Physics - What Is a Centripetal Force?
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an introduction to centripetal force, explaining how it influences the movement of objects in circular paths. It discusses how forces, such as tension, static friction, and gravity, act as centripetal forces in different scenarios, like swinging a ball, a car turning on a road, or the Earth orbiting the Sun. The video also covers the relationship between centripetal force, mass, velocity, and radius, offering various examples to help illustrate these concepts. Additionally, it offers links to practice problems and other related physics topics.
Takeaways
- 🌀 Centripetal force is the force that causes an object to turn in a circular path, always directed toward the center of the circle.
- 🏃♂️ When force and velocity vectors are in the same direction, the object's speed increases, while in the opposite direction, the object slows down.
- 🔄 A perpendicular force to the velocity vector doesn't change speed but causes the object to change direction.
- 🧲 Centripetal force isn't a standalone force but is provided by other forces such as tension or friction, depending on the situation.
- ⚖️ For a car turning on a road, static friction provides the centripetal force, keeping the vehicle on its curved path.
- 🌍 The gravitational force acts as the centripetal force that keeps the Earth in orbit around the Sun, preventing it from flying off into space.
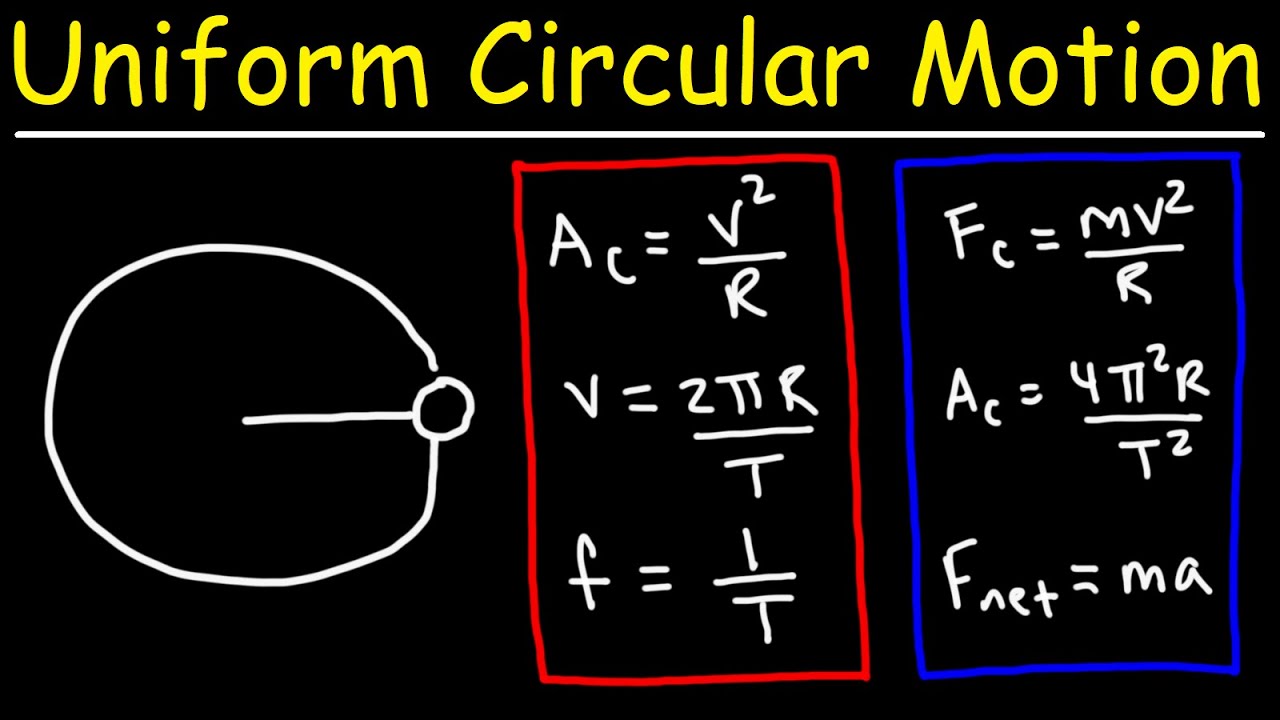
- 📐 The equation for centripetal force is F = mv²/r, where increasing mass or speed increases the centripetal force, while increasing the radius decreases it.
- ⚖️ Doubling the mass of an object doubles the required centripetal force, while doubling speed increases it by a factor of 4.
- 🌀 Decreasing the radius by a factor of 4 increases the centripetal force by a factor of 4.
- 📊 Tripling the mass, quadrupling the speed, and halving the radius increases the centripetal force by a factor of 96.
Q & A
What happens to an object if a force is applied in the same direction as its velocity vector?
-If a force is applied in the same direction as the velocity vector, the object's speed will increase, causing it to speed up.
How does an object react if the force is applied in the opposite direction of its velocity vector?
-If a force is applied in the opposite direction of the velocity vector, the object will slow down.
What effect does a force perpendicular to the velocity vector have on an object's motion?
-A force perpendicular to the velocity vector will cause the object to turn, but it will neither speed up nor slow down the object.
What is centripetal force and how does it affect an object's movement?
-Centripetal force is a force that keeps an object moving in a circular path. It always acts towards the center of the circle.
What force provides the centripetal force when swinging a ball attached to a rope in a circle?
-In this case, the tension force in the rope provides the centripetal force that keeps the ball moving in a circle.
What force provides the centripetal force for a car turning on a road?
-Static friction provides the centripetal force for a car turning on a road, allowing it to follow the curve without sliding.
How does gravity function as a centripetal force for the Earth orbiting the Sun?
-Gravity acts as the centripetal force that keeps the Earth in orbit around the Sun. Without gravity, the Earth would move away from the Sun in a straight line.
What is the formula for centripetal force, and what factors affect it?
-The formula for centripetal force is F = (mv^2) / r, where 'm' is mass, 'v' is velocity, and 'r' is the radius of the circular path. Factors affecting centripetal force include mass, velocity, and radius of the path.
How does increasing the mass of an object affect the centripetal force required to keep it in a circular path?
-If the mass of an object increases, the centripetal force required to keep it in a circular path will also increase because mass is directly proportional to the force.
What happens to the centripetal force if the radius of the circle is increased?
-If the radius of the circle is increased, the centripetal force required to maintain the object in a circular path will decrease, as radius is inversely proportional to the centripetal force.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)