8. VÍDEO - Processos Físicos Industriais
Summary
TLDRThis video explores key industrial processes, such as machining, welding, plastic molding, and cutting, through the lens of physics. It explains how principles like energy conservation, thermodynamics, and electrodynamics play a vital role in shaping materials and manufacturing products. The video also highlights the importance of processes like electric discharge machining, adhesive bonding, and assembly lines, showcasing their relevance to modern technology. Through detailed demonstrations and explanations, it illustrates the practical applications of physics in industrial production, making it an engaging resource for understanding the connection between science and real-world manufacturing.
Takeaways
- 😀 Machining processes like lathe, milling, and electric erosion are key manufacturing methods where material is removed to create specific shapes.
- 😀 Welding techniques, including gas welding and electric arc welding, use heat to fuse metal parts together, enabling the production of complex objects.
- 😀 Industrial adhesives have evolved, allowing for molecular bonding between materials without requiring heat, and are now widely used in industries like aerospace.
- 😀 Material cutting processes, such as plasma cutting, laser cutting, and water jet cutting, utilize different forms of energy to break atomic bonds and shape materials.
- 😀 Stamping, both hot and cold, involves deforming metal under high pressure to create precise shapes, commonly used in manufacturing large quantities of parts.
- 😀 Plastic injection molding is a process that melts plastic and injects it into molds to form parts, widely used in the production of everyday plastic objects.
- 😀 The concept of the assembly line maximizes production efficiency by breaking down tasks into smaller steps performed by both human workers and automated machines.
- 😀 The importance of ergonomics and balancing human effort with automation in assembly lines is crucial to maintaining both efficiency and worker motivation.
- 😀 The energy required in machining processes is significant, with heat generation playing a role in shaping materials like metals and plastics.
- 😀 Technologies like laser cutting and water jet cutting have revolutionized precision in material cutting, offering accuracy down to millimeters and the ability to work with a variety of materials.
Q & A
What is the primary principle behind machining processes like turning and milling?
-Machining processes, such as turning and milling, primarily rely on the mechanical principle of material removal through friction and relative motion between a tool and the workpiece. These processes involve forces of abrasion and cutting that reshape the material to achieve the desired geometry.
How does electric discharge machining (EDM) differ from traditional machining methods?
-Electric discharge machining (EDM) differs from traditional machining methods as it uses electrical discharges (sparks) to erode material from a workpiece. This process is particularly suited for complex geometries and small-scale production, whereas traditional methods involve direct mechanical cutting or grinding.
What are the main physical principles involved in the welding process?
-The main physical principles involved in welding include the transfer of heat to melt metals and the manipulation of atomic bonds. As metals are heated to their melting point, molecular bonds are broken and, upon cooling, reformed, creating a solid bond between the materials.
What is the role of heat in soldering and welding processes?
-Heat plays a critical role in both soldering and welding processes by causing the material to melt and form a bond. In welding, high temperatures are applied to the edges of materials to melt and fuse them, while in soldering, lower temperatures are used to melt a filler material that bonds the workpieces.
How does the principle of heat transfer relate to cutting methods like plasma cutting and laser cutting?
-In both plasma cutting and laser cutting, heat transfer is essential. Plasma cutting uses an electrically charged gas (plasma) to transfer heat at extremely high temperatures to melt the metal, while laser cutting uses focused light energy to rapidly heat and vaporize the material.
What is the significance of polymerization in the industrial use of adhesives?
-Polymerization is crucial in adhesive technology as it involves the chemical reaction where monomers (small molecules) link together to form long chains, creating a strong bond between materials. This process can be activated by heat, light, or chemical agents, providing durability and resistance.
Why is injection molding a widely used process in plastics manufacturing?
-Injection molding is widely used in plastics manufacturing because it allows for precise shaping and high-volume production of complex parts. The process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold, where it cools and solidifies, producing consistent and detailed parts.
How does stamping (both hot and cold) work in metal forming, and what physical principles are at play?
-Stamping works by applying mechanical force to metal sheets using molds or dies, either at high temperatures (hot stamping) or room temperature (cold stamping). The physical principles at play include plastic deformation, where the metal is reshaped under pressure without breaking, and the material's resistance to this deformation.
What are the advantages of using a CNC (computer numerical control) machine in manufacturing?
-CNC machines offer high precision and automation in manufacturing. They reduce human error, increase productivity, and allow for complex, repeatable tasks to be performed with minimal intervention. CNC systems can be programmed to handle various processes like milling, turning, and drilling.
How do the concepts of force and motion apply to the assembly line process?
-In the assembly line process, force and motion are applied in a systematic way to efficiently move parts through various stages of production. Machines and workers apply controlled forces to position, assemble, or test components, while the coordinated movement ensures smooth transitions and optimal production speed.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

How Things Are Made | An Animated Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
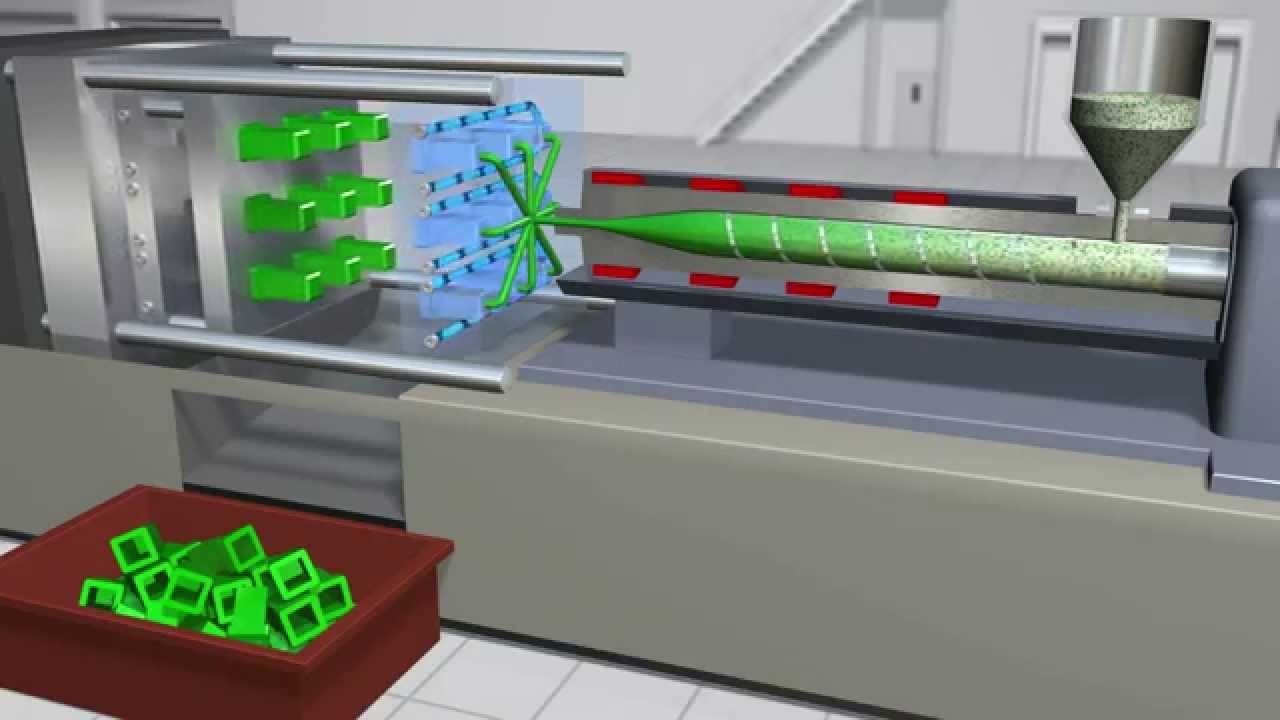
Plastic Processing Overview

CNC machining - What is it and How Does it Work? (Must Know Basics)

INJECTION MOLDING - DEFINISI, CARA KERJA, DAN BAGIAN-BAGIAN MESIN INJECTION MOLDING
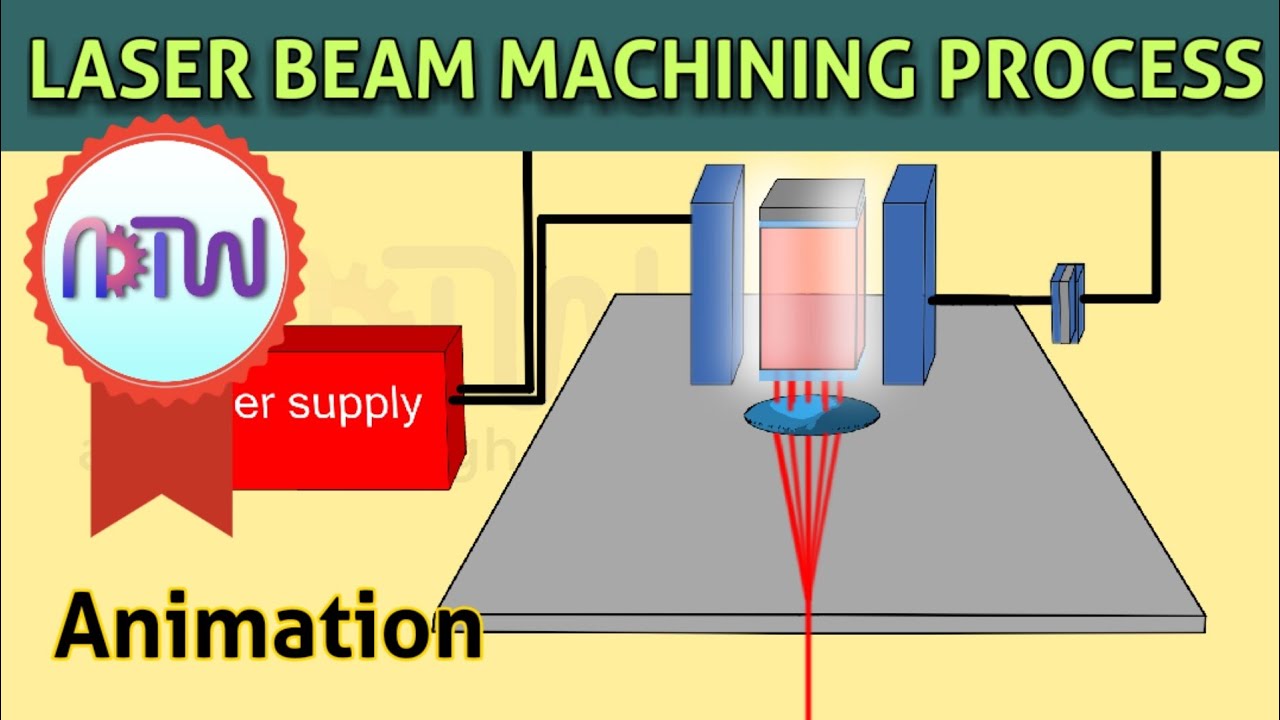
LASER BEAM MACHINING PROCESS (Animation): Working of LASER beam machining process.

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção - Usinagem convencional: conceitos
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
