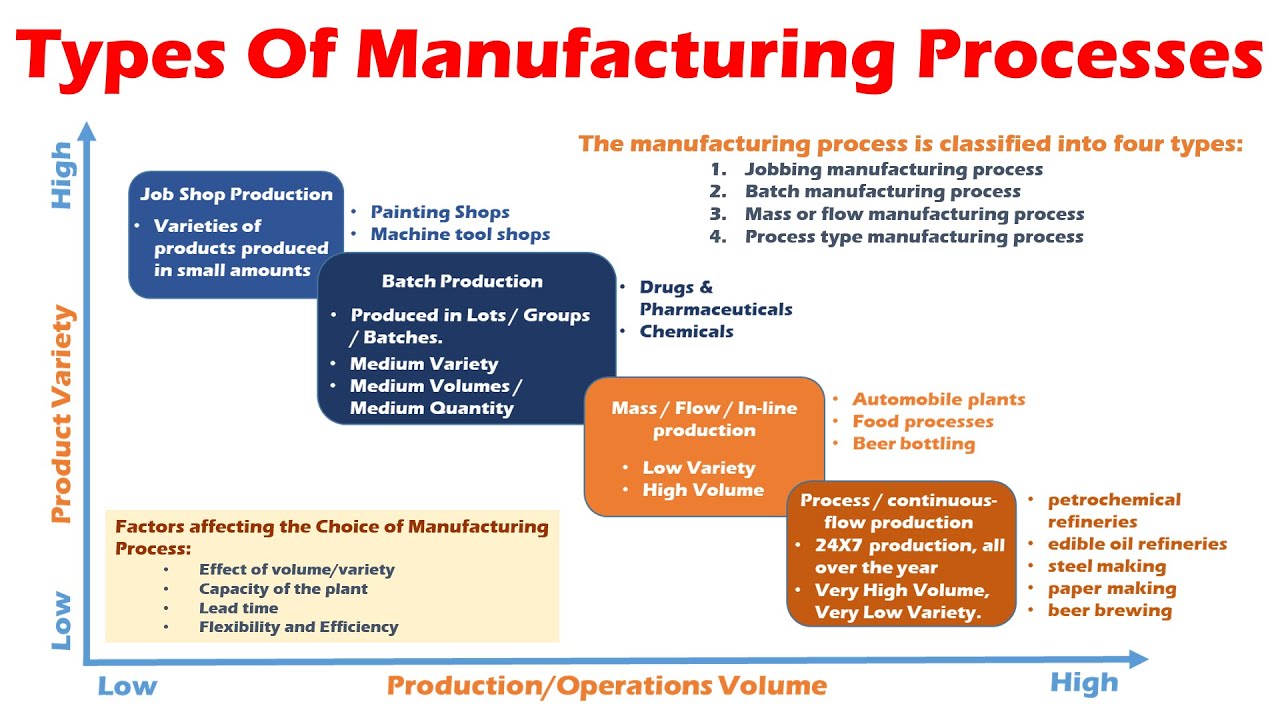
What is the significance of the product process matrix?
-The product process matrix is a graphical representation that helps in determining the most efficient production or manufacturing processes. It uses variety and volume as the vertical and horizontal axes, respectively, and the most efficient processes are found along the diagonal points on the graph.
Why is a continuous process the best manufacturing choice for a very standardized product needed in large volumes?
-A continuous process is the best manufacturing choice for a very standardized product needed in large volumes because it uses highly specialized equipment with very little flexibility and is almost completely automated, ensuring cost-effectiveness and high output.
How does BP's refinery process impact its profitability and cost-effectiveness?
-BP's refineries operate 24/7 to maintain cost-effectiveness and match output to demand. Stopping production for just a few days can undermine a plant's profitability for an entire year due to the large capacity and high cost of shutdown.
What is the role of chemical engineers in the refining process at BP's refineries?
-Chemical engineers determine the mix of products added during the conversion and treatment stages of the refining process. They also monitor elements such as the water used in the refinery to ensure it's safe to return to the environment.
How does Honda of America's assembly line process differ from a continuous process?
-Honda's assembly line process, also known as mass production, involves a connected workflow where the product moves along a conveyor system past a series of workstations. Unlike a continuous process, workers interact with tools more and much of the work such as welding is performed through automation.
What is the advantage of using batch processing in manufacturing?
-Batch processing allows for the creation of products in small lots or batches, which is suitable for manufacturing a variety of products at relatively low volume with flexible equipment. It is ideal for situations where a high degree of customization is required.
How does the job shop process differ from other manufacturing processes?
-The job shop process is characterized by creating highly specialized products in very low volumes based on individual customer orders. It involves using general-purpose tools in a variety of ways, with a focus on customization and flexibility.
What are the challenges faced by manufacturers in achieving mass customization?
-Achieving mass customization involves creating high-quality products with the efficiency of a continuous process while building in as much flexibility as possible to allow for more customization. Manufacturers must understand the dynamics of the product process matrix to balance these requirements.
Why is flexibility important in manufacturing processes?
-Flexibility in manufacturing processes allows manufacturers to adapt to varying product requirements and customer demands. It enables the production of a variety of products, customization, and the ability to respond quickly to changes in the market.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
Types Of Manufacturing Processes (Job Shop, Batch, Mass, Flow, Process Type Manufacturing Processes)

Process Strategies and Design overview in Operations Management

Understanding Production Volume & Plant Layout: Job, Batch, and Mass Production Explained!

03. Production Planning - Theory
Automation Migration Strategy.

為何台灣稱霸半導體產業? 半導體的極限到了嗎?|Taiwan Keywords EP10(ft.吳志毅、陳昌昇、黃逸平、顏誠廷)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
