Electric potential and potential difference || 3D animated explanation || class 12th & 10th Physics
Summary
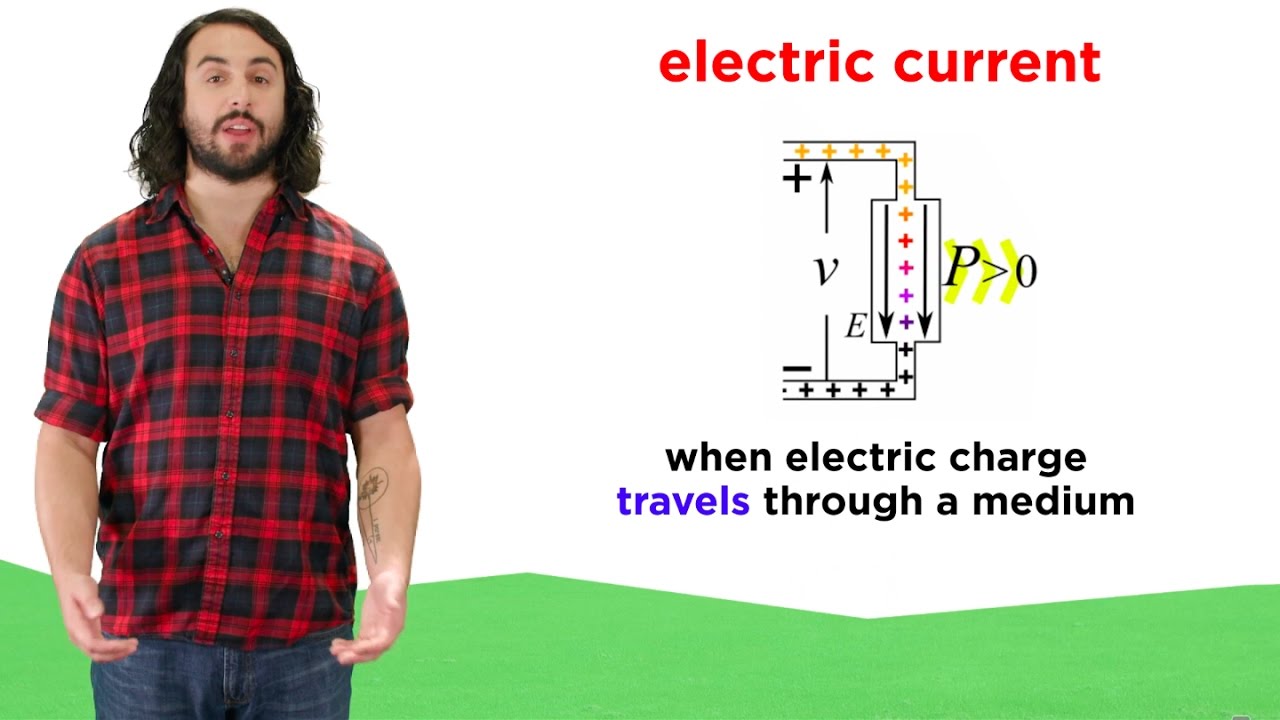
TLDRThis video explains the concept of electric potential and potential difference. It begins by describing how electrons in a wire don't move on their own but require an external force, like that from a battery, to generate current. The battery has two terminals, positive and negative, where a chemical reaction produces charged ions. This causes an electric charge to build up on the electrodes, creating electric potential. The difference in charge between the two electrodes is known as potential difference or voltage. The video further explains how electrons flow from the negative to the positive terminal, creating an electric current.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electrons in wires do not move on their own; they require an external force to move in a particular direction.
- 😀 The flow of electrons generates electric current.
- 😀 The external force required to move electrons is provided by a battery.
- 😀 A battery has two terminals: a positive terminal and a negative terminal, which are called electrodes.
- 😀 Initially, the electrodes of a battery are neutral, meaning they carry no charge.
- 😀 Chemical reactions inside the battery lead to the production of positive and negative charged ions.
- 😀 The electrodes have the property of attracting charged particles, leading to the accumulation of positive and negative charges on the electrodes.
- 😀 The charge created on the electrodes is known as electric potential.
- 😀 The difference in electric potential between the two electrodes is called the potential difference.
- 😀 Electrons are repelled by negative charge and attracted to positive charge, which causes them to flow from the negative to the positive electrode, generating current.
- 😀 The potential difference between the two terminals is also referred to as electric potential or voltage.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the video?
-The video aims to explain the concepts of electric potential, potential difference, and the generation of electric current through external force provided by a battery.
How do electrons move in a wire?
-Electrons do not move by themselves in a wire; they require an external force to move in a particular direction, which is provided by a battery or another source of electrical energy.
What is the role of a battery in generating current?
-A battery provides the external force that pushes the electrons to move in a specific direction, thus generating an electric current.
What are the two terminals of a battery called?
-The two terminals of a battery are called the positive terminal and the negative terminal, and these are also referred to as electrodes.
What happens to the electrodes of a battery at the start?
-Initially, the electrodes are neutral, meaning they do not carry any charge. However, a chemical reaction inside the battery produces charged ions.
What is the role of the chemical reaction inside the battery?
-The chemical reaction inside the battery produces positive and negative charge ions, which create an electric potential difference between the two electrodes.
What is electric potential?
-Electric potential refers to the amount of charge that accumulates on the electrodes of the battery, which is generated due to the chemical reactions taking place inside the battery.
What is potential difference?
-Potential difference, also known as voltage, refers to the difference in electric potential between the two electrodes of a battery, which drives the flow of electrons.
Why do electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal?
-Electrons are negatively charged and are repelled by the negative terminal and attracted to the positive terminal, leading them to flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
What is the relationship between electric potential difference and current?
-The electric potential difference between the two terminals of the battery causes electrons to flow, creating an electric current in the circuit.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Diferença de Potencial Elétrico | Tensão Elétrica

ruangbelajar - Fisika IX SMP - Listrik Dinamis (part 1) | bimbel online

Voltage | Physics | Khan Academy

Intro to electric potential | Electric potential and capacitance | Physics | Khan Academy

Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference
Electric Potential, Current, and Resistance
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)