Grade 10 - Cell Theory and Cell Parts and Function
Summary
TLDRThis video script provides an engaging and informative exploration of plant and animal cells, focusing on their structures and functions. Key concepts such as the nucleus, nucleolus, ribosomes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are discussed, highlighting their roles in processes like protein production, energy generation, and photosynthesis. The script contrasts plant and animal cells, emphasizing differences such as the presence of cell walls and chloroplasts in plant cells, and centrioles in animal cells. The content is designed to help students understand cellular biology concepts through relatable examples and clear explanations.
Takeaways
- 😀 The nucleus is the control center of the cell, responsible for regulating activities such as cell division and protein production.
- 😀 Ribosomes are essential for protein synthesis, and they can be found both in the cytoplasm and attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- 😀 The rough ER is involved in transporting proteins, while the smooth ER aids in the transportation of other substances without ribosomes attached.
- 😀 Chloroplasts in plant cells are responsible for photosynthesis, converting sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen.
- 😀 The vacuole in plant cells is large and stores water, and it can release water when a plant is bitten or broken.
- 😀 Centrioles are key to cell division in animal cells, and their dysfunction can lead to issues such as cancer.
- 😀 Animal cells lack a cell wall, whereas plant cells have a rigid cell wall that provides structural support.
- 😀 Plant cells have a square shape, while animal cells are typically round in shape.
- 😀 Plant cells contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis, but animal cells do not have chloroplasts.
- 😀 The central vacuole in plant cells is large and singular, while animal cells have multiple small vacuoles.
- 😀 Understanding the differences between plant and animal cells helps clarify their unique structures and functions, such as the presence of centrioles in animal cells and the lack of them in plant cells.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the nucleolus in a cell?
-The nucleolus is responsible for producing ribosomes, which are essential for protein synthesis.
How does the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) aid in protein production?
-The rough ER is lined with ribosomes that synthesize proteins, and as products move through this structure, the ribosomes add components to finalize the proteins.
What role does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) play in the cell?
-The smooth ER acts as a transport network for substances within the cell but does not have ribosomes, unlike the rough ER.
Why is the vacuole so important in plant cells?
-The vacuole stores a large amount of water in plant cells, and when broken, it releases water, like when you bite into an apple.
What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells, converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using the sun's energy.
What is the role of the mitochondria in both plant and animal cells?
-The mitochondria generate energy for the cell by converting glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water through cellular respiration.
What are centrioles, and why are they important in animal cells?
-Centrioles are barrel-shaped structures found in animal cells, and they are crucial for cell division. They help organize the mitotic spindle during mitosis and meiosis.
How does the shape of plant and animal cells differ?
-Plant cells typically have a square or rectangular shape due to the cell wall, whereas animal cells are round or irregular in shape.
What is the main difference between plant and animal cells regarding vacuoles?
-Plant cells have one large central vacuole that stores water, while animal cells have several small vacuoles.
How does the nucleus position differ in plant and animal cells?
-In plant cells, the large vacuole pushes the nucleus to the side, while in animal cells, the nucleus is typically located at the center of the cell.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

CARA MUDAH MEMPELAJARI SEL HEWAN DAN SEL TUMBUHAN

General Biology 1. Cell Types of Plant and Animal Tissues

Understanding Cell Functions in the Human Body.

WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL
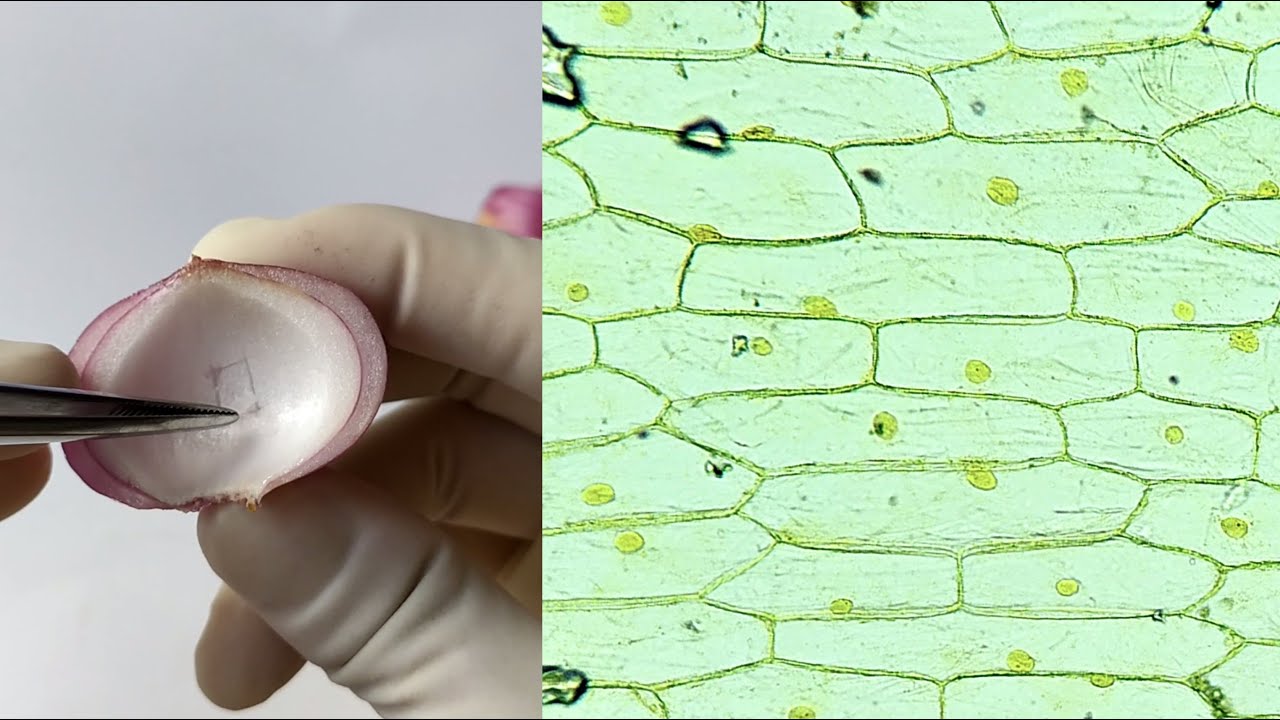
Onion Epidermal Cell Peel Slide Preparation Practical Experiment

Overview of animal and plant cells | Biology | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
