Plant Tissues [Explained and Designed by IIT Alumnus]
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the structure and function of plant tissues. It covers two main types: meristematic tissue, responsible for plant growth, and permanent tissue, which forms from matured meristematic cells. The script delves into the subdivisions of permanent tissue, including parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma, each with unique functions like storage, support, and photosynthesis. It also discusses complex tissues like xylem and phloem, which are involved in transporting water, minerals, and food. Additionally, protective tissues like the epidermis and cork are explained, highlighting their roles in plant defense and water retention.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Multicellular organisms are composed of many cells, and similar cells group together to form tissues that perform specific functions.
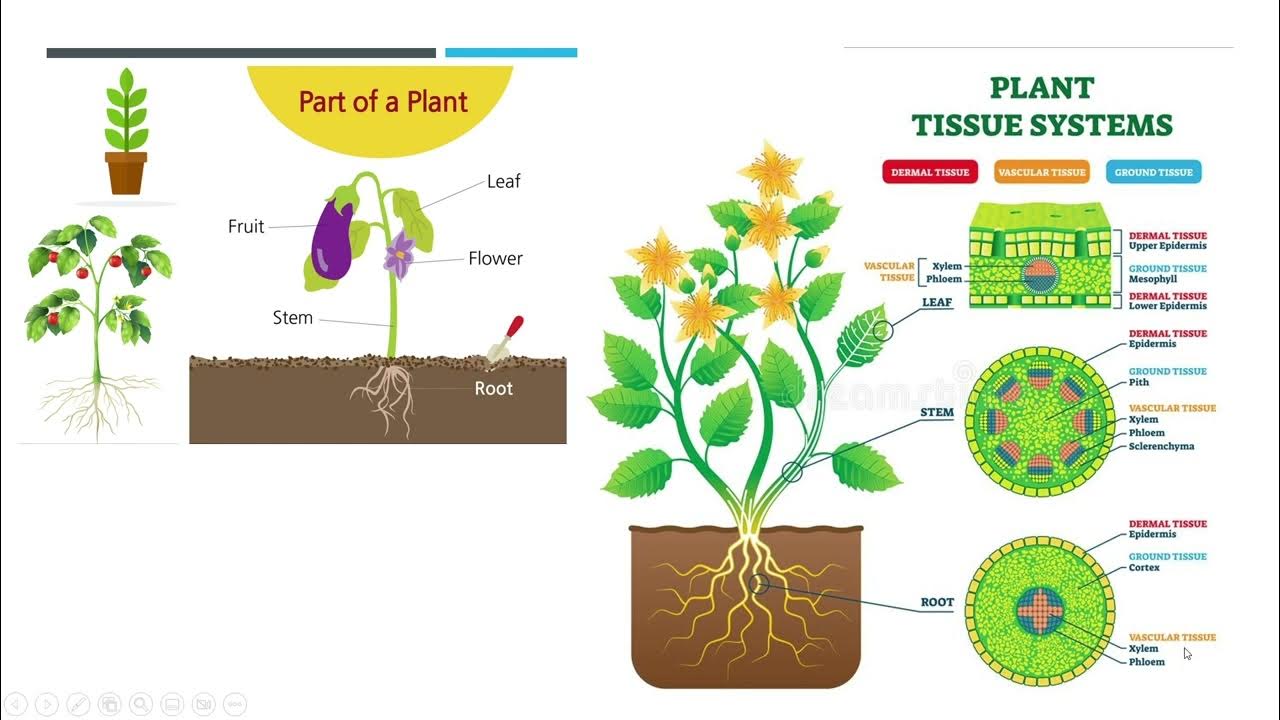
- 🌱 Plant tissues can be classified into two types: meristematic tissue and permanent tissue.
- 🌱 Meristematic tissues are active, dividing cells with a dense cytoplasm and distinct nucleus, contributing to plant growth in height and girth.
- 🌱 There are three types of meristematic tissues: apical (root/shoot growth), intercalary (leaf and node growth), and lateral (stem girth growth).
- 🌱 Permanent tissues are formed when meristematic cells lose the ability to divide and differentiate into either simple (one type of cell) or complex (multiple types of cells) tissues.
- 🌱 Simple permanent tissues include parenchyma (storage/photosynthesis), collenchyma (flexibility), and sclerenchyma (support), with various functions depending on cell structure.
- 🌱 Complex permanent tissues include xylem (conducts water/minerals and provides support) and phloem (conducts food in both directions).
- 🌱 Xylem consists mostly of dead cells except for xylem parenchyma, while phloem is made up of living cells like sieve tubes, companion cells, and fibers.
- 🌱 Epidermis is a protective tissue on plant surfaces, preventing water loss and microbial infections, with specialized structures like root hairs for absorption and stomata for gas exchange.
- 🌱 Histology is the study of plant and animal tissues, while histopathology focuses on diseased tissues, playing a vital role in diagnosing conditions like cancer.
Q & A
What is the fundamental unit of life according to the script?
-The fundamental unit of life is a single cell.
What are multicellular organisms, and how do they function efficiently?
-Multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell, and they function efficiently by having similar types of cells grouped into tissues, which perform particular functions, leading to division of labor.
What is meristematic tissue, and what is its role in plants?
-Meristematic tissue consists of actively dividing cells that have dense cytoplasm and a distinct nucleus. It plays a key role in the growth of plants by increasing height, producing leaves, and expanding the girth of the stem.
What are the three types of meristems based on location?
-The three types of meristems are: apical meristem (present at root and shoot apex, responsible for plant height), intercalary meristem (present at the base of leaves and nodes), and lateral meristem (present at the sides of the stem, responsible for increasing the girth).
What are permanent tissues, and how are they formed?
-Permanent tissues are derived from older meristematic tissues that lose their ability to divide and become differentiated. They are divided into simple tissues (made of one cell type) and complex tissues (made of different cell types).
What are the three types of simple permanent tissues?
-The three types of simple permanent tissues are parenchyma (for storage and photosynthesis), collenchyma (provides flexibility), and sclerenchyma (provides mechanical support).
What is the role of xylem and phloem in plants?
-Xylem transports water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant, and also provides mechanical support. Phloem transports food in both directions throughout the plant and consists mostly of living cells.
What are the functions of epidermis in plants?
-The epidermis protects the inner parts of the plant from injury, water loss, and microbial infections. In roots, it forms root hairs for water and mineral absorption, and in leaves, stomata in the epidermis allow gas exchange and transpiration.
How is cork or bark formed in plants?
-Cork or bark is formed by secondary meristem as the outer layer of the stem grows older. It consists of dead cells and provides protection by preventing water loss.
What is the difference between histology and histopathology?
-Histology is the study of cells and tissues in plants and animals, while histopathology is the study of diseased tissues, often used for diagnosing diseases such as cancer.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)