Trigonometry For Beginners!
Summary
TLDRThis video script offers an in-depth exploration of right triangle trigonometry, focusing on the SOHCAHTOA mnemonic to understand and calculate the sine, cosine, and tangent of an angle in a right triangle. The lesson explains the relationship between the angle, the sides adjacent to and opposite it, and the hypotenuse. It demonstrates how to find missing sides using the Pythagorean theorem and how to calculate the values of the six trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent) for given sides of a triangle. The script also covers special right triangles, such as the 3-4-5 triangle, and provides methods to solve for missing angles and sides using trigonometric functions. Additionally, it touches on the application of these concepts in real-world problems and teases an upcoming comprehensive trigonometry course on Udemy, covering topics from angles and the unit circle to trigonometric identities and equations.
Takeaways
- 📐 **SOHCAHTOA**: A mnemonic for right triangle trigonometry, where Sine is Opposite over Hypotenuse, Cosine is Adjacent over Hypotenuse, and Tangent is Opposite over Adjacent.
- 🔢 **Pythagorean Theorem**: Applies to right triangles as \( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \), where \( c \) is the hypotenuse.
- 🔁 **Reciprocal Functions**: Cosecant is the reciprocal of sine, secant is the reciprocal of cosine, and cotangent is the reciprocal of tangent.
- 🔍 **Finding Missing Sides**: Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side in a right triangle when two sides are known.
- 📈 **Special Triangles**: Memorizing special right triangles like 3-4-5, 5-12-13, 8-15-17, and multiples of these can help quickly find missing sides.
- 📌 **Trigonometric Values**: Calculate the values of sine, cosine, and tangent using the sides of a right triangle relative to an angle.
- 🔮 **Finding Angles**: Use inverse trigonometric functions (arcsin, arccos, arctan) to find the measure of an angle when the ratio of sides is known.
- 🔗 **Related Functions**: Tangent relates the opposite and adjacent sides, while cosine and sine relate to the adjacent/hypotenuse and opposite/hypotenuse, respectively.
- 🧮 **Calculator Usage**: Utilize a calculator in degree mode to find the values of trigonometric functions and their inverses for specific angles.
- 📚 **Trigonometry Course**: The speaker offers a course on Udemy covering various topics from angles and the unit circle to trigonometric identities and applications.
- 📈 **Graphing Trigonometric Functions**: Learn how to graph sine, cosine, secant, cosecant, and tangent functions, as well as understand their properties and applications.
Q & A
What is the expression 'sohcahtoa' used for in trigonometry?
-The expression 'sohcahtoa' is a mnemonic for remembering the definitions of the primary trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent in terms of the sides of a right triangle. 'S' stands for sine, 'O' for opposite, 'H' for hypotenuse, 'C' for cosine, 'A' for adjacent, and 'TOA' for tangent.
What are the three sides of a right triangle that are relevant to trigonometry?
-The three sides of a right triangle relevant to trigonometry are the opposite side (to the angle theta), the adjacent side (next to the angle theta), and the hypotenuse (the longest side, across from the right angle).
What is the Pythagorean theorem, and how does it apply to right triangles?
-The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (c) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides (a and b). Expressed as an equation, it is a^2 + b^2 = c^2.
How do you find the missing side of a right triangle when given the values of two sides?
-To find the missing side of a right triangle when two sides are given, you use the Pythagorean theorem (a^2 + b^2 = c^2). Substitute the known side lengths for 'a' and 'b', solve for 'c', and then take the square root of the result to find the length of the hypotenuse.
What are the reciprocal trigonometric functions, and how are they related to the primary ones?
-The reciprocal trigonometric functions are cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot). Cosecant is the reciprocal of sine (csc θ = 1/sin θ), secant is the reciprocal of cosine (sec θ = 1/cos θ), and cotangent is the reciprocal of tangent (cot θ = 1/tan θ).
What are some special right triangles with whole number side lengths?
-Special right triangles with whole number side lengths include the 3-4-5 triangle, the 5-12-13 triangle, the 8-15-17 triangle, and the 7-24-25 triangle. These triangles are derived from the Pythagorean theorem and have side lengths that are multiples of the smallest Pythagorean triple (3, 4, 5).
How do you calculate the values of the six trigonometric functions for a given right triangle?
-To calculate the values of the six trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent) for a given right triangle, you first identify the lengths of the opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse sides relative to the angle in question. Then, apply the definitions of each trigonometric function using these side lengths.
How can you find the missing side of a right triangle if you know the angle and one side?
-If you know one side and an angle in a right triangle, you can find the missing side by using the appropriate trigonometric function related to the known side: sine for the opposite side, cosine for the adjacent side, or tangent for the ratio of the opposite to the adjacent side. Then, apply the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotenuse if needed.
What is the process to find the angle theta in a right triangle if you are given the lengths of the opposite and adjacent sides?
-To find the angle theta when the lengths of the opposite and adjacent sides are known, use the tangent function, which is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side (tan θ = opposite/adjacent). Then, use the inverse tangent function (arctan or tan^(-1)) to find the angle theta.
How do you find the value of an angle in a right triangle if you know the lengths of the hypotenuse and the adjacent side?
-To find the value of an angle in a right triangle when the lengths of the hypotenuse and the adjacent side are known, use the cosine function (cos θ = adjacent/hypotenuse). Then, apply the inverse cosine function (arccos or cos^(-1)) to determine the angle.
What is the purpose of the trigonometry course mentioned in the script?
-The purpose of the trigonometry course is to provide a comprehensive understanding of trigonometry concepts, including angles, the unit circle, right triangle trigonometry, trigonometric functions, and their applications. The course also covers solving trigonometric equations, verifying trig identities, and using trigonometric functions to solve real-world problems.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Maths Tutorial: Trigonometry SOH CAH TOA (trigonometric ratios)
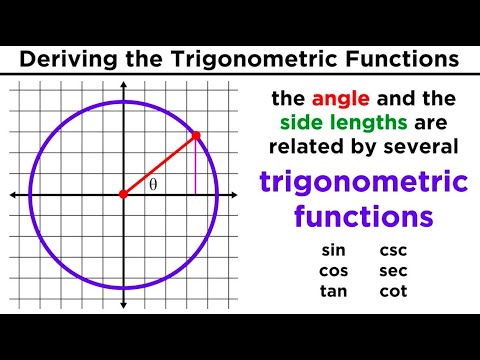
Trigonometric Functions: Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosecant, Secant, and Cotangent
Calculer la mesure d'un angle - Trigonométrie 3ème
When Do I use Sin, Cos or Tan?

Perbandingan Trigonometri Pada Segitiga SIku-siku #Trigonometri

Menentukan Nilai Trigonometri Segitiga Siku Siku Perbandingan Trigonometri segitiga Siku Siku
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
