PERBEDAAN ANTARA LISTRIK 1 PHASE DAN LISTRIK 3 PHASE | PASTI BANYAK YANG BELUM PAHAM INI
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the difference between single-phase and three-phase electricity in a simple and engaging way. It covers the basics of each system, how they work, and their applications, from household to industrial uses. Single-phase power is ideal for home appliances, while three-phase power is used in industries for higher power demands, such as motors. The video also highlights the advantages of three-phase systems, including higher efficiency, lower current, and improved safety. Viewers are invited to learn more and share their thoughts on the topic.
Takeaways
- 😀 A single-phase electrical system (1-phase) is commonly used in households to power small appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and water pumps.
- 😀 A three-phase electrical system (3-phase) is designed to power larger loads, such as industrial machinery, and provides a higher power output.
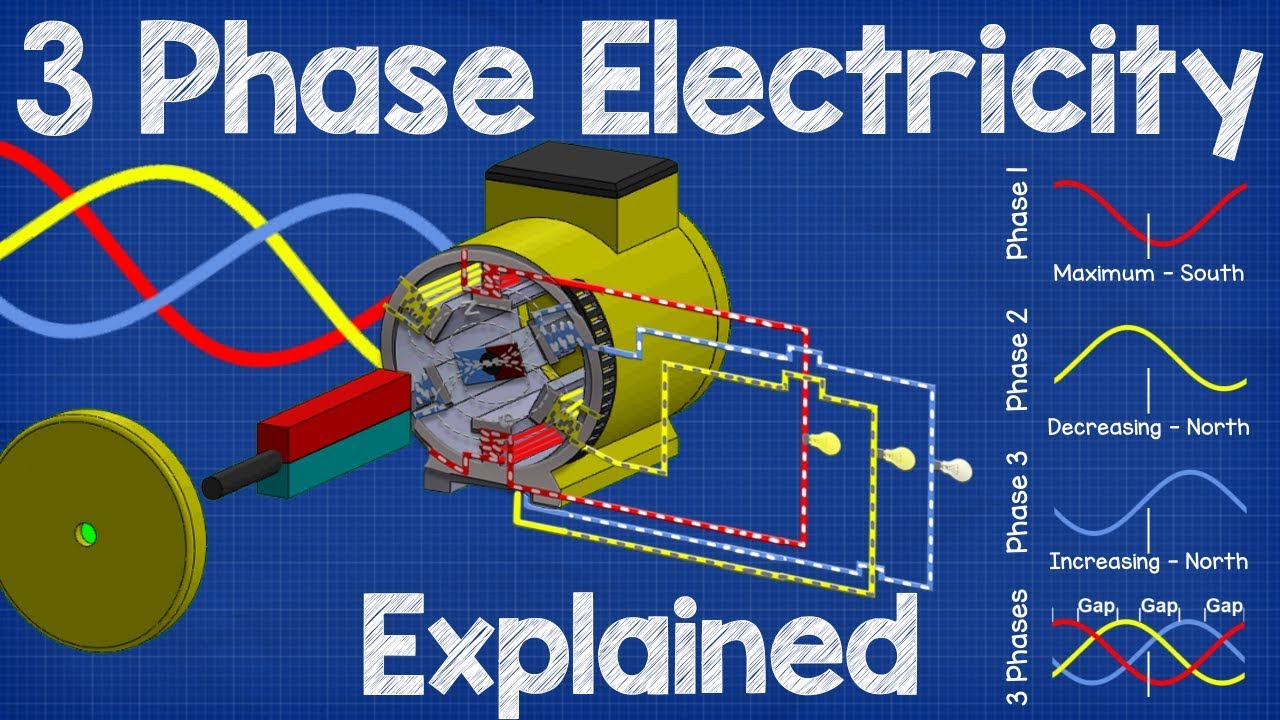
- 😀 Both 1-phase and 3-phase systems are alternating current (AC) systems, with sine waveforms that alternate between positive and negative values.
- 😀 A single-phase system has one sine wave that completes a full cycle (360 degrees) with one peak (positive) and one valley (negative).
- 😀 In a three-phase system, there are three sine waves, each 120 degrees apart, which prevents the phases from overlapping and ensures a continuous power supply.
- 😀 The three-phase system is more efficient and can handle larger loads, as each phase is spaced out to avoid interference and reduce power fluctuations.
- 😀 Electricity is delivered to homes via power transmission lines that distribute three-phase electricity, which is then converted to single-phase for residential use.
- 😀 In residential areas, power is split from three-phase transmission into three separate single-phase lines for different homes, each using one phase.
- 😀 For industrial applications, three-phase power provides a steady and reliable flow of energy to run heavy machinery, such as three-phase induction motors.
- 😀 The advantages of a three-phase system include higher voltage levels, which reduce the current and the size of wires needed, making the system more efficient and cost-effective.
Q & A
What is the main difference between single-phase and three-phase electricity systems?
-The main difference is that single-phase electricity is used for smaller loads, like home appliances, while three-phase electricity is used for larger industrial loads, offering higher power output and more efficiency.
What types of appliances use single-phase electricity?
-Single-phase electricity is used to power household appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and water pumps.
Why is three-phase electricity used in industrial settings?
-Three-phase electricity is ideal for powering large equipment like induction motors, which require more power to operate efficiently, such as in industrial applications.
How do the waveforms differ between single-phase and three-phase electricity?
-In single-phase electricity, there is only one sinusoidal wave, while in three-phase electricity, there are three sinusoidal waves, each offset by 120 degrees from the others, ensuring smoother and more stable power delivery.
What is the purpose of using three-phase electricity with 120-degree phase differences?
-The 120-degree phase difference between the three phases prevents the waves from colliding, enabling the system to provide more stable and higher power output, which is essential for heavy industrial loads.
How does the transmission of three-phase electricity reach households?
-Three-phase electricity is first transmitted through medium-voltage lines (around 20 kV), and then stepped down by transformers to lower voltages, which are distributed to homes. Each house receives a phase of the three-phase supply.
How is three-phase electricity distributed to residential homes?
-In residential areas, three-phase electricity is divided so that each home receives a single-phase supply, typically with a voltage of 220-240V per phase, even though the overall system is three-phase.
What is the voltage difference between phase-to-phase and phase-to-neutral in a three-phase system?
-In a three-phase system, the voltage between phases (phase-to-phase) is 380V, while the voltage between a phase and neutral (phase-to-neutral) is typically 220-240V.
What are the advantages of using a three-phase system over a single-phase system?
-The advantages include the ability to handle larger power demands, reduced current flow for the same power, more efficient motor operation, and the ability to power both three-phase and single-phase loads simultaneously.
Why is the current lower in a three-phase system compared to a single-phase system?
-In a three-phase system, the current is lower because the power is distributed across three phases, resulting in more efficient energy transmission and requiring smaller cables, which reduces the risk and cost.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
How Three Phase Electricity works - The basics explained
Power Inverters Explained - How do they work working principle IGBT

AC Basics: Learn All About Alternating Current

Sistem Tenaga Listrik - Bagaimana kita bisa menikmati listrik PLN

5 Formulas Electricians Should Have Memorized!

Single phase Induction Motor / Capacitor start capacitor run motor / Capacitor start induction motor
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
