PROJECTILE MOTION | Physics Animation
Summary
TLDRThis educational video introduces the concept of projectile motion, explaining how an object moves in both horizontal and vertical directions simultaneously. Using the example of a cannonball fired at an angle, the script describes how its velocity in the X direction remains constant while the Y velocity changes, reaching zero at the peak height before descending. The only force acting on the projectile is gravity, affecting its motion. The video emphasizes key concepts like maximum height and distance traveled, and ends with a fun fact about the optimal firing angle for maximum distance being 45 degrees.
Takeaways
- 😀 Projectile motion is when an object moves both horizontally and vertically at the same time.
- 😀 The initial velocity of a projectile can be split into two components: horizontal (X) and vertical (Y).
- 😀 The velocity in the X direction remains constant throughout the flight of the projectile.
- 😀 The velocity in the Y direction changes, starting from an upward motion, reaching zero at the maximum height, and then reversing as it moves downward.
- 😀 At the maximum height, the velocity along the Y direction becomes zero.
- 😀 The velocity in the Y direction becomes negative after reaching the maximum height, indicating downward motion.
- 😀 The only acceleration acting on a projectile is gravity, which is constant at 9.8 m/s² and points downward.
- 😀 The maximum height of the projectile is reached when the vertical velocity becomes zero.
- 😀 The distance traveled by the projectile depends on the angle at which it is fired.
- 😀 To achieve the maximum distance traveled by a projectile, it should be fired at a 45-degree angle.
Q & A
What is projectile motion?
-Projectile motion is the motion of an object that is moving both horizontally and vertically at the same time, following a curved path called a parabolic trajectory.
What was covered in the previous video before this one?
-The previous video covered straight-line motion, such as a car moving along a straight path and a stone falling vertically from a building.
How is the velocity of a cannonball in projectile motion described?
-The initial velocity of the cannonball can be resolved into two components: one along the X direction (horizontal) and one along the Y direction (vertical).
What happens to the velocity of the cannonball in the X direction during its flight?
-The velocity in the X direction remains constant throughout the cannonball's flight.
How does the velocity in the Y direction change during the cannonball's flight?
-The velocity in the Y direction changes during the flight. It initially increases upward until it reaches zero at the maximum height, and then it becomes negative as the cannonball falls back down.
What is the significance of the velocity becoming zero in the Y direction?
-When the velocity in the Y direction becomes zero, the cannonball has reached its maximum height before starting to fall back to the ground.
What is the acceleration acting on the cannonball during its flight?
-The only acceleration acting on the cannonball during its flight is the acceleration due to gravity, which is constant at 9.8 meters per second squared and points downward.
How does the velocity of the cannonball change when it falls back to the ground?
-As the cannonball falls, the velocity in the Y direction increases negatively, reaching a value equal in magnitude to the initial velocity but with the opposite direction.
What are the two key distances to consider in projectile motion?
-The two key distances to consider are the maximum height (when the velocity in the Y direction is zero) and the horizontal distance traveled by the cannonball during its flight.
At what angle should an object be fired to achieve maximum horizontal distance in projectile motion?
-To achieve maximum horizontal distance, the object should be fired at a 45-degree angle.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

How Do Horizontally Launched Projectiles Behave? | Physics in Motion
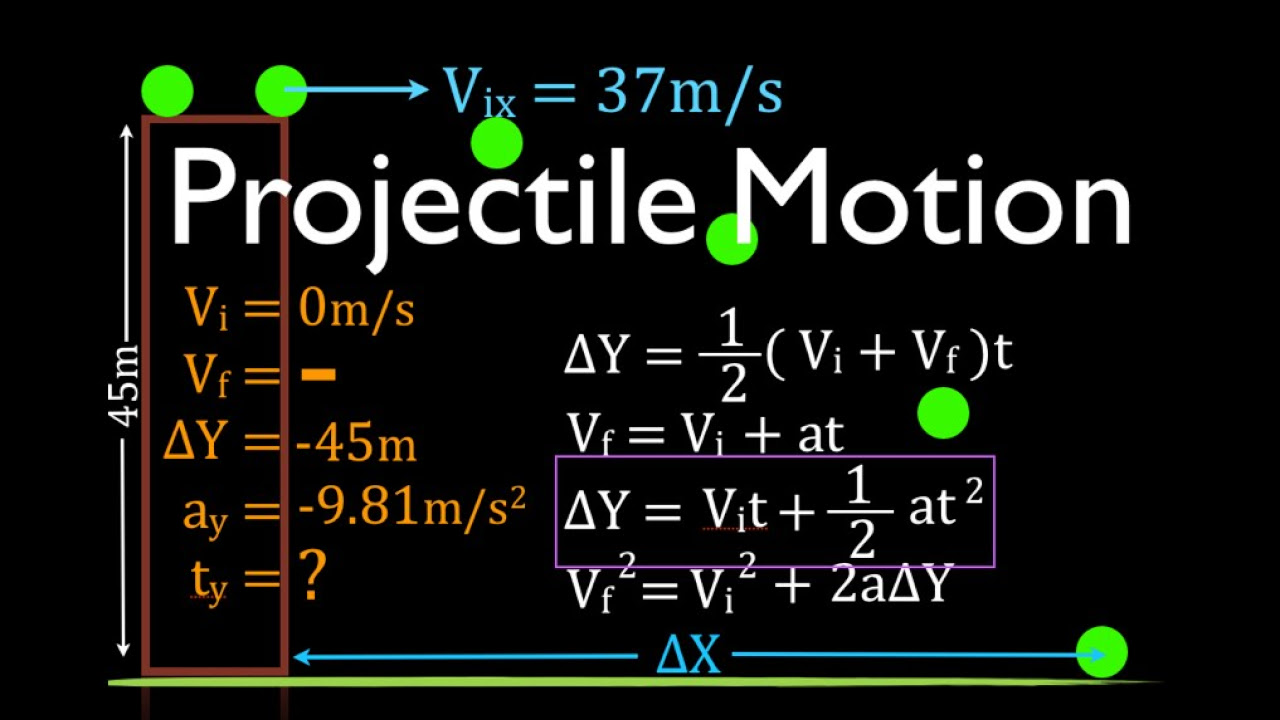
Two Dimensional Motion (4 of 4) Horizontal Projection, Worked Example

Movimiento parabólico - Ecuaciones
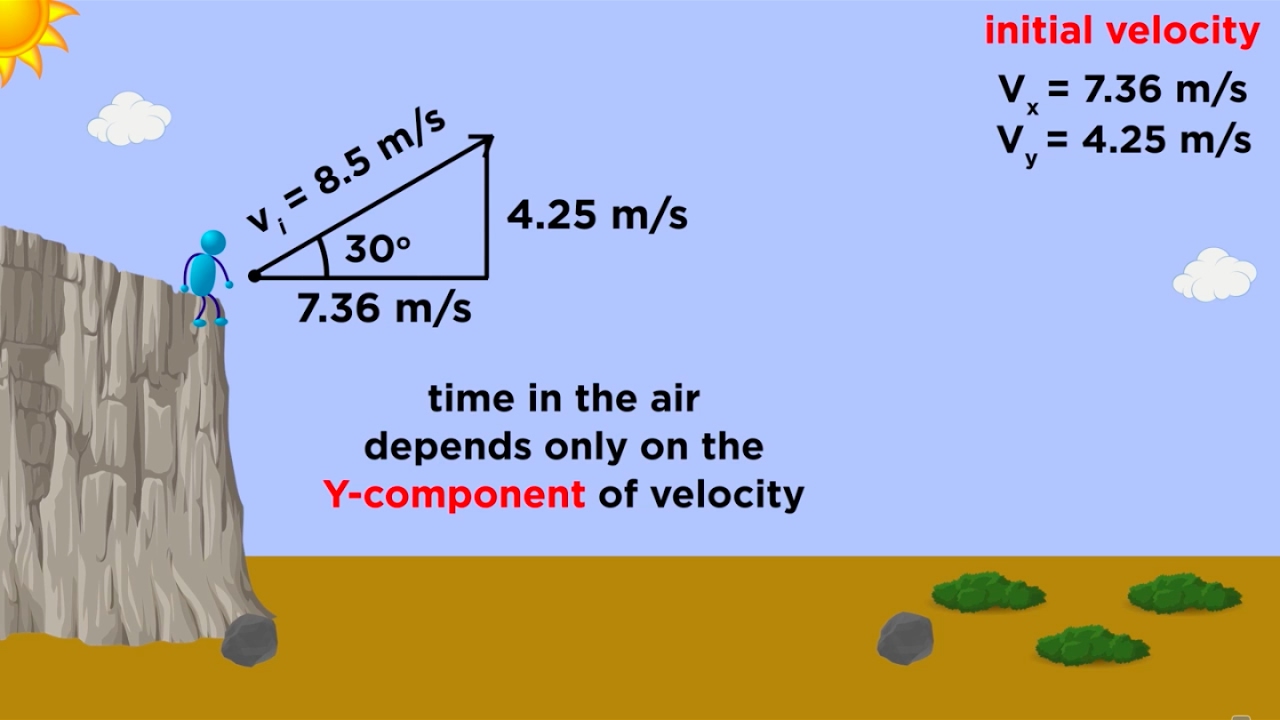
Kinematics Part 3: Projectile Motion
Projectile motion graphs | Two-dimensional motion | AP Physics 1 | Khan Academy

Gerak Parabola - Fisika Kelas 10 (Quipper Video)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
