Konsep Dasar Pengujian Hipotesis
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture introduces the fundamental concepts of hypothesis testing in statistics. It differentiates between statistical hypotheses and research hypotheses, emphasizing the role of hypothesis testing in inferring population parameters from sample data. The lecture covers types of hypotheses, including descriptive, comparative, and associative, and their use in statistical analysis. Key topics include significance levels, types of errors (Type 1 and Type 2), and estimation methods. The video also explains the importance of confidence intervals and the potential risks of statistical errors, offering a comprehensive overview of how hypothesis testing works in both research and statistical analysis.
Takeaways
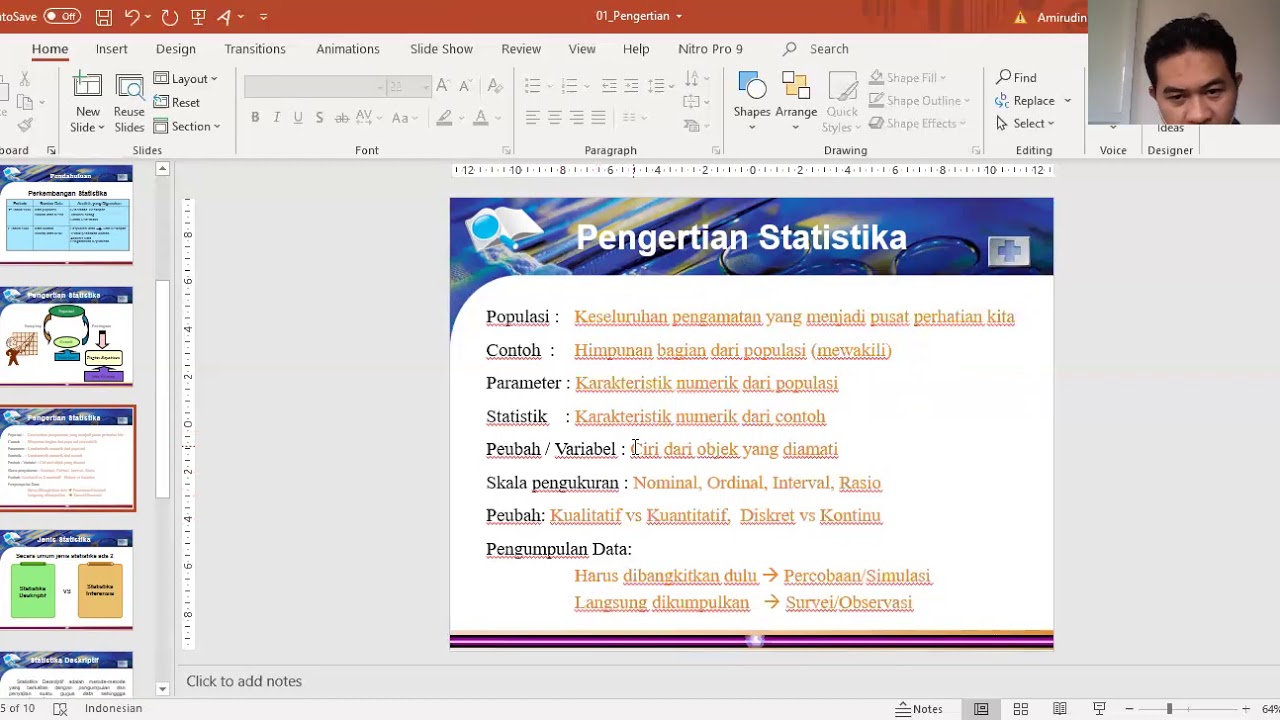
- 😀 Hypothesis in statistics is a statement or assumption about a population parameter, based on sample data.
- 😀 The difference between statistics and parameters is that statistics refer to sample data, while parameters describe the population as a whole.
- 😀 In research, a hypothesis is a temporary answer to a research question, while in statistics it estimates population parameters.
- 😀 Descriptive hypotheses predict a single variable or parameter without making comparisons or establishing relationships.
- 😀 Comparative hypotheses involve comparing two or more variables to detect differences (e.g., gender and job waiting times).
- 😀 Associative hypotheses explore the relationships between two or more variables (e.g., GPA and job waiting times).
- 😀 The null hypothesis (H₀) suggests no difference or relationship, while the alternative hypothesis (H₁) suggests a difference or relationship.
- 😀 Type 1 error occurs when a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected, while Type 2 error occurs when a false null hypothesis is incorrectly accepted.
- 😀 The significance level (α) indicates the likelihood of making a Type 1 error, typically set at 1% or 5%.
- 😀 Interval estimation provides a range of possible values for population parameters, reducing error compared to point estimates.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic of the video is the basic concept of hypothesis testing, focusing on statistical hypotheses, their definitions, and how they are used in research and statistics.
What is the difference between statistics and parameters as discussed in the video?
-Statistics refers to the measures used for sample data, while parameters refer to the measures for an entire population. For example, the sample mean is denoted by 'x-bar', while the population mean is denoted by the symbol 'μ'.
How does the concept of hypothesis differ between statistics and research?
-In statistics, a hypothesis is an estimate of a population parameter, while in research, a hypothesis is a provisional answer to a research question that suggests relationships between variables or predicts outcomes.
What are the key differences between a descriptive hypothesis and a comparative hypothesis?
-A descriptive hypothesis predicts a characteristic of a single variable, such as the time it takes for graduates to find a job. A comparative hypothesis compares two or more variables, like comparing the waiting times for male and female graduates.
What is an associative hypothesis?
-An associative hypothesis suggests a relationship between two or more variables, such as whether there is a correlation between GPA and the time it takes graduates to find a job.
What are the two types of hypothesis in statistical testing?
-The two types of hypothesis are the null hypothesis (H₀), which suggests no difference or relationship, and the alternative hypothesis (H₁), which suggests a difference or relationship exists.
How do the null and alternative hypotheses relate to each other?
-The null and alternative hypotheses are complementary. If one is rejected, the other is accepted. They always exist in pairs and are tested together in hypothesis testing.
What is the significance of the level of significance (α) in hypothesis testing?
-The level of significance (α) represents the probability of making a Type 1 error, where the null hypothesis is wrongly rejected. A smaller α (e.g., 0.01) indicates higher confidence in the results, while a larger α (e.g., 0.05) indicates a greater risk of error.
What are the two types of errors in hypothesis testing?
-Type 1 error occurs when the null hypothesis is wrongly rejected, and Type 2 error occurs when the null hypothesis is wrongly accepted. Type 1 error is denoted by α, and Type 2 error is denoted by β.
How does the margin of error impact hypothesis testing?
-The margin of error indicates the uncertainty in estimating population parameters. A smaller margin of error improves the precision of the estimate, while a larger margin of error increases the potential for mistakes in interpreting the data.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)