Sistema Nervoso Periférico 4/6 | Anatomia e etc
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explains the structure and function of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The PNS connects the body to the central nervous system (CNS) through cranial and spinal nerves. The speaker discusses the 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves, highlighting their mixed functions, involving both sensory and motor neurons. The PNS is divided into the somatic nervous system, controlling voluntary actions, and the autonomic nervous system, managing involuntary functions. The speaker also covers the role of ganglia, nerve roots, and the anatomical organization of the nervous system, providing a comprehensive overview of how the PNS functions in the body.
Takeaways
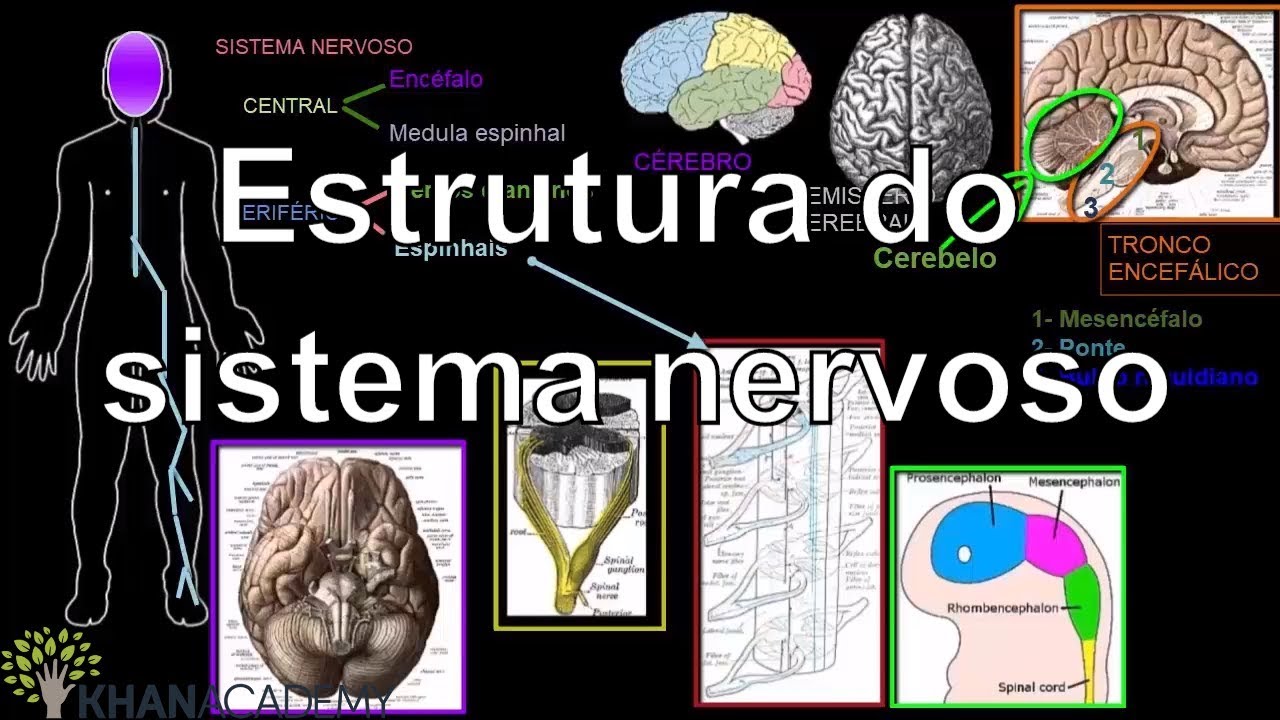
- 😀 The peripheral nervous system connects the central nervous system to various body structures through nerves.
- 😀 The peripheral nervous system consists of cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and ganglia.
- 😀 Cranial nerves originate from the brain, and there are 12 pairs of them, each with a name and a Roman numeral indicating its anatomical location.
- 😀 Spinal nerves, totaling 31 pairs, emerge from the spinal cord and are grouped by their location along the spine.
- 😀 Cranial nerves can have both sensory and motor functions, meaning they contain both sensory neurons and motor neurons.
- 😀 Spinal nerves are also mixed nerves, containing both sensory and motor neurons, with sensory neurons entering the spinal cord and motor neurons exiting.
- 😀 Sensory neurons enter the spinal cord through the posterior horn, while motor neurons exit through the anterior horn.
- 😀 Spinal nerves are named based on their location in the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions.
- 😀 The peripheral nervous system is functionally divided into the somatic nervous system (voluntary control) and the autonomic nervous system (involuntary control).
- 😀 The peripheral nervous system is essential for body functions such as muscle control and autonomic processes like heart rate and digestion.
Q & A
What is the peripheral nervous system and how does it interact with the central nervous system?
-The peripheral nervous system connects the central nervous system (CNS) to various parts of the body. It transmits signals from the brain and spinal cord to the body, and vice versa. The system consists of nerves that emerge from the brain (cranial nerves) and the spinal cord (spinal nerves).
What are cranial nerves and how are they classified?
-Cranial nerves are nerves that emerge from the brain, and there are 12 pairs of them. These nerves are named and numbered using Roman numerals based on their anatomical position, starting from the front (anterior) part of the brain to the back (posterior) part.
What is the function of the cranial nerves?
-Most cranial nerves are mixed, meaning they have both sensory and motor functions. This allows them to transmit sensory information as well as control motor functions. Each cranial nerve has specific areas it controls or senses, such as vision, smell, and facial movements.
What are the different types of cranial nerves, and can you name a few of them?
-There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves, including the olfactory, optic, and oculomotor nerves. The names of these nerves are related to the structures they innervate, such as the facial nerve (facial movements) and the vestibulocochlear nerve (balance and hearing).
How are spinal nerves classified?
-Spinal nerves are classified into 31 pairs based on the region of the spinal cord where they emerge. These include cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal nerves, with cervical nerves being an exception as there are 8 pairs despite only 7 cervical vertebrae.
Why do we have 8 pairs of cervical nerves despite having only 7 cervical vertebrae?
-The first cervical nerve emerges above the first cervical vertebra, which is why we have 8 pairs of cervical nerves. The remaining cervical nerves correspond one-to-one with the cervical vertebrae.
What is the role of sensory and motor neurons in spinal nerves?
-Spinal nerves are mixed, containing both sensory and motor neurons. Sensory neurons enter the spinal cord via the posterior horn, while motor neurons exit through the anterior horn. These neurons come together to form a single spinal nerve that transmits both types of signals.
What is the function of ganglia in the peripheral nervous system?
-Ganglia are clusters of neuronal cell bodies located outside the central nervous system. They play an essential role in transmitting signals, acting as relay stations for sensory or motor information.
What are the differences between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems?
-The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements, such as the contraction of skeletal muscles. The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing.
How does the structure of spinal nerves contribute to their mixed function?
-Spinal nerves are mixed because they contain both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers enter the spinal cord via the posterior root, while motor fibers exit through the anterior root. These roots join together to form the mixed spinal nerve.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Nervous System
Estrutura do sistema nervoso | Saúde e medicina anatomia e fisiologia humana | Khan Academy

Sistem Saraf Manusia: Bagian-Bagian dan Fungsinya

Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 3 Module 3 | The Power and Control of the Nervous System
Nervous System - Get to know our nervous system a bit closer, how does it works? | Neurology

A Struktur dan Fungsi pada Sistem Saraf
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
