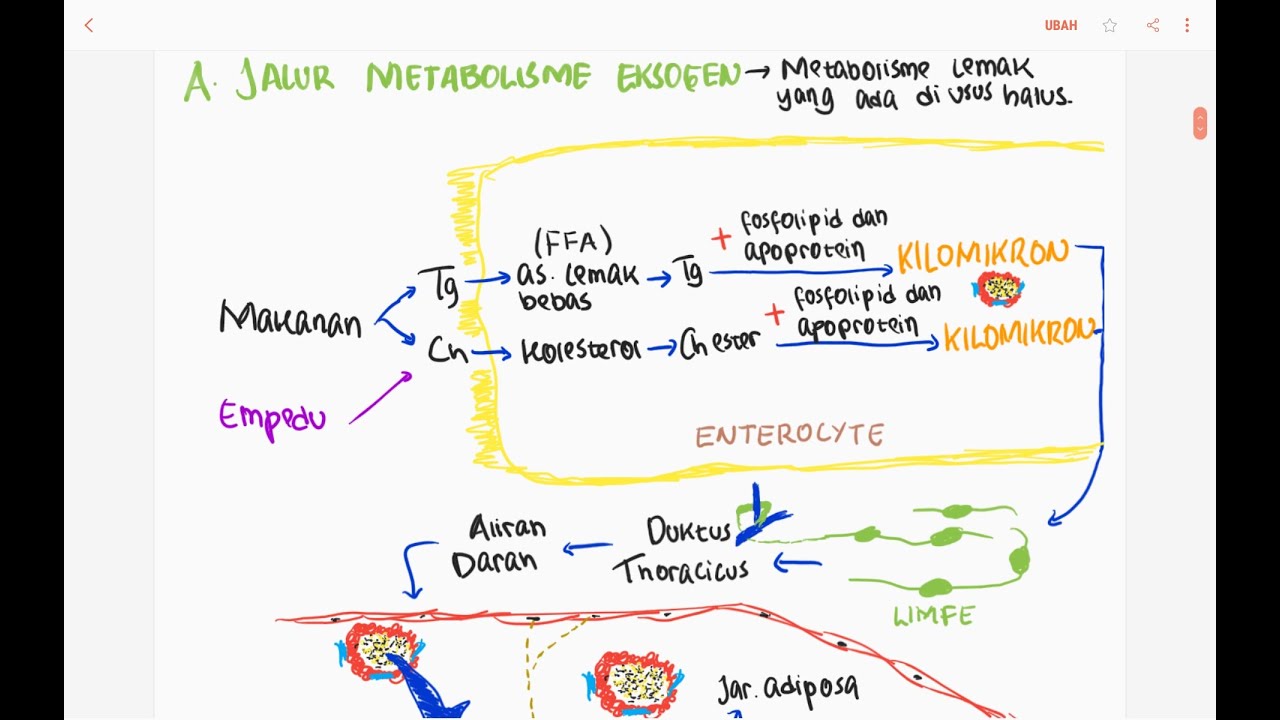
Penjabaran Metabolisme Lemak Oleh Peni Patriani, S.Pt., M.P
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the metabolism of fats, explaining how triglycerides are broken down into free fatty acids and glycerol through lipolysis. These molecules are then processed in the body, with glycerol entering glycolysis and fatty acids undergoing beta-oxidation to form acetyl-CoA, which fuels the Krebs cycle for ATP production. The video highlights the vital roles of fats in energy storage, organ protection, and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. It also touches on ketogenesis, where excess fat is converted into ketone bodies during fasting, ensuring energy supply when carbohydrates are scarce.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lipid metabolism refers to a series of processes involving the breakdown and remodeling of fats (lipids) within living organisms through chemical reactions.
- 😀 Triglycerides, composed of glycerol and three fatty acids, are a key form of fat in the body and play vital roles in energy storage and other metabolic functions.
- 😀 Fats serve multiple essential functions in the body, including energy storage, insulation to prevent heat loss, and protection of vital organs.
- 😀 Fat is crucial for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and provides essential fatty acids needed for the synthesis of reproductive hormones.
- 😀 In animal feed technology, fats also act as lubricants, improving pellet formation, reducing dust, and enhancing palatability.
- 😀 There are three main metabolic pathways: catabolism (breakdown of complex molecules), anabolism (synthesis of complex molecules), and amphibolic processes (connecting both pathways, such as the Krebs cycle).
- 😀 Catabolic processes include cell respiration mechanisms like glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and the Krebs cycle, whereas anabolic processes synthesize molecules like proteins and lipids.
- 😀 Lipid metabolism begins with lipolysis, where triglycerides are broken down into free fatty acids and glycerol, which then enter further metabolic pathways.
- 😀 Glycerol is converted into glycerol phosphate and then into dihydroxyacetone phosphate, eventually forming glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, which enters glycolysis before reaching the Krebs cycle.
- 😀 Free fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation within mitochondria, producing acetyl-CoA, which then enters the Krebs cycle to generate ATP (energy).
- 😀 Excess fat in the body is stored in adipose tissue and can be converted into ketone bodies during ketosis, providing an alternative energy source during starvation or low carbohydrate availability.
Q & A
What is lipid metabolism?
-Lipid metabolism refers to the series of biochemical processes in living organisms that involve the breakdown and synthesis of fats (lipids), mainly triglycerides, for energy production and other bodily functions.
What are the main components of triglycerides?
-Triglycerides are composed of three fatty acids linked to a glycerol molecule through ester bonds.
Why are lipids important for the body?
-Lipids play several vital roles, including acting as a major energy source, providing insulation to prevent heat loss, protecting vital organs, aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), and serving as precursors for reproductive hormones.
What are the three main metabolic pathways in lipid metabolism?
-The three main metabolic pathways are catabolism (breakdown of complex molecules), anabolism (synthesis of complex molecules), and amphibolic pathways (which connect catabolic and anabolic processes).
What is the process of catabolism in lipid metabolism?
-Catabolism involves breaking down complex molecules like triglycerides into simpler molecules, such as fatty acids and glycerol, to produce energy.
What role does anabolism play in lipid metabolism?
-Anabolism is responsible for the synthesis of complex molecules, including lipids, proteins, and enzymes, from simpler molecules, contributing to the body's growth and repair processes.
How does the process of lipolysis occur?
-Lipolysis is the breakdown of triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol, which then enter various metabolic pathways to produce energy.
What is the role of glycerol in lipid metabolism?
-Glycerol, derived from triglycerides, is converted into glycerol-3-phosphate, which then enters glycolysis to eventually produce ATP through the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle).
What happens to free fatty acids during lipid metabolism?
-Free fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation in the mitochondria, where they are converted into acetyl-CoA, which then enters the Krebs cycle to produce ATP.
What is ketogenesis, and why does it occur?
-Ketogenesis is the process by which excess fatty acids are converted into ketone bodies during periods of fasting or starvation. Ketone bodies act as an alternative energy source to carbohydrates when glucose is unavailable.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)