APRENDA TODAS AS CONDICIONAIS EM INGLÊS | Do Zero à Fluência
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, the instructor explains the four main types of English conditionals: Zero, First, Second, and Third. Each conditional is illustrated with practical examples, demonstrating how they express scientific facts, possible future outcomes, hypothetical situations, and past regrets. The video also covers mixed conditionals, which combine different types to describe more complex scenarios. The speaker encourages viewers to actively participate, share the content, and subscribe for more lessons. The goal is to help learners understand and confidently use conditionals in real-life conversations.
Takeaways
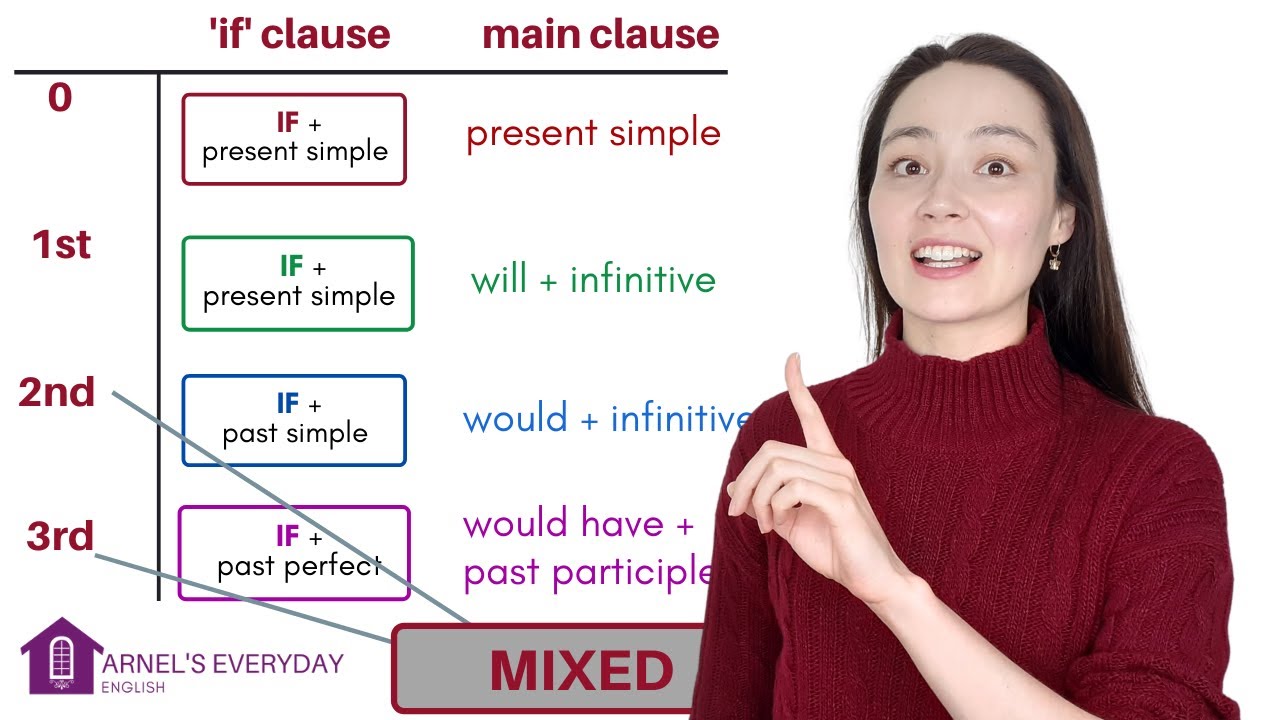
- 😀 Zero Conditional expresses universal truths or scientific facts, where the result always happens if the condition is met (e.g., 'If you freeze water, it turns into ice').
- 😀 First Conditional is used for real possibilities in the future, where one event depends on another (e.g., 'If I leave work early, I’ll meet you at the bar').
- 😀 Second Conditional is used for hypothetical or unreal situations in the present or future (e.g., 'If I were rich, I would buy a bigger house').
- 😀 Third Conditional refers to past situations that did not happen, expressing regret or what could have been (e.g., 'If I had studied harder, I would have passed the test').
- 😀 Mixed Conditionals combine elements from different conditional types to express complex situations (e.g., 'If I had gone to bed early last night, I wouldn’t be tired today').
- 😀 The Zero Conditional uses present simple in both clauses to describe facts or situations that are always true.
- 😀 The First Conditional uses present simple in the if-clause and will + base verb in the result, referring to likely future events.
- 😀 The Second Conditional uses past simple in the if-clause and would + base verb in the result, referring to unreal or hypothetical situations.
- 😀 The Third Conditional uses past perfect in the if-clause and would have + past participle in the result, referring to situations in the past that didn’t happen.
- 😀 To form mixed conditionals, you can combine the structure of the second conditional in the if-clause with the third conditional in the result, or vice versa, depending on the scenario.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lesson in the transcript?
-The main topic of the lesson is the use of conditionals in English, explaining the different types: zero, first, second, third, and mixed conditionals, along with examples of how they are used in everyday contexts.
What is the structure of the zero conditional and when is it used?
-The zero conditional is structured as: 'If + present tense, present tense.' It is used to describe general truths, scientific facts, or things that always happen under certain conditions, such as laws of nature.
Can you give an example of the zero conditional from the lesson?
-An example of the zero conditional from the lesson is: 'If you freeze water, it turns into ice.' This describes a scientific fact that is always true.
What does the first conditional express, and what is its structure?
-The first conditional expresses real or possible situations in the future based on present conditions. Its structure is: 'If + present tense, will + verb.'
Provide an example of the first conditional from the transcript.
-An example of the first conditional is: 'If I leave work early, I will meet you at the bar.' This describes a future possibility depending on a present action.
What is the second conditional used for, and how is it structured?
-The second conditional is used for hypothetical or unreal situations, usually in the present or future. Its structure is: 'If + past simple, would + verb.'
Give an example of the second conditional from the lesson.
-An example of the second conditional is: 'If I were rich, I would buy a bigger house.' This expresses an imaginary scenario in the present or future.
How does the third conditional differ from the other conditionals?
-The third conditional is used to talk about past situations that didn’t happen, expressing regret or hypothetical outcomes that are no longer possible to change. Its structure is: 'If + past perfect, would have + past participle.'
Can you provide an example of the third conditional from the transcript?
-An example of the third conditional is: 'If I had studied harder, I would have passed the test.' This talks about a past regret where the situation cannot be changed.
What are mixed conditionals, and how do they combine different types of conditionals?
-Mixed conditionals occur when elements from different conditionals are combined. For example, one might mix the second and third conditionals to talk about how a past situation could have influenced the present or future. An example is: 'If you hadn’t stayed up late last night, you wouldn’t be so tired today.'
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

The 4 Conditionals (Stop Confusing Them)

English Conditional Sentences (with examples!)
ALL CONDITIONALS | 0,1,2,3 and MIXED CONDITIONALS - English Grammar | if....

CONDITIONALS | Learn all the conditionals | English grammar

THE CONDITIONALS - 0,1,2 & 3 Conditionals& QUIZ - English Grammar Lesson (+ Free PDF & Quiz)

CONDITIONALS in Expressing Arguments | GRADE 9 || MELC-based VIDEO LESSON | QUARTER 1| MODULE 2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
