Peluang • Part 1: Percobaan, Ruang Sampel, Kejadian, dan Peluang Suatu Kejadian
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of probability is explored, starting with basic terms such as experiments, sample space, and events, revisiting fundamental knowledge from earlier schooling. The video demonstrates how to solve probability problems using counting principles, with a focus on more complex scenarios. Through examples like rolling a die, viewers are taught how to calculate the probability of specific outcomes, understand relative frequency, and distinguish between theoretical and experimental probabilities. The video emphasizes the relationship between the frequency of events and their probability as experiments are repeated, providing clear explanations of key probability concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses the basics of probability, including experiments, sample spaces, outcomes, and events.
- 😀 Probability for simple events has already been covered in middle school, and this video aims to review and deepen that knowledge using counting principles.
- 😀 A 'trial' in probability refers to an activity conducted once or multiple times, with a specific outcome that can be concluded, like rolling a die.
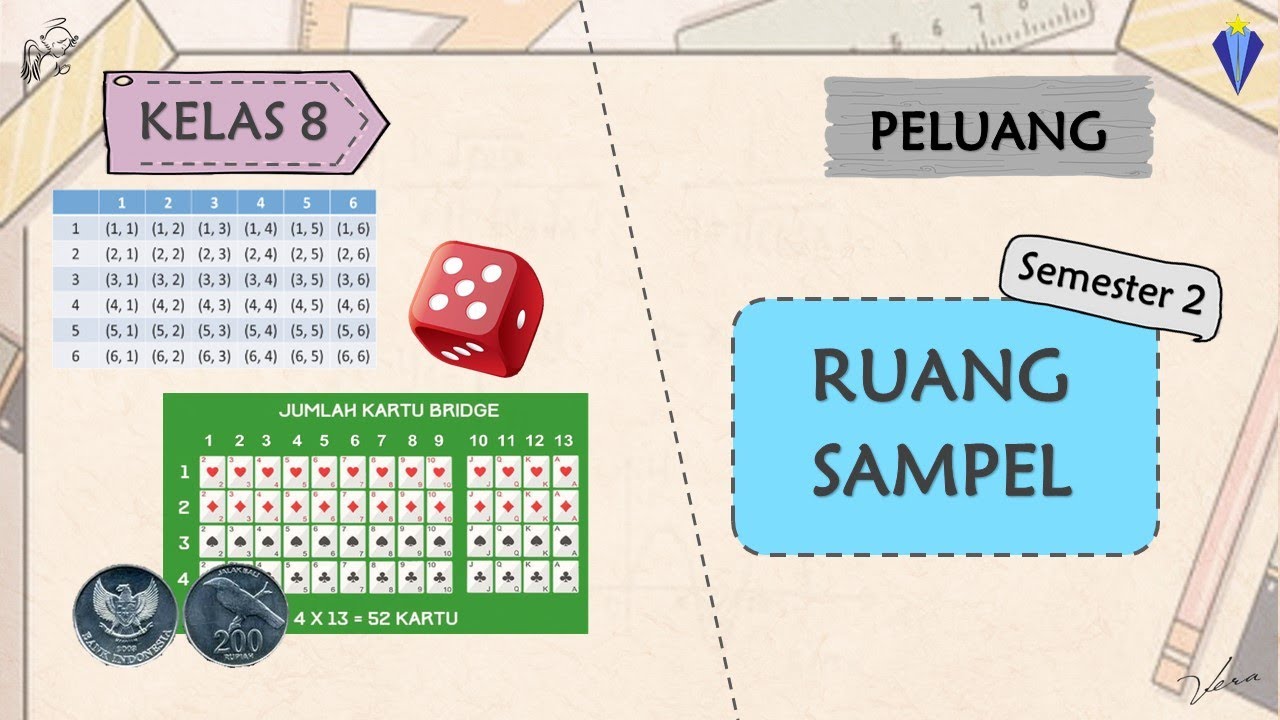
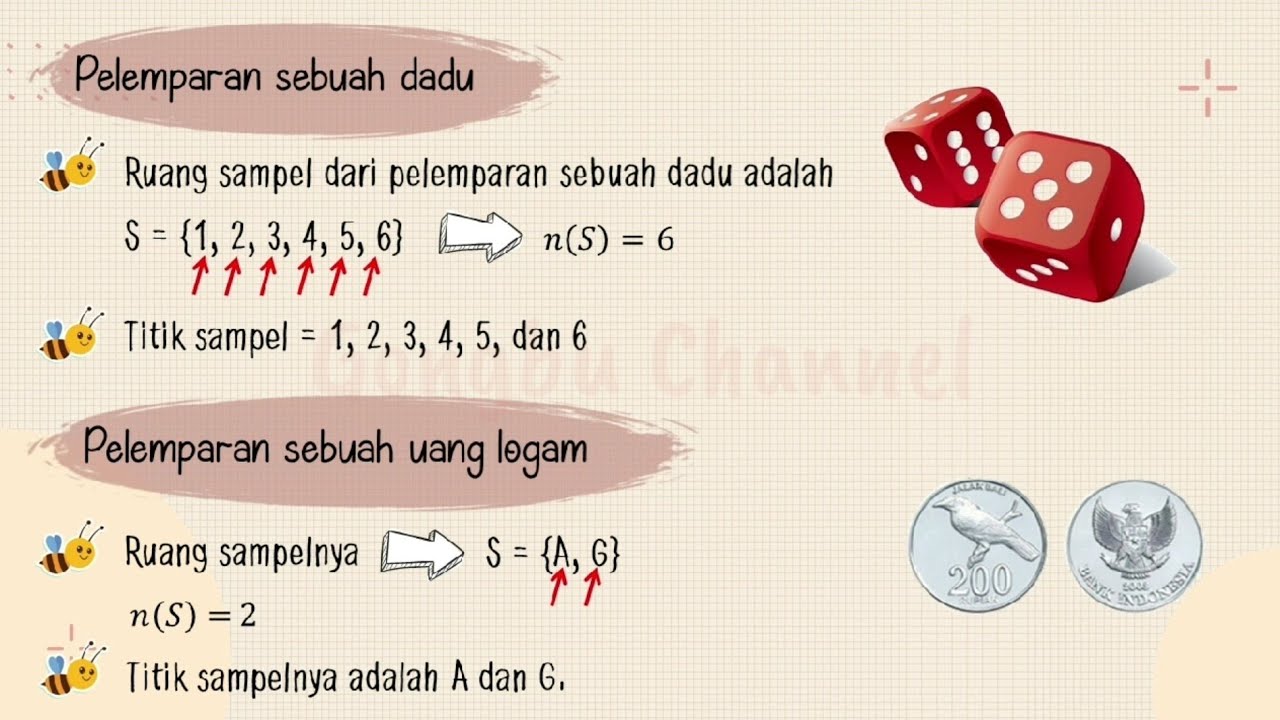
- 😀 A 'sample space' is the set of all possible outcomes in an experiment, such as {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} for rolling a die.
- 😀 'Sample points' are the individual outcomes that make up the sample space, such as 1, 2, 3, etc., when rolling a die.
- 😀 An 'event' is a subset of the sample space that is of interest, like the occurrence of an odd prime number when rolling a die (3, 5).
- 😀 Relative frequency is the ratio of the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials, calculated as frequency divided by total trials.
- 😀 As the number of trials increases, the relative frequency of an event will approach its theoretical probability.
- 😀 The theoretical probability of an event is calculated as the ratio of the favorable outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes in the sample space.
- 😀 Probability values always fall between 0 and 1. A probability of 0 indicates an impossible event, and a probability of 1 indicates a certain event.
- 😀 If the probability of an event is between 0 and 1, it indicates uncertainty about whether the event will occur.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic of the video is probability, including concepts such as experiments, sample space, events, and the calculation of probability using relative frequency.
What is an experiment in the context of probability?
-An experiment in probability refers to an activity performed once or more times, where the outcome can be observed and recorded. For example, rolling a die is considered an experiment.
What is a sample space?
-A sample space is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment. For example, the sample space for rolling a six-sided die is {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.
What is a sample point in probability?
-A sample point is an individual outcome of an experiment that is an element of the sample space. For example, when rolling a die, a sample point could be getting a '4'.
How is an event defined in probability?
-An event is a subset of the sample space. It refers to a specific outcome or set of outcomes that we are interested in. For instance, the event of rolling an odd number on a die is {1, 3, 5}.
What is the formula for relative frequency?
-The formula for relative frequency is: Frequency of event A / Total number of trials. It represents how often an event occurs relative to the total number of experiments conducted.
How does the number of trials affect relative frequency?
-As the number of trials increases, the relative frequency tends to approach the theoretical probability of an event, making the results more reliable.
What is the relationship between relative frequency and probability?
-Relative frequency is the observed frequency of an event occurring in a series of trials, while probability is the theoretical chance of an event occurring. With more trials, relative frequency approximates the theoretical probability.
What is the probability of rolling an odd prime number on a six-sided die?
-The odd prime numbers on a die are 3 and 5. Therefore, the probability is 2/6 or 1/3.
What is the range of possible values for the probability of an event?
-The probability of an event must lie between 0 and 1, inclusive. A probability of 0 means the event is impossible, and a probability of 1 means the event is certain to occur.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
1. RUANG SAMPEL - PELUANG - KELAS 8 SMP

Peluang ( probabilitas ) - peluang statistika materi dan contoh soal

Materi "PELUANG" Matematika Kelas 10 Semester 2

STATISTIKA | KONSEP DASAR PROBABILITAS
Percobaan, Ruang Sampel dan Kejadian ||Materi, Soal & Pembahasan||

Probabilitas 01 Pengenalan Probabilitas Dasar | Belajar Probabilitas
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
