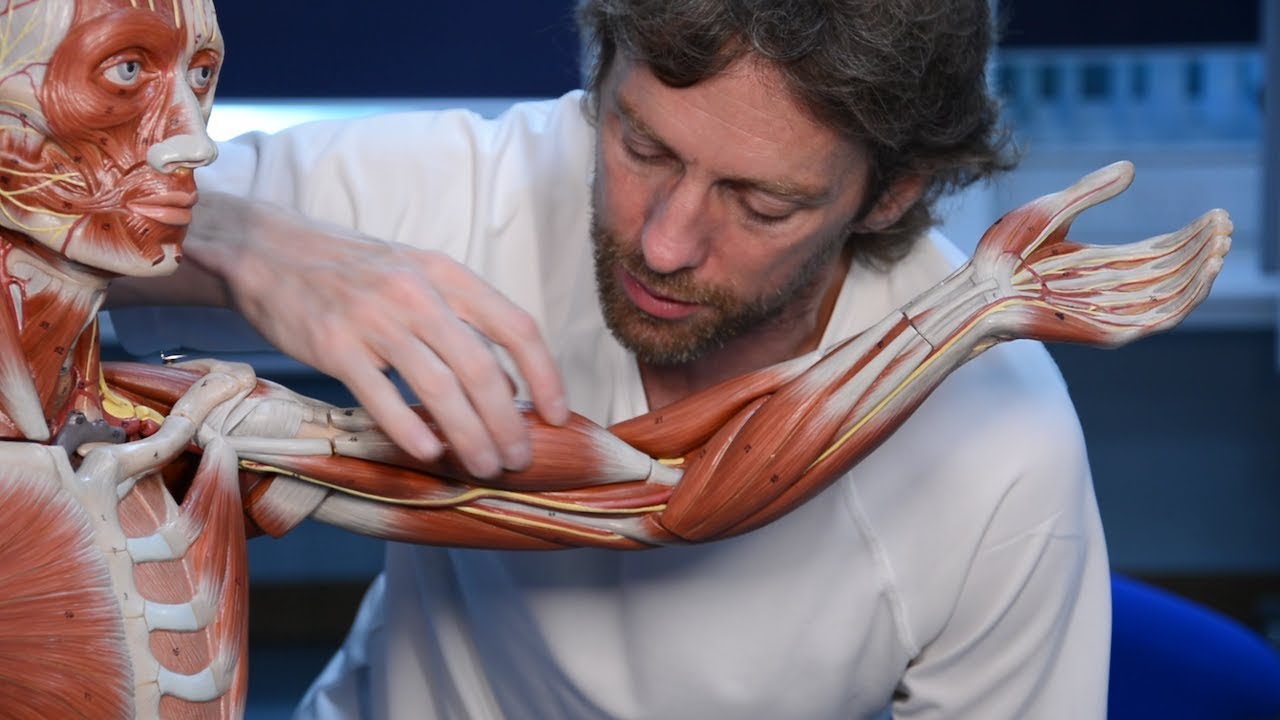
How To Remember Every Muscle in the Upper Limb and Arm | Corporis
Summary
TLDRThis educational video, sponsored by Kenhub, offers a comprehensive guide to memorizing the skeletal muscles of the upper limb. Host Patrick breaks down the complex anatomy into manageable sections, providing tips and tricks for remembering key muscles such as the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and the pectoralis major. He covers muscles related to the shoulder joint, upper arm, forearm, and intricate hand muscles, using mnemonic devices and anatomical insights to facilitate learning. The video also highlights Kenhub's resources, including quizzes and in-depth articles, as valuable tools for mastering anatomy.
Takeaways
- 💪 The video is sponsored by Kenhub, a resource for learning anatomy.
- 😀 The video focuses on tips and tricks for remembering skeletal muscles of the upper limb, presented in small sections for beginners.
- 🦴 The trapezius muscle is large, spans from the base of the skull to the lowest thoracic vertebrae, and is named for its trapezoid shape.
- 🏋️♂️ The latissimus dorsi, or 'lats', is the widest muscle in the body and spans from the thoracic vertebrae to the sacrum.
- 🗺️ Rhomboid major and minor muscles originate on the spine and insert on the scapula, aiding in shoulder retraction.
- 🏋️♂️ The pectoralis major and minor muscles are in the chest, with the major being the large superficial muscle and the minor being smaller and underneath.
- 🦵 The deltoid muscle is the most superficial shoulder muscle, shaped like a triangle, and is involved in moving the shoulder joint.
- 🖐️ The muscles of the upper arm, including biceps brachii and triceps brachii, are named for their number of heads and location.
- 🤲 The forearm muscles, like the flexor carpi radialis and extensor carpi ulnaris, are named for their functions and locations on the forearm.
- 👐 The hand muscles, including the thenar and hypothenar masses, control thumb and pinky movements respectively.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the video?
-The main purpose of the video is to teach viewers tips and tricks for remembering the skeletal muscles of the upper limb as seen in an anatomy class.
How is the list of muscles presented in the video?
-The list of muscles is presented in smaller chunks of 4 to 8 muscles to make the lesson more manageable for beginners.
What is the significance of the trapezius muscle?
-The trapezius is a large muscle that inserts on the scapula and clavicle and originates from the base of the skull to the lowest thoracic vertebrae, playing a crucial role in shoulder movement.
How is the latissimus dorsi muscle described in the video?
-The latissimus dorsi is described as the widest muscle in the body, spanning from shoulder to shoulder and from the thoracic vertebrae down to the sacrum, and inserting on the humerus.
What is the function of the rhomboid muscles?
-The rhomboid major and rhomboid minor muscles originate on the spine and insert on the scapula, helping to retract the shoulder blades and maintain good posture.
What is the pectoralis major muscle's primary function?
-The pectoralis major, also known as the 'big chest muscle,' is responsible for various movements of the arm and shoulder.
What is the role of the serratus anterior muscle?
-The serratus anterior muscle is named for its serrated or sawtooth-like pattern and is involved in the movement of the scapula, such as when punching forward with a straight arm.
What is the deltoid muscle and its function?
-The deltoid muscle is the largest and most superficial muscle around the shoulder joint, resembling the Greek letter delta in shape, and is involved in shoulder movements.
What are the four muscles of the rotator cuff and their locations?
-The four muscles of the rotator cuff are the supraspinatus (superior to the spine of the scapula), infraspinatus (inferior to the spine of the scapula), teres minor, and subscapularis (under the scapula).
What is the function of the biceps brachii and triceps brachii muscles?
-The biceps brachii is a two-headed muscle of the upper arm primarily responsible for flexing the forearm at the elbow, while the triceps brachii, a three-headed muscle, is responsible for extending the forearm at the elbow.
How does the video suggest remembering the forearm muscles?
-The video suggests using the action and anatomical region naming patterns of the forearm muscles, such as flexors on the anterior side and extensors on the posterior side, to remember them.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)