Overview of Coronary Artery Disease
Summary
TLDRThe video explains coronary artery disease (CAD), detailing how LDL cholesterol can lead to atherosclerosis and plaque formation in the arteries. Patients may remain asymptomatic or experience stable angina, where chest pain occurs during exertion. However, plaque can rupture, leading to acute coronary syndromes, including unstable angina and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The importance of rapid therapy—such as thrombolysis and angioplasty—is emphasized, as restoring blood flow quickly can alleviate symptoms and reduce myocardial damage, highlighting the urgency of addressing acute thrombotic events.
Takeaways
- ❤️ The heart's blood supply comes from major coronary arteries: left anterior descending, left circumflex, and right coronary arteries.
- 🔴 Red blood cells deliver oxygen to the heart muscle, known as the myocardium.
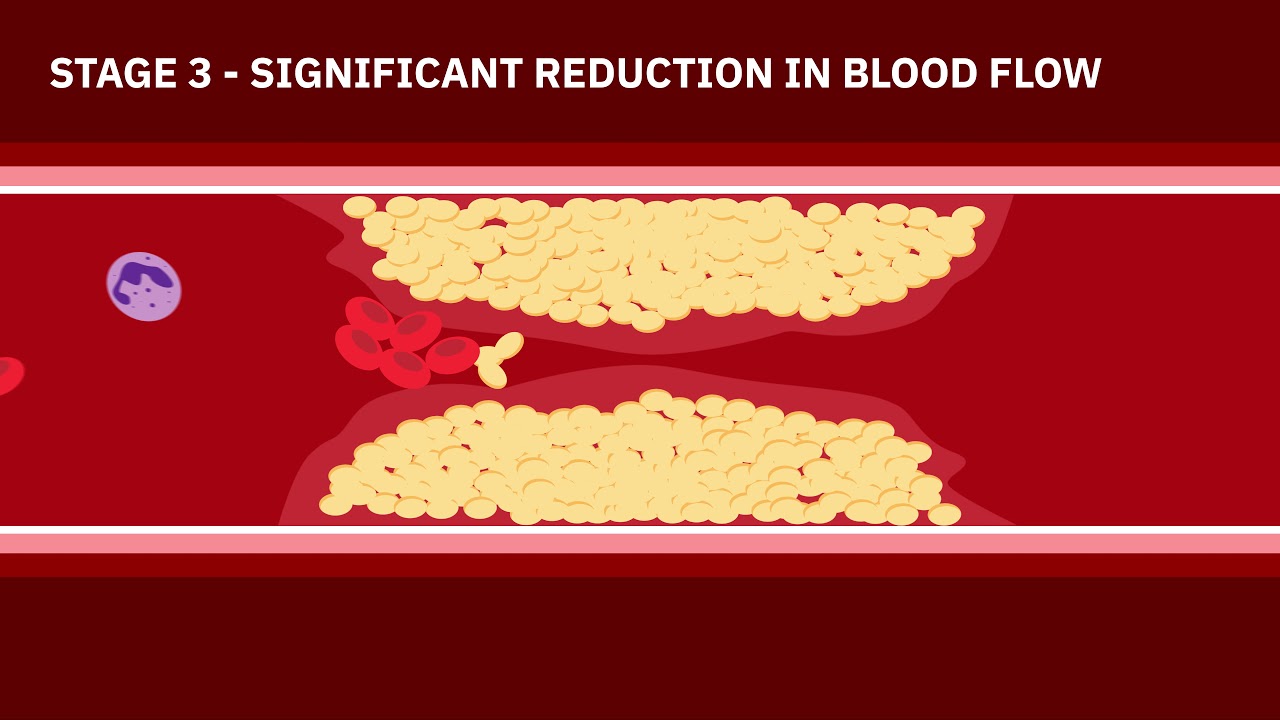
- ⚠️ Atherosclerosis starts with LDL cholesterol accumulation in arterial walls, forming plaques.
- 📉 Some plaques may not obstruct blood flow, leading to asymptomatic coronary disease without chest pain.
- 🏃♂️ Stable angina occurs when blood flow is compromised during exertion, resulting in chest pain.
- 🚑 Patients with stable angina are still at risk for acute events due to potential plaque rupture.
- 💔 Acute coronary syndrome arises from thrombotic occlusions, presenting in two forms: non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) and unstable angina.
- 📉 Unstable angina involves chest pain at rest and ST segment depression on ECG.
- 🔥 ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) occurs when a thrombus completely occludes a vessel, injuring the myocardium.
- 💊 Emergency therapies like thrombolysis, angioplasty, or thrombectomy are vital for restoring blood flow and minimizing myocardial damage.
Q & A
What are the major coronary arteries supplying the heart?
-The major coronary arteries include the left anterior descending artery, the left circumflex coronary artery, and the right coronary artery.
What role do red blood cells play in heart function?
-Red blood cells deliver oxygen to the heart muscle, known as the myocardium.
What initiates atherosclerosis in the arteries?
-Atherosclerosis begins when low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol accumulates in the arterial wall, forming plaque.
What is stable angina?
-Stable angina is chest pain that occurs only with exertion and is not considered a clinical emergency.
What are the risks associated with asymptomatic coronary disease?
-Patients with asymptomatic coronary disease can still be at risk for acute life-threatening events, such as plaque rupture and coronary thrombosis.
What is the difference between non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction and unstable angina?
-Non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction involves chest pain at rest with ST segment depression, while unstable angina presents similarly but may lead to complete blockage.
What happens when a thrombus completely occludes a coronary vessel?
-When a thrombus completely occludes a vessel, it results in ST segment elevation myocardial infarction, injuring the myocardium.
What emergency therapies are used for acute coronary syndromes?
-Emergency therapies include thrombolysis, angioplasty, or thrombectomy, which aim to restore blood flow quickly.
What are the potential outcomes of rapid restoration of blood flow?
-Rapid restoration of blood flow relieves symptoms and minimizes myocardial damage.
What is the most common cause of acute life-threatening coronary artery disease?
-Plaque rupture with coronary thrombosis is the most common cause of acute life-threatening coronary artery disease.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)