STATISTIKA PENDIDIKAN PERTEMUAN 1-PENGANTAR STATISTIKA DAN STATISTIK
Summary
TLDRIn this introductory session of a statistics course, the lecturer, Fitri Azzahra Kumala, outlines the key topics to be covered, including statistics, data presentation techniques, probability distributions, hypothesis testing, and regression analysis. The session also defines key terms such as statistics and statistical analysis, differentiating between descriptive and inferential statistics. The lecture further explains data types, measurement scales, and data collection methods, emphasizing the importance of sampling and various techniques like probability sampling. The session concludes with an overview of the course structure, grading criteria, and resources.
Takeaways
- 😀 The course begins with an introduction to statistics and its various fields, focusing on the basics of data analysis.
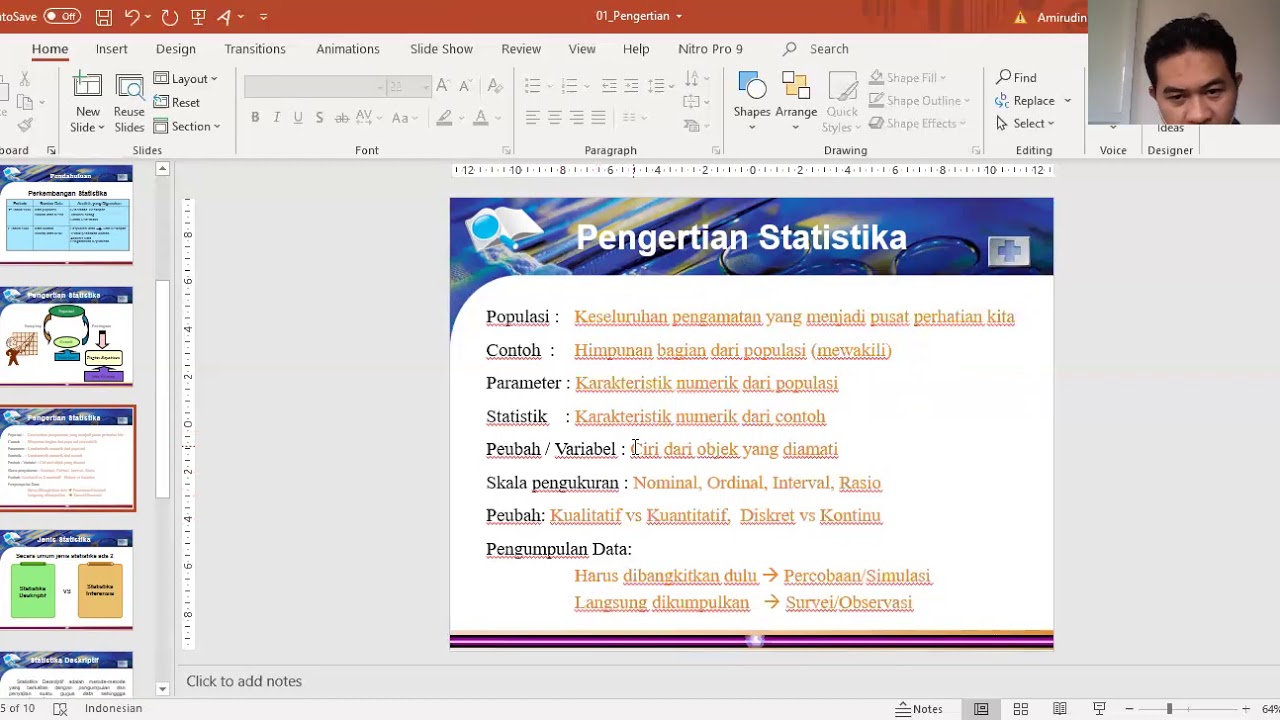
- 😀 Statistics is defined as a collection of data, both numerical and non-numerical, that can be represented in tables or diagrams to illustrate problems.
- 😀 'Statistika' has its origins in the term 'status speed' or 'tas,' referring to state-related data, but has since expanded to other fields.
- 😀 Statistics in its narrow sense includes summarizing data with numbers or as a representative measure of a data set.
- 😀 'Inferential Statistics' refers to making conclusions about a population based on data from a sample, typically using hypothesis testing.
- 😀 Statistics can be categorized based on data processing methods, the disciplines using it, and the type of parameters involved.
- 😀 Descriptive Statistics deals with methods to summarize and visually represent data, making it easier to understand.
- 😀 Inferential Statistics uses sample data to infer characteristics of a larger population, typically involving hypothesis testing and estimation.
- 😀 The course covers various forms of data, including quantitative (numerical) and qualitative (categorical), and different scales of measurement such as nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio.
- 😀 Data collection methods include 'census' (where data from the entire population is gathered) and 'sampling' (where only a subset of the population is studied).
- 😀 Sampling methods can be divided into probability sampling (with equal chances for all participants to be selected) and non-probability sampling (where selections are subjective).
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the first meeting in the Statistics course?
-The first meeting focuses on an introduction to statistics, covering basic concepts such as the definition of statistics, its applications, and the different branches of statistics.
What are the evaluation criteria for this Statistics course?
-The evaluation consists of UAS (30%), UTS (30%), participation (20%), and assignments (20%).
What is the difference between 'statistics' and 'statistika'?
-'Statistics' refers to data collections and summaries, while 'statistika' has an etymological link to the state or country, initially used for national matters but now expanded to various fields like education.
What are the two main definitions of statistics mentioned in the lecture?
-Statistics can be defined narrowly as a summary of data, such as average scores or gender distribution, or as a broad field that includes the methods and concepts for interpreting data and drawing conclusions in uncertain situations.
What is the difference between descriptive statistics and inferential statistics?
-Descriptive statistics focuses on summarizing and presenting data to make it easier to understand, while inferential statistics involves drawing conclusions from sample data to make generalizations about a larger population.
What is a sample in the context of inferential statistics?
-A sample is a subset of the population that is used to represent the characteristics of the entire population.
How are statistical methods classified based on their processing technique?
-Statistical methods are classified into two types: descriptive statistics, which describes data, and inferential statistics, which uses sample data to make inferences about the population.
What are the four levels of measurement scales in statistics?
-The four levels of measurement scales are: nominal (categorical data without order), ordinal (data with order but no meaningful difference), interval (numerical data with no true zero), and ratio (numerical data with a true zero point).
What is the difference between primary and secondary data?
-Primary data is collected directly from the source by the researcher, while secondary data refers to data that has already been collected and processed by others, typically available in publications or reports.
What is the difference between census and sampling in data collection methods?
-A census involves collecting data from every member of the population, while sampling involves collecting data from a subset of the population to infer information about the entire group.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
Statistics For Data Analytics | Complete Syllabus | Data Science | Statistics Tutorial | Part 1

Statistics Course Overview | Best Statistics Course | MarinStatsLectures

[Statistika]: Macam-Macam Distribusi Probabilitas (Binomial, Poisson, Normal dan Student-T)

100+ Statistics Concepts You Should Know

Pengantar Statistika 1
Pertemuan 1 Statistika sosial
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
