Metabolism, Anabolism, & Catabolism - Anabolic vs Catabolic Reactions
Summary
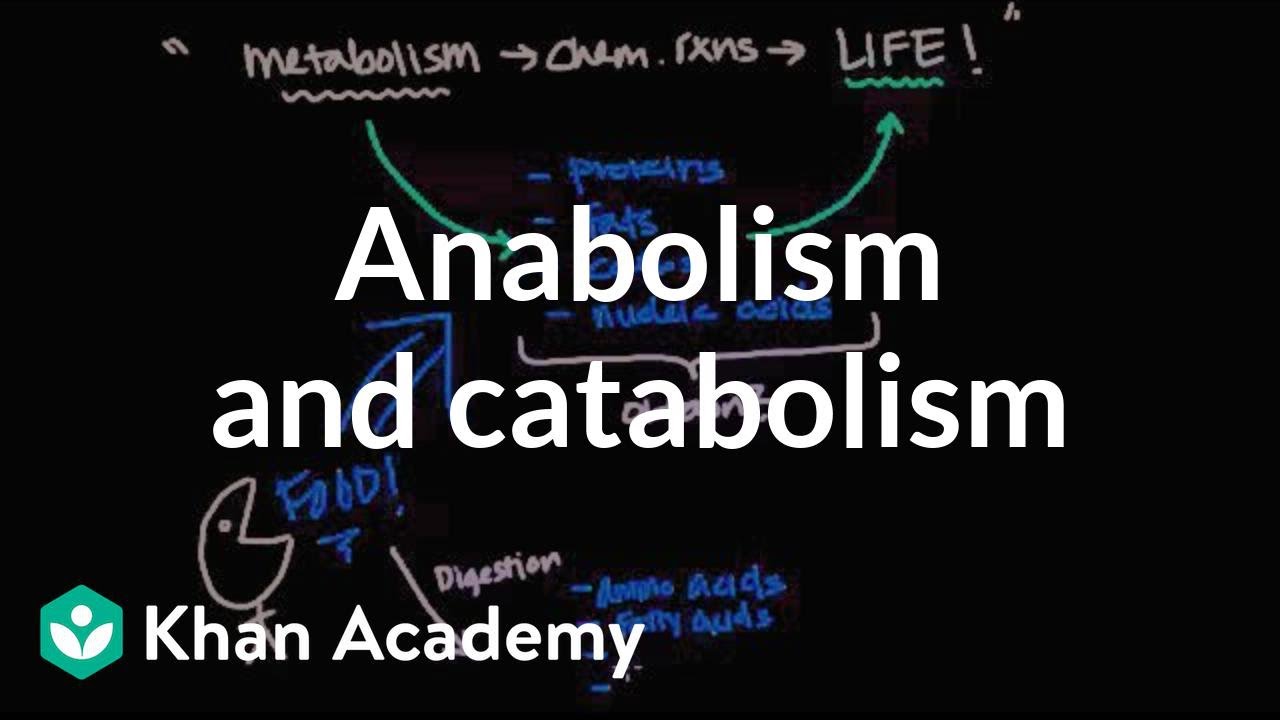
TLDRThe video explains metabolism, the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism, divided into anabolism and catabolism. Anabolism involves building large molecules from smaller ones, like glucose molecules forming polysaccharides, and requires energy (endergonic reactions). Catabolism, on the other hand, breaks down large molecules into smaller ones, like sucrose splitting into glucose and fructose, and releases energy (exergonic reactions). Key examples include cellular respiration (catabolic) and photosynthesis (anabolic), while glycolysis and protein synthesis are also discussed in terms of their metabolic roles.
Takeaways
- 🧪 Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism, consisting of two main processes: anabolism and catabolism.
- 🔨 Anabolism refers to the process of building up molecules, such as synthesis reactions, and typically requires energy (endergonic).
- 🔧 Catabolism involves breaking down molecules, like decomposition reactions, and often releases energy (exergonic).
- 🍬 An anabolic reaction example is combining glucose molecules to form polysaccharides, which requires ATP and releases water (dehydration synthesis).
- 💥 A catabolic reaction example is breaking down sucrose into glucose and fructose, using water in the process (hydrolysis).
- 🌱 Cellular respiration is a catabolic process, where glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy.
- ☀️ Photosynthesis is an anabolic process, converting small molecules (CO2 and H2O) into glucose and oxygen using light energy.
- 💡 Glycolysis is a catabolic process, breaking down glucose into smaller pyruvate molecules.
- 🧬 Protein synthesis (converting amino acids into proteins) is an anabolic process, building large molecules from smaller ones.
- 🔬 Breaking down nucleic acids into nucleotides is a catabolic process, where large polymers are reduced to smaller monomers.
Q & A
What is metabolism?
-Metabolism is the total of all chemical reactions carried out by an organism. It consists of two main processes: anabolism and catabolism.
What is anabolism?
-Anabolism refers to processes that build up molecules, typically involving synthesis reactions. It is an energy-requiring process known as endergonic.
What is catabolism?
-Catabolism refers to processes that break down molecules, often involving decomposition or hydrolysis reactions. These processes typically release energy and are called exergonic reactions.
How are anabolism and catabolism related to metabolism?
-Metabolism is the sum of both anabolic and catabolic processes. Anabolism builds up larger molecules from smaller ones, while catabolism breaks down larger molecules into smaller ones.
Can you give an example of an anabolic reaction?
-An example of an anabolic reaction is the combination of glucose molecules to form a polysaccharide. This process requires energy and is an endergonic reaction.
What type of reaction is typically involved in catabolism?
-Catabolism typically involves hydrolysis reactions, where a large molecule is broken down into smaller molecules with the use of water. This process is often exergonic, meaning it releases energy.
Is cellular respiration anabolic or catabolic?
-Cellular respiration is a catabolic process because it involves breaking down a large molecule (glucose) into smaller molecules (carbon dioxide and water), releasing energy in the process.
What kind of process is photosynthesis: anabolic or catabolic?
-Photosynthesis is an anabolic process because it takes small molecules like carbon dioxide and water and builds them into a larger molecule, glucose, using light energy.
Why is glycolysis considered a catabolic process?
-Glycolysis is catabolic because it breaks down a large glucose molecule into two smaller pyruvate molecules, releasing energy in the process.
How is converting amino acids into proteins an anabolic process?
-Converting amino acids into proteins is anabolic because it involves taking many small amino acid molecules and combining them to form a larger molecule, such as a polypeptide chain or protein.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Metabolisme (pengertian dan perbedaan Katabolisme dan Anabolisme)

Metabolism: Anabolism and Catabolism

[BAKTERIOLOGI] Part 1 Metabolisme Bakteri

Biologi part 4: Energi & Metabolisme

Enzim dan Metabolisme Sel | Biologi SMA
Overview of metabolism: Anabolism and catabolism | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
