Mekanisme Osmoregulasi dan Termoregulasi - Biologi sma kelas 11 bab.sistem hormonal/endokrin
Summary
TLDRThis video explains two key mechanisms of the endocrine system: osmoregulation and thermoregulation. It details how the body maintains water balance and temperature through hormones like ADH, aldosterone, and thyroid hormones. The video describes how osmoregulation works when the body is dehydrated, triggering thirst and kidney function adjustments to restore normal blood fluid levels. For thermoregulation, it covers how the body reacts to overheating or cold by sweating, shivering, and using thyroid hormones to regulate metabolism and body temperature. It concludes by encouraging viewers to stay tuned for more educational content.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video discusses two hormonal mechanisms in the endocrine system: osmoregulation and thermoregulation.
- 💧 Osmoregulation helps maintain the blood's osmolarity (thickness) by controlling the body's water levels.
- 🧠 The hormone ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) is secreted when blood osmolarity increases, prompting the kidneys to reabsorb water and decrease osmolarity.
- 💦 ADH also triggers the feeling of thirst, encouraging water intake to normalize blood osmolarity.
- 🔄 When blood osmolarity decreases (too much water), ADH secretion is reduced, and excess water is expelled through urine.
- 💡 Aldosterone is another hormone involved in osmoregulation, which helps increase blood volume by promoting water reabsorption when blood volume drops.
- 🔥 Thermoregulation helps maintain body temperature between 36.5°C and 37.5°C.
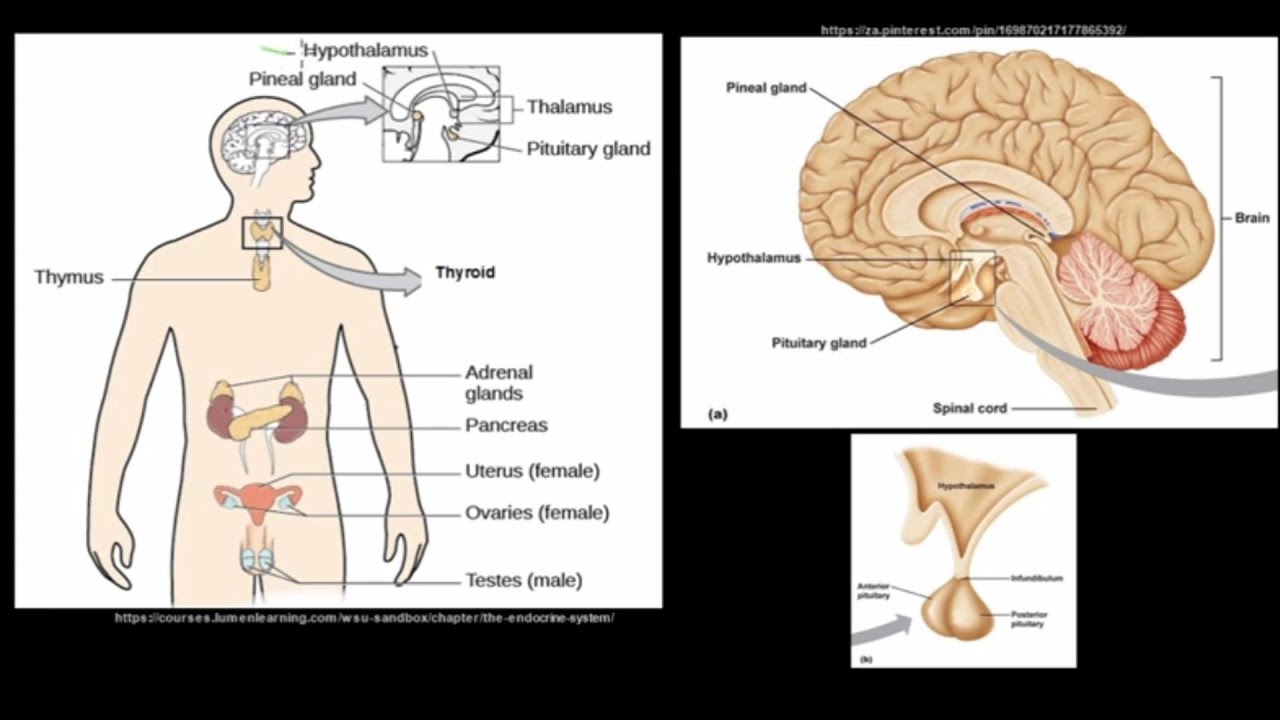
- 🌡️ When the body gets too cold, the hypothalamus triggers muscle contractions (shivering) and vasoconstriction to conserve heat and increase temperature.
- 💧 When the body gets too hot, the hypothalamus triggers sweating and vasodilation to release heat and cool the body down.
- 🌬️ The thyroid hormones T3 and T4, controlled by the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland, regulate metabolism and heat production, playing a key role in thermoregulation.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of this video script?
-The primary focus of this video script is to explain the mechanisms of hormonal regulation in the body, specifically focusing on osmoregulation and thermoregulation.
What is osmoregulation and why is it important?
-Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining the balance of water and electrolytes in the body to stabilize the osmotic pressure of extracellular fluids. It is important for maintaining normal cell function and overall health.
How does the body respond to dehydration?
-When the body is dehydrated, the osmolality of blood increases, triggering osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus to stimulate the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which increases water reabsorption in the kidneys and reduces blood osmolality.
What is the role of ADH in osmoregulation?
-ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) is secreted in response to increased blood osmolality and acts on the kidneys to increase water reabsorption, thereby reducing blood osmolality back to normal levels.
What is the function of aldosterone in osmoregulation?
-Aldosterone is a hormone produced by the adrenal cortex that helps regulate blood volume and blood pressure by increasing sodium and water reabsorption in the kidneys, which in turn increases blood volume.
How does the body regulate body temperature?
-The body regulates its temperature through a process called thermoregulation, which involves mechanisms such as sweating to release excess heat and shivering to generate heat when needed.
What are the roles of the hypothalamus in thermoregulation?
-The hypothalamus acts as a thermostat for the body, detecting changes in body temperature and initiating responses through the nervous and endocrine systems to maintain a stable internal temperature.
How do thyroid hormones contribute to thermoregulation?
-Thyroid hormones, such as T3 and T4, stimulate metabolism, which increases heat production in the body, helping to maintain a normal body temperature.
What happens when body temperature is below the normal range?
-When body temperature drops below the normal range, the hypothalamus triggers responses such as shivering and vasoconstriction to generate heat and reduce heat loss, aiming to raise body temperature back to normal.
What is the effect of high body temperature on the body's regulatory mechanisms?
-High body temperature triggers responses such as vasodilation and sweating to increase heat loss. Additionally, the hypothalamus may reduce the secretion of thyroid hormones to decrease metabolism and heat production.
What is the normal range of body temperature mentioned in the script?
-The normal range of body temperature mentioned in the script is between 36.5 and 37.5 degrees Celsius.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Homeostasis Mini Unit Concept 1 Notes

Lesson 5: Nervous System Working Together with the Endocrine System to Maintain Homeostasis

Overview and Anatomy & Physiology | Endocrine System (Part 1)

Sistema endócrino - Introdução - Fisiologia veterinária - Aula 1

Sistem Hormon Manusia / Endokrin ( Pendahuluan)
Grade 12 Life Sciences Responding to the Environment The Endocrine System
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
