01. Introduction to Chemical Reaction | SSC Chemistry | English Version | Fahad's Tutorial
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial provides a comprehensive overview of chemical reactions, a fundamental chapter in chemistry. It explains the types of reactions based on direction (irreversible and reversible), electron transfer (redox and non-redox), and heat change (exothermic and endothermic). Key reaction types, including addition, decomposition, substitution, combustion, neutralization, precipitation, hydrolysis, hydration, isomerization, and polymerization, are highlighted with examples. The tutorial also emphasizes crucial concepts like oxidation numbers, redox as a simultaneous process, and Le Chatelier’s Principle, providing students with a structured understanding of reaction mechanisms and study strategies for mastering this chapter effectively.
Takeaways
- 😀 Chemical reactions are a fundamental chapter in chemistry, building on knowledge of atoms, periodic table, bonding, and stoichiometry.
- 😀 Changes in matter are classified into physical changes and chemical changes.
- 😀 Chemical reactions can be classified based on direction: irreversible (one-way) and reversible (products can revert to reactants).
- 😀 Electron transfer determines if a reaction is a redox reaction (involving oxidation and reduction) or a non-redox reaction.
- 😀 Redox reactions include addition, decomposition, substitution, and combustion reactions.
- 😀 Non-redox reactions include neutralization, precipitation, hydrolysis, hydration, isomerization, and polymerization.
- 😀 Heat changes classify reactions as exothermic (heat released, ΔH < 0) or endothermic (heat absorbed, ΔH > 0).
- 😀 Oxidation numbers are crucial for understanding redox reactions, and redox is always a simultaneous process.
- 😀 Understanding the rate of reactions involves measuring how much product forms per unit time.
- 😀 Le Chatelier’s principle is important for predicting how chemical equilibrium responds to changes, and should be studied after understanding equilibrium.
- 😀 Memorization tips include recognizing reaction types through their names and symbols, and focusing on key concepts for exams.
Q & A
What are the two main types of changes in matter?
-The two main types of changes in matter are physical changes, which do not alter the chemical composition of a substance, and chemical changes, which result in the formation of a new substance.
How are chemical reactions classified based on direction?
-Chemical reactions based on direction are classified as irreversible, where reactants permanently form products (e.g., heating calcium carbonate), and reversible, where products can revert back to reactants (represented by the ⇌ symbol).
What defines a redox reaction?
-A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons, where one substance is oxidized (loses electrons) and another is reduced (gains electrons).
Can you name the four main types of redox reactions?
-The four main types of redox reactions are addition reactions, decomposition reactions, substitution reactions, and combustion reactions.
What is the difference between hydrolysis and hydration reactions?
-In hydrolysis, water reacts to break molecules into smaller fragments. In hydration, water molecules are added as lattice water to a compound without breaking it.
What is an example of isomerization in chemistry?
-An example of isomerization is the conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea, where the molecular formula remains the same but the structure and properties change.
How are chemical reactions classified based on heat changes?
-Chemical reactions based on heat changes are classified as exothermic, where heat is released and ΔH is negative, and endothermic, where heat is absorbed and ΔH is positive.
What is a neutralization reaction?
-A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to produce a salt and water, and it is classified as a non-redox reaction since no electron transfer occurs.
Why is the concept of oxidation numbers important in studying redox reactions?
-Oxidation numbers help identify which atoms are oxidized and reduced, allowing students to track electron transfer in redox reactions, which is crucial for understanding reaction mechanisms.
What is the significance of the La Chandeleur Principle mentioned in the script?
-The La Chandeleur Principle relates to chemical equilibrium, explaining how reactions proceed to balance reactants and products. Understanding this principle requires first understanding reversible reactions and equilibrium concepts.
What is polymerization and can you give an example?
-Polymerization is the process where small molecules (monomers) combine to form large molecules (polymers). Examples include the formation of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or the polymerization of ethylene to form polyethylene.
What distinguishes exothermic from endothermic reactions in terms of energy change?
-Exothermic reactions release energy, resulting in a negative ΔH, whereas endothermic reactions absorb energy, resulting in a positive ΔH.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Penyetaraan Persamaan Reaksi Kimia dengan Cepat- Kimia Kelas 10
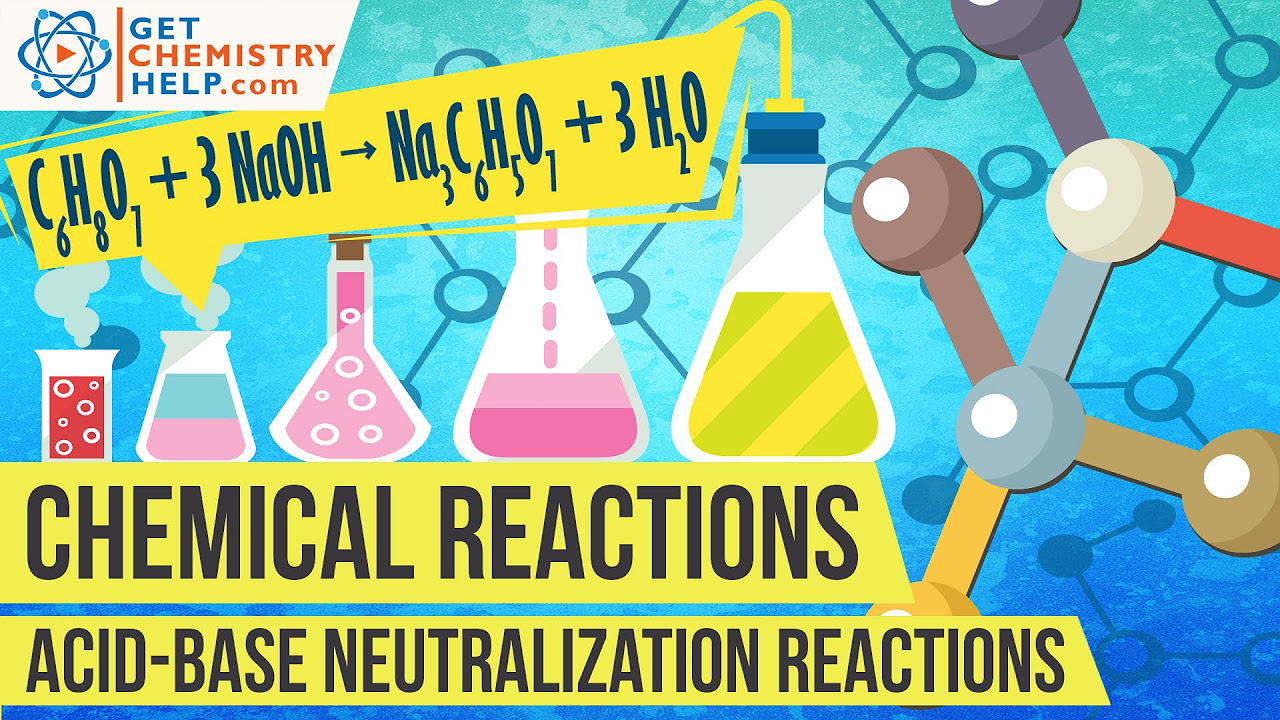
Chemistry Lesson: Acid-Base Neutralization Reactions

All of AQA CHEMISTRY Paper 1 in 30 minutes - GCSE Science Revision

Pembuatan dan Reaksi Logam Alkali | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti

The Ideal Gas equation | A level Chemistry

Hukum Hukum Kimia part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
