Pengertian Arus Listrik - Fisika Kelas X
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of electric charge and current, detailing how objects become charged by either gaining or losing electrons. When objects with different charges interact, electrons flow from the more negative object to the more positive one, creating an electric current. The video explains the formula for electric current (I = Q/t), the unit of electric current (ampere), and how the movement of electrons relates to charge flow. A practical example is provided, calculating the current in a conductor when a known charge flows over a set period.
Takeaways
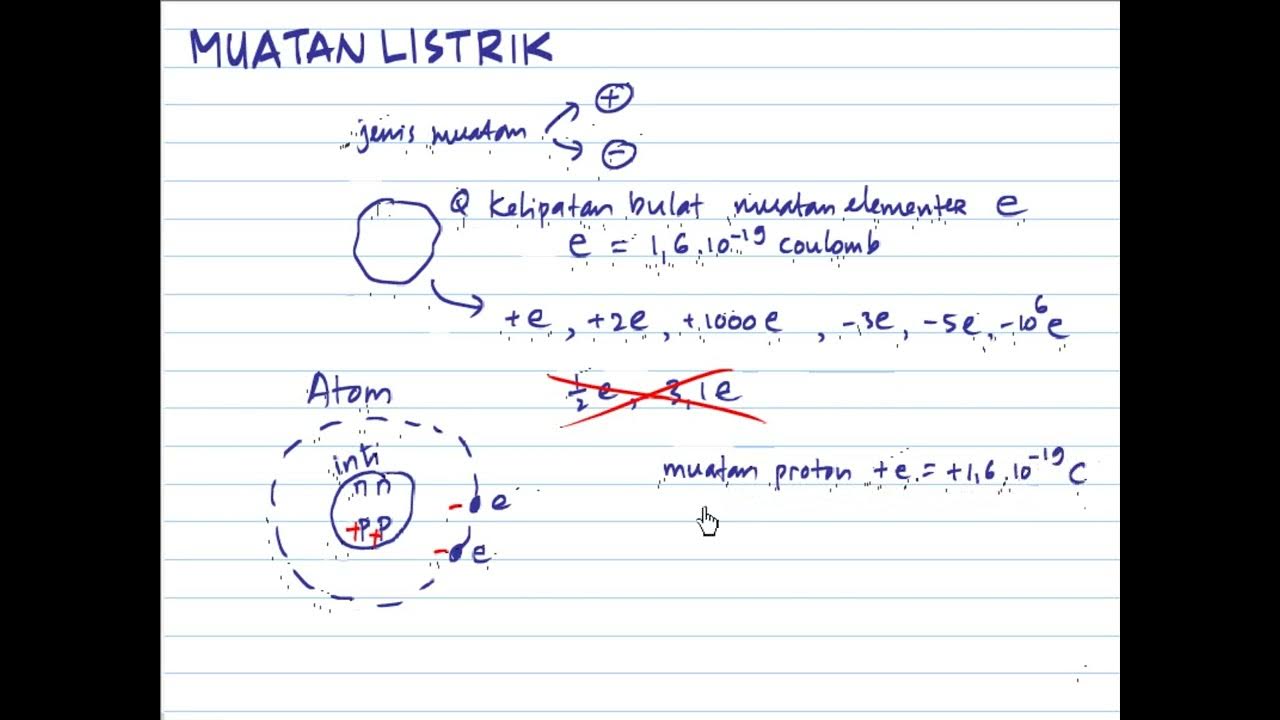
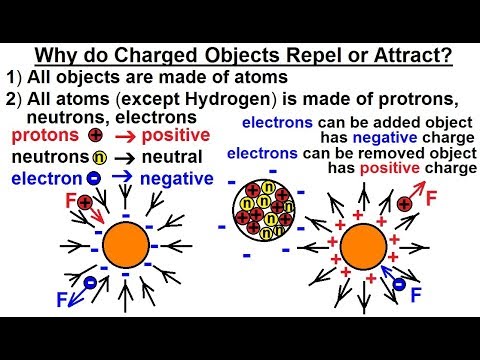
- 😀 An object is charged if it has an excess or lack of electrons.
- 😀 An object with excess electrons is negatively charged, while one with a lack of electrons is positively charged.
- 😀 The flow of positive charge moves from the more positive object to the more negative object.
- 😀 In reality, the flow of electrons is what occurs, and it moves from the negative to the positive object.
- 😀 The direction of electric current is opposite to the flow of electrons.
- 😀 When a light bulb is connected to a battery, the electric charge flows through the cable to light it up.
- 😀 Electric current is the amount of electric charge that flows per unit of time.
- 😀 The formula for electric current is i = q / t, where i is the current, q is the charge, and t is the time.
- 😀 The unit of electric current is the ampere, defined as one coulomb of charge passing through a conductor in one second.
- 😀 The flow of charge in a conductor is a multiple of the magnitude of the electron charge (1.6 × 10^-19 C).
- 😀 If the electric charge is 30 coulombs and the time is 6 seconds, the current is 5 amperes (I = q / t).
Q & A
What does it mean for an object to be charged?
-An object is charged if it has either an excess or a lack of electrons. An object with excess electrons will be negatively charged, while an object with a lack of electrons will be positively charged.
What happens when two objects with different charges come into contact?
-When two objects with different charges come into contact, the flow of positive charge will move from the object with more positive charge to the object with less positive charge. However, in reality, it is the electrons that flow.
How is electric current defined?
-Electric current is defined as the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is the amount of charge that flows per unit of time.
What is the mathematical formula for electric current?
-The formula for electric current is i = q / t, where 'i' represents electric current, 'q' represents electric charge, and 't' represents time.
What is the unit of electric current?
-The unit of electric current is the ampere (A), which is defined as the electric charge of one coulomb passing through a conductor in one second.
How is one ampere defined?
-One ampere is defined as the flow of one coulomb of electric charge passing through a conductor in one second.
What role do electrons play in the flow of electric charge?
-Electrons are the particles that actually flow through a conductor to create an electric current. The flow of electrons moves from areas of negative charge to areas of positive charge.
How can the total current be calculated if the number of electrons flowing is known?
-The total current can be calculated using the formula Q = n * e, where 'n' is the number of electrons and 'e' is the charge of an electron.
What is the electric current if the charge is 30 coulombs and the time is 6 seconds?
-If the electric charge is 30 coulombs and the time is 6 seconds, the electric current can be calculated as I = q / t = 30 / 6 = 5 amperes.
What happens in the example when the current flows through a light bulb?
-When the current flows through a light bulb, it powers the bulb, causing it to light up, as the electric charge flows through the conductor connected to the bulb.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

CARGA ELÉTRICA | ELETRODINÂMICA | AULA 1 - Professor Boaro

CARGA ELÉTRICA - ELETRIZAÇÃO - FÍSICA BÁSICA (Física do Zero) - Teoria e Exercícios - AULA 01
1 MUATAN LISTRIK

Electric potential and potential difference || 3D animated explanation || class 12th & 10th Physics

01. Conceptos Básicos de la Electrostática (Introducción)
Physics - E&M: Ch 35.1 Coulumb's Law Explained (1 of 28) Why do Charged Objects Repel or Attract?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
