Rust: Prevention & Treatment | Environmental Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of rusting and how to prevent it. It starts by demonstrating a simple experiment with iron nails submerged in different solutions to show how water, oxygen, and salt accelerate rusting. The script highlights various methods to prevent rust, including painting, oiling, and using galvanization. The galvanizing method uses zinc, which sacrifices itself to protect iron from corrosion. The video not only describes the chemical reactions involved in rusting but also emphasizes the practical applications of these techniques in everyday objects like cars and bicycles.
Takeaways
- 😀 Rusting occurs when iron and steel are exposed to oxygen and moisture, causing corrosion.
- 😀 Corrosion refers to the breakdown of metals when they react with the environment, forming oxides.
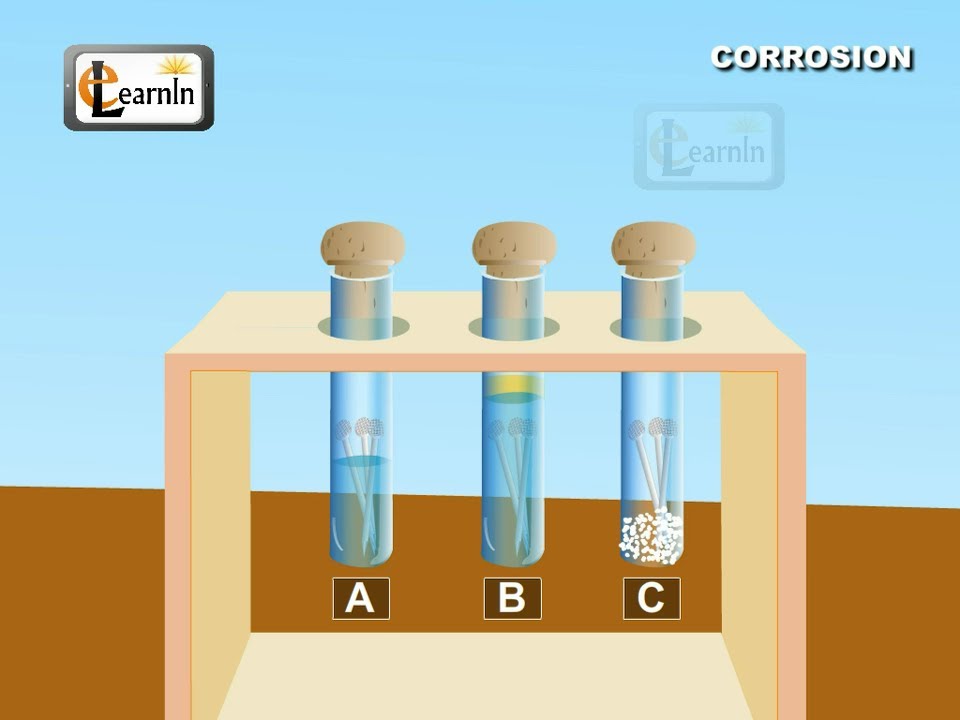
- 😀 A simple experiment can demonstrate rusting by placing an iron nail in different test tubes with varying conditions.
- 😀 Salt accelerates rusting by acting as a catalyst, making the nail in the salt solution rust more quickly than in just water.
- 😀 Nails exposed only to water or only to oxygen did not rust, indicating both moisture and oxygen are required for rusting.
- 😀 Rusting can be prevented by painting metal surfaces, which creates a protective barrier from oxygen and moisture.
- 😀 Oil or grease layers can also prevent rust by lubricating parts and reducing friction, especially on bicycle chains.
- 😀 Galvanizing is a method of sacrificial protection, where zinc, a more reactive metal, corrodes instead of iron, protecting the iron or steel.
- 😀 Zinc’s corrosion forms a protective zinc oxide layer, which can be removed and reformed to continue protecting the underlying metal.
- 😀 Rusting is costly in terms of maintenance and replacement of affected iron and steel items, making prevention methods crucial.
Q & A
Why is car paint important beyond aesthetics?
-Car paint not only makes the car look attractive but also serves the vital purpose of preventing rusting, which occurs when iron and steel are exposed to moisture and oxygen.
What is rusting, and how does it happen?
-Rusting is the corrosion of iron and steel caused by their reaction with oxygen and moisture, forming hydrated iron(III) oxide, commonly known as rust.
How can rusting be demonstrated experimentally?
-Rusting can be demonstrated by placing an iron nail in four test tubes under different conditions: one with water, one with water and salt, one with boiled water and oil, and one with calcium chloride to remove moisture.
What is the role of sodium chloride in the rusting experiment?
-Sodium chloride (table salt) accelerates rusting by acting as a catalyst in the oxidation reaction between iron, water, and oxygen, leading to more rapid rust formation.
What happens in the test tube with boiled water and oil?
-In the test tube with boiled water and oil, the water has no dissolved oxygen, and the oil prevents further oxygen from dissolving, which stops the rusting process.
Why do the nails in the third and fourth test tubes not rust?
-The nails in the third and fourth test tubes do not rust because they are either deprived of moisture (in the case of calcium chloride) or deprived of oxygen (in the case of boiled water and oil). Both are necessary for rusting.
What is the significance of the reddish-brown precipitate observed in the experiment?
-The reddish-brown precipitate observed in the first and second test tubes is iron oxide, or rust, which forms when iron undergoes oxidation in the presence of oxygen and moisture.
How does sacrificial protection work in preventing rusting?
-Sacrificial protection involves using a more reactive metal, such as zinc, to protect iron. Zinc corrodes faster than iron, sacrificing itself and forming a protective layer around the iron.
Where is galvanizing commonly used to prevent rusting?
-Galvanizing is commonly used to protect ships and other metal structures from rust by coating them with a layer of zinc, which corrodes instead of the underlying iron.
What advantage does the galvanizing process offer beyond rust prevention?
-Besides preventing rusting, the zinc oxide layer formed during galvanizing can be removed, exposing fresh zinc to continue protecting the iron by corroding first.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)