Histologi Lengkap Sistem Pernapasan | Histology 101
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the histology of the respiratory system, beginning with the nasal cavity. It covers the structure of the epithelium in different areas, including the olfactory and respiratory regions, and details their functions such as air filtration and lubrication. The transcript then delves into the histology of the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, highlighting specific cell types like pseudostratified columnar and squamous epithelium. The video concludes with a discussion on alveolar structures and the crucial role of pneumocytes in gas exchange, providing a comprehensive understanding of the respiratory system's cellular architecture.
Takeaways
- 😀 The nasal cavity is divided into three parts: the vestibule, respiratory zone, and olfactory zone, each with different types of epithelial tissue.
- 😀 The respiratory zone is lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium that contains cilia and goblet cells to filter and moisten incoming air.
- 😀 The olfactory zone is lined with specialized epithelium that includes olfactory neurons, supporting cells, and basal cells responsible for scent detection.
- 😀 The larynx has two types of vocal cords: true vocal cords (covered with non-keratinized squamous epithelium for friction resistance) and false vocal cords (lined with respiratory epithelium).
- 😀 The trachea is lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium and contains hyaline cartilage rings and smooth muscle to maintain the airway structure.
- 😀 The bronchi also have pseudostratified columnar epithelium, but the cartilage decreases as the bronchi become smaller, and smooth muscle increases.
- 😀 As airways narrow towards the bronchioles, the epithelium changes from columnar to simple cuboidal, with cilia and goblet cells disappearing in the smaller bronchioles.
- 😀 The alveoli are the main site of gas exchange in the lungs, with Type I pneumocytes facilitating diffusion and Type II pneumocytes secreting surfactant.
- 😀 Alveolar macrophages (dust cells) are immune cells that clear out debris in the alveolar space.
- 😀 The blood-air barrier, formed by the thin walls of Type I pneumocytes, allows oxygen and carbon dioxide to diffuse easily between the alveoli and capillaries.
Q & A
What are the three parts of the nasal cavity according to the script?
-The nasal cavity is divided into three parts: the vestibulum (nostrils), the respiratory region (concha nasalis), and the olfactory region.
What type of epithelium lines the vestibulum and respiratory regions?
-The epithelium in the vestibulum and respiratory regions is pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia, also known as respiratory epithelium.
Why is the epithelium in the respiratory region referred to as 'pseudostratified'?
-It is called 'pseudostratified' because it appears multilayered, but all cells are attached to the basement membrane, making it technically a single layer.
What is the function of Goblet cells in the respiratory epithelium?
-Goblet cells secrete mucus, which lubricates the respiratory passages and helps trap foreign particles.
What modifications are found in the epithelium of the olfactory region?
-The epithelium in the olfactory region is similar to respiratory epithelium but lacks Goblet cells and contains specialized olfactory cells and supporting cells.
What are the types of cells found in the olfactory region?
-The olfactory region contains olfactory cells (bipolar neurons), supporting cells (similar to neuroglia), basal cells (stem cells), and brush cells (involved in general sensation).
What is the function of olfactory cells?
-Olfactory cells are responsible for detecting smells and transmitting signals to the olfactory bulb, which processes the sensory information.
How does the epithelium of the larynx differ in the true and false vocal cords?
-The epithelium of the true vocal cords (plika vokalis) is non-keratinized squamous epithelium, while the epithelium of the false vocal cords (plika vestibularis) is respiratory epithelium with cilia and Goblet cells.
What type of epithelium is found in the trachea and bronchi?
-The trachea and bronchi are lined with respiratory epithelium, which includes pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia and Goblet cells.
What changes occur in the epithelial structure as the respiratory airways get smaller?
-As the airways become smaller, the epithelium transitions from pseudostratified columnar epithelium to simple columnar, then to simple cuboidal epithelium in the bronchioles and finally squamous epithelium in the alveoli.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Układ oddechowy! Drogi oddechowe i płuca, budowa i funkcje narządów. Głęboki wdech...i zaczynamy!!!

Nasal Anatomy (Cartilage, Nasal Cavity, Sinuses, Meatuses, Nasal Mucosa)
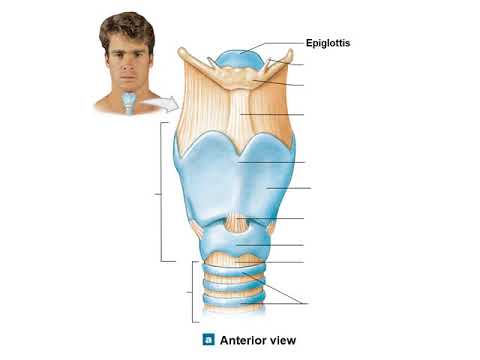
Anatomi Sistem Respirasi | Materi Kedokteran Dasar

IPA Kelas 8 : Sistem Pernapasan 1 (Proses Dasar dalam Pernapasan dan Organ-organ Sistem Pernapasan)

BIOLOGI SMA Kelas 11 - Sistem Pernapasan | GIA Academy
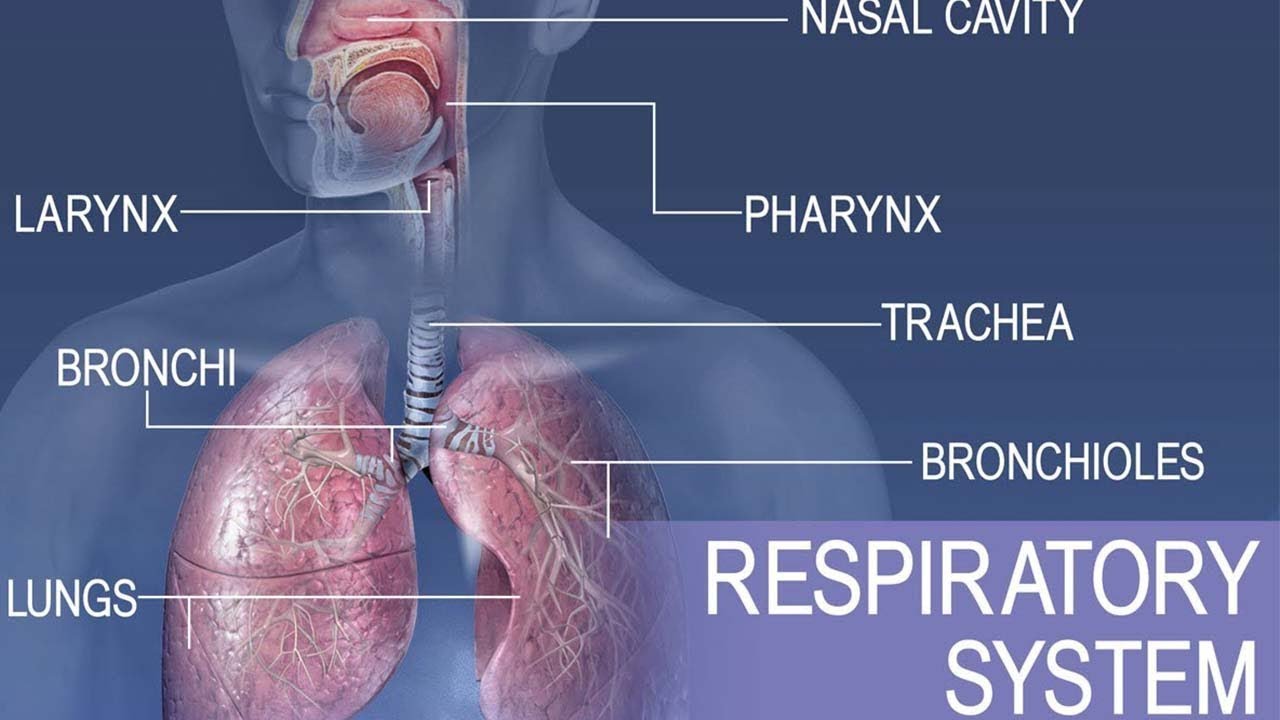
Anatomy and physiology of Respiratory system
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
