Equation of Lines (Standard and General) - Analytic Geometry
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive introduction to analytic geometry, focusing on the general equation of a straight line and its various forms. Key concepts such as the general equation of a line, slope-intercept form, point-slope form, two-point form, and intercept form are explained in detail. Through step-by-step examples, the video demonstrates how to derive the equation of a line given different conditions such as slope, y-intercept, and two points. It also covers the relationship between parallel lines and provides methods to find the slope and y-intercept from general equations.
Takeaways
- 😀 The general equation of a line is ax + by + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants.
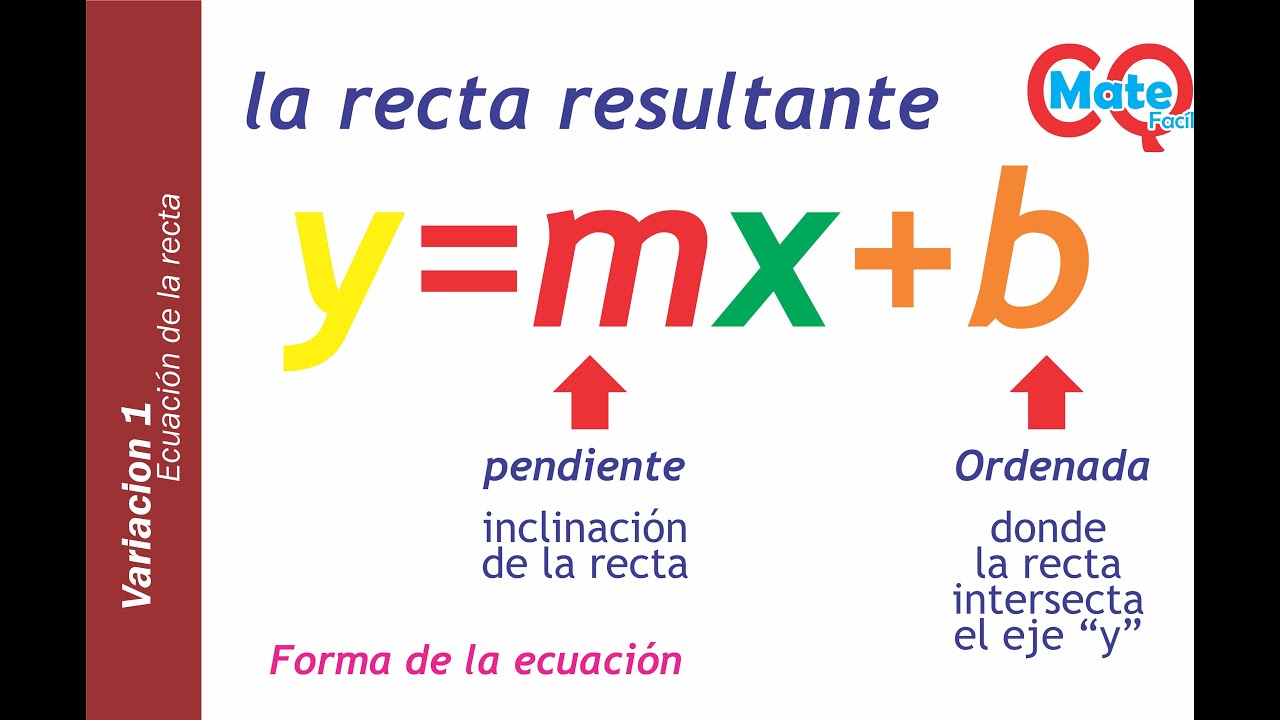
- 😀 The slope-intercept form of a line is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
- 😀 To find the y-intercept from the general equation, set x = 0 and solve for y.
- 😀 The point-slope form of a line is y - y₁ = m(x - x₁), where m is the slope and (x₁, y₁) is a point on the line.
- 😀 The slope of a line can also be calculated using two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) with the formula: m = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁).
- 😀 To convert from slope-intercept form to general form, multiply the equation by a constant to eliminate fractions.
- 😀 For a line's general equation with a slope and y-intercept given, plug these values into the slope-intercept formula and then convert to general form.
- 😀 When solving for the equation of a line passing through two points, first find the slope and then use the point-slope form.
- 😀 In finding the equation of a line, ensure to carefully simplify and rearrange terms into the desired form (general, point-slope, etc.).
- 😀 Parallel lines have identical slopes, which means the slope of a given line can be used to find the equation of a parallel line passing through a point.
Q & A
What is the general equation of a line in analytic geometry?
-The general equation of a line is expressed as ax + by + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants.
What is the slope-intercept form of a line?
-The slope-intercept form is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line, and b represents the y-intercept.
How do you find the y-intercept from the general equation of a line?
-To find the y-intercept from the general equation, set x = 0 and solve for y. This gives the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
What is the point-slope form of a line, and when is it used?
-The point-slope form is y - y₁ = m(x - x₁), where (x₁, y₁) is a point on the line and m is the slope. This form is used when you know a point on the line and the slope.
What is the relationship between two parallel lines in terms of their slopes?
-Two parallel lines have the same slope. This means that if one line has a slope m, any line parallel to it will also have a slope of m.
How can you find the equation of a line passing through two points?
-To find the equation of a line passing through two points, first calculate the slope using the formula m = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁), and then use the point-slope form to find the equation.
What is the intercept form of a line, and how is it written?
-The intercept form of a line is written as (x/a) + (y/b) = 1, where a is the x-intercept and b is the y-intercept, representing the points where the line crosses the x and y axes.
How do you convert the slope-intercept form into the general form?
-To convert the slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) into the general form (ax + by + c = 0), rearrange the equation so that all terms are on one side of the equation.
What happens when you multiply the entire equation of a line by a constant?
-Multiplying the entire equation of a line by a constant helps eliminate fractions or decimals and can simplify the equation, making it easier to work with, especially when converting to the general form.
How do you find the slope and y-intercept from a given equation in standard form?
-To find the slope from a line in standard form (ax + by = c), rewrite the equation in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b). The slope is given by -a/b, and the y-intercept is c/b.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Persamaan Garis Lurus [Part 3] - Menyusun Persamaan Garis Lurus

Persamaan Garis Lurus (2) | Gradien Garis | Matematika Kelas 8

Review on Circles
y=mx+b Ecuacíon de la recta, relación funcional

Geometria Analitica nello Spazio : Equazione Parametrica della Retta

Persamaan Garis Lurus [Part 1] - Mengenal Persamaan Garis Lurus
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
