Nervous System
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into the diversity and specialization of cells in the human body, with a focus on the nervous system. It outlines the structure of the nervous system, including the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS), and highlights the roles of the brain's regions. The script emphasizes the importance of neurons and glial cells in the nervous system and explains the concept of action potentials and neurotransmitters, which facilitate communication between neurons. The video aims to dispel common myths about the brain and explores the intricacies of the nervous system's function and structure.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Cell diversity is vast, with specialized cells performing unique functions in different body systems.
- 🧠 The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- 🌟 The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes all other components like nerves throughout the body.
- 💡 The brain is divided into the hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain, each with distinct functions such as regulation, alertness, and higher cognitive processes.
- 🏃♂️ The somatic nervous system (SNS) is involved with voluntary motor functions and somatic reflexes.
- 🔄 The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the body's internal environment and can be further divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
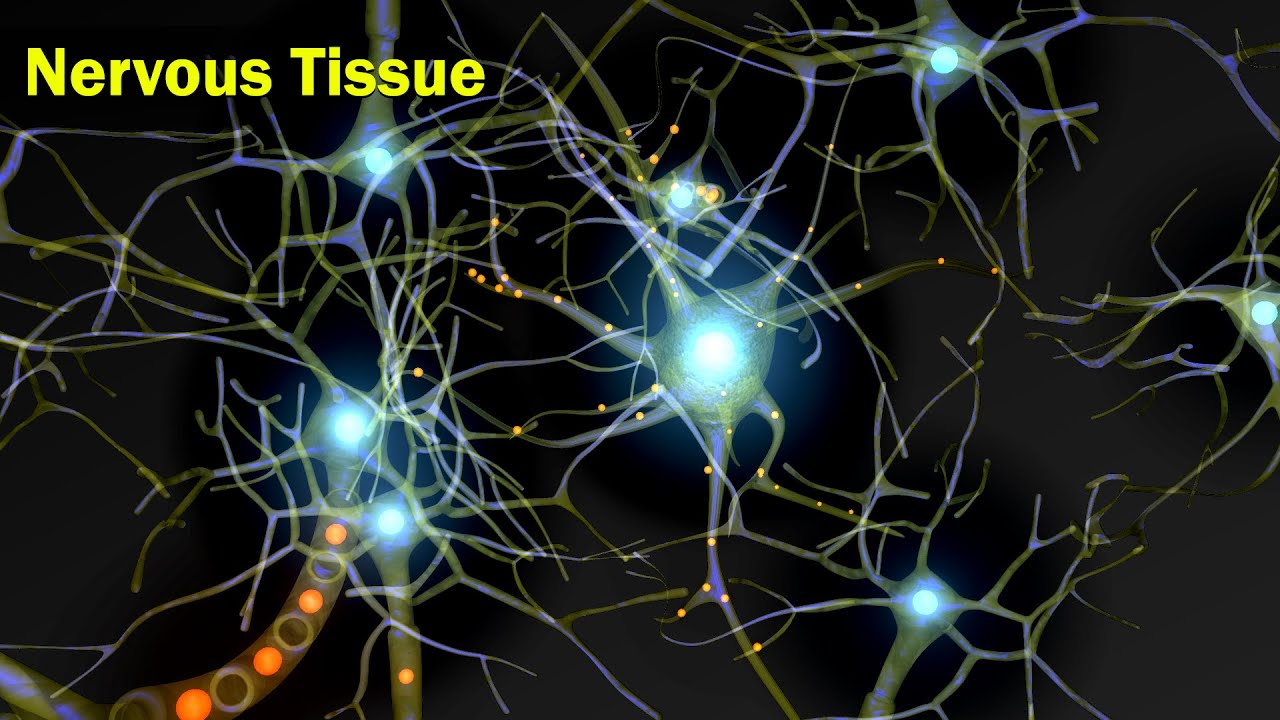
- 🌐 Neurons and glial cells are the two major types of cells in the nervous system, with neurons being the primary communicators and glial cells providing essential support.
- 🚀 Action potentials allow neurons to communicate rapidly by changing the electrical charge along the axon in a process that is 'all or none'.
- 🔌 Synapses are the junction points where neurons communicate, and neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles to bind specific receptors on neighboring neurons.
- 🧠 The brain's structure and function are complex, with myths like 'we only use 10% of our brain' being debunked.
- 🔍 Ongoing research in neurology aims to better understand and treat diseases and conditions of the nervous system.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the nervous system, its structure, function, and the cells that comprise it.
What are the two general regions the nervous system can be divided into?
-The nervous system can be divided into the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes all other components of the nervous system such as nerves throughout the body.
What are the three general regions the human brain is divided into?
-The human brain is divided into the hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain.
What are the primary functions of the medulla in the hindbrain?
-The medulla has many regulatory functions such as the regulation of breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate.
How is the peripheral nervous system (PNS) functionally divided?
-Functionally, the PNS is divided into the somatic nervous system (SNS), which is involved with motor functions of skeletal muscle, and the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which deals with the internal environment and involuntary functions.
What are the two major types of cells that make up nervous tissue?
-The two major types of cells that make up nervous tissue are neurons and glial cells.
What is the role of glial cells in the nervous system?
-Glial cells, or glia, play critical roles in the nervous system, including structural support, maintaining the blood-brain barrier, producing myelin to insulate axons, and participating in immune functions within the nervous system.
What is an action potential and why is it important for neurons?
-An action potential is a rapid change in the electrical charge of a neuron that allows it to communicate with other cells. It is important because it enables the fast transmission of signals along the neuron's axon, which is essential for the neuron's function in communication and processing information.
What happens when an action potential reaches the end of an axon?
-When an action potential reaches the end of an axon, it signals synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse, the space between two neurons. These neurotransmitters then bind to specific receptors on the next neuron, potentially initiating a new action potential in that neuron.
What is the significance of the 'fight or flight' response in the sympathetic nervous system?
-The 'fight or flight' response in the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for rapid action in response to a perceived threat or stressor. It increases heart rate, blood flow to muscles, and alertness, while temporarily reducing functions like digestion that are not immediately necessary for survival in the short term.
How does the parasympathetic nervous system contrast with the sympathetic nervous system?
-The parasympathetic nervous system is often referred to as the 'rest and digest' system. It works to conserve resources, reduce heart rate, promote digestion, and generally maintain homeostasis in the body, in contrast to the activating effects of the sympathetic nervous system.
What is the myth about the brain that the video aims to dispel?
-The video aims to dispel the myth that 'humans only use 10% of their brain.' This is incorrect, as we use virtually every part of our brain, though not all areas are active at the same time.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

GCSE Biology - Nervous System and Reflex Arc #58
Nervous Tissue | Structural Organization in Animals | Anatomy | Inter 2nd year Class 11 Biology

Sel Saraf / Neuron ( Sistem Saraf)

BAB 2 Sistem Koordinasi Manusia || Sistem Saraf Manusia || IPA SMP/MTs Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka

Sinir Sistemi : Nöron Yapısı ve İşlevleri , Nöroglia Hücreleri

The Nervous System In 9 Minutes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)